INTRODUCTION
Adenosine is an endogenous purine nucleoside composed of an adenine attached to a ribose sugar molecule moiety, and is present ubiquitously in all the organs, tissues and cells. One of the major roles of adenosine is as an energy supplier by conversion to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The adenosine concentration in organs and tissues is approximately 300 nmol/L under the normal conditions, but elevates to 600-1200 nmol/L under the inflammatory or ischemic conditions, where adenosine exhibits a protective effect against inflammatory or ischemic damage. Moreover, adenosine is implicated in a wide-range of signal transduction pathways relevant to cell proliferation and differentiation, cellular metabolism, apoptosis and cognitive function.
Accumulating evidence has shown that adenosine induces apoptosis in a variety of cancer cells via an intrinsic pathway linked to adenosine uptake into cells and the ensuing signaling cascades; its also functions through an extrinsic pathway linked to adenosine receptors[1,2]. The present study focused upon the antitumor effect of adenosine on gastric cancer cells and discussed the underlying mechanism.
ADENOSINE-INDUCED APOPTOSIS THROUGH THE EXTRINSIC PATHWAY
Adenosine receptors are coupled to G-proteins and are classified into A1, A2a, A2b and A3 receptors[3,4]. A1, A2a and A2b adenosine receptors are well conserved during evolution and are highly homologous; however, the A3 adenosine receptor varies, depending upon species[5]. A1, A2a and A3 adenosine receptors are activated by physiological concentrations of adenosine (10-100 nmol/L), while the A2b adenosine receptor is activated by much higher concentrations (over 1 μmol/L).
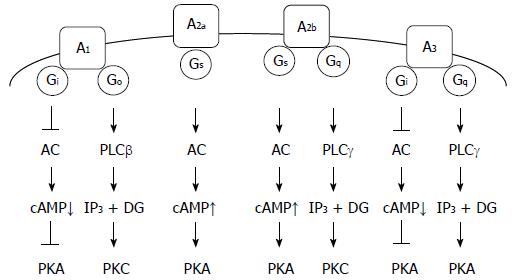
The A1 adenosine receptor is linked to Gi/Go proteins, causing inhibition of the Gi protein effector adenylate cyclase (AC), to reduce cAMP production and inhibit protein kinase A (PKA). Activation of the Go protein effector phospholipase C-β (PLCβ) produces inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DG) followed by activation of protein kinase C (PKC) (Figure 1)[6,7]. The A1 adenosine receptor mediates apoptosis of CW2 human colon cancer cells and RCR-1 astrocytoma cells by activating caspase-3, -8, and -9[8,9]. In addition, evidence implicates the A1 adenosine receptor in the apoptosis of breast cancer cells and gastric cancer cells[10,11].
Figure 1 Adenosine receptors and their relevant signaling pathways.
A1: A1 adenosine receptor; A2a: A2a adenosine receptor; A2b: A2b adenosine receptor; A3: A3 adenosine receptor; PLC: Phospholipase C; IP3: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; DG: Diacylglycerol; PKA: Protein kinase A; PKC; Protein kinase C.
The A2a adenosine receptor is linked to the GS protein, which activates the effector AC, to produce cAMP and activate PKA (Figure 1). The A2a adenosine receptor, expressed in the striatum, is linked to the Golf protein, causing AC activation, similar to Gs protein[12]. The A2a adenosine receptor mediates apoptosis of Caco-2 human colon cancer cells by activating caspase-3/-9[13], and HepG2 human hepatoma cells by downregulating expression of Bcl-XL and upregulating expression of Bid[14].
The A2b adenosine receptor is linked to Gs/Gq proteins, causing the activation of the Gs protein effector AC, to produce cAMP and activate PKA, and activation of the Gq protein effector PLCγ, to produce IP3 and DG followed by activation of PKC (Figure 1). The A2b adenosine receptor mediates apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating Bcl-2, upregulating Bax and activating caspase-3[15]. The A2b adenosine receptor signaling, stimulated in a p73-dependent manner, enhances the apoptosis of a variety of cancer cells[16]. Conversely, blockage of the A2b adenosine receptor inhibited the growth of prostate cancer cells[17]. This suggested that A2b adenosine receptor promotes growth of prostate cancer cells.
The A3 adenosine receptor is linked to Gi/Gq proteins, causing inhibition of the Gi protein effector AC, to reduce cAMP production and inhibit PKA, and activation of the Gq protein effector PLCγ, to produce IP3 and DG, followed by activation of PKC (Figure 1)[18,19]. A recent review highlighted the A3 adenosine receptor as a new target for cancer therapy. Chloro-N6-(3-iodobenzyl)-adenosine-5’-N-methyl-uronamide (Cl-IB-MECA), an agonist of the A3 adenosine receptor, arrests the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase and induces apoptosis of lung cancer cells by downregulating cyclin D1, c-myc, and CDK4, activating caspase-3 and -9, cleaving poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, and inhibiting Akt[20]. Alternatively, Cl-IB-MECA suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of bladder cancer cells through an extracellular signal-regulated kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway[21]. CF102, another agonist of the A3 adenosine receptor, induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by de-regulating Wnt/NF-κB signal transduction pathways[22]. Overexpression of the A3 adenosine receptor suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of malignant mesothelioma cells by inhibiting an Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway[23]. Overall, the A3 adenosine receptor appears to suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis of cancer cells through diverse signaling pathways.
ADENOSINE-INDUCED APOPTOSIS THROUGH AN INTRINSIC PATHWAY
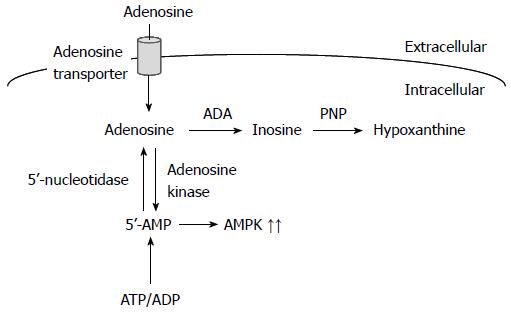
Adenosine also induces apoptosis of cancer cells through an intrinsic pathway. Extracellular adenosine is taken up into cells through adenosine transporters and converted to AMP by adenosine kinase, and AMP activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) (Figure 2)[24,25]. Adenosine, on the other hand, is metabolized into inosine by adenosine deaminase. In turn, inosine is metabolized into hypoxanthine by purine nucleoside phosphorylase (Figure 2). AMP derived from intracellularly transported adenosine upregulates p53 expression, to induce caspase-independent apoptosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma cells[26]. AMP also induces apoptosis of HuH-7 human hepatoma cells by downregulating c-FLIP expression, which is responsible for caspase-8 activation, followed by activation of the effector caspase-3[27]. Alternatively, intracellularly transported adenosine upregulates the expression of DIABLO and stimulates DIABLO release from the mitochondria, which neutralizes the inhibition of caspase-3 caused by inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP), together with downregulation of IAP2 expression, which leads to activation of caspase-3, to induce apoptosis of HuH-7 cells[28]. AMPK, activated by intracellularly transported adenosine and the ensuing conversion to AMP, phosphorylates Bcl-XL, causing disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential and stimulation of DIABLO release from the mitochondria in HuH-7 cells[29]. Furthermore, intracellularly transported adenosine, but not AMP or AMPK, induces apoptosis of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by accumulating AMID in the nucleus in a caspase-independent manner[30].
Figure 2 Intracellularly transported adenosine and the ensuing signaling pathways.
AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate.
ADENOSINE-INDUCED APOPTOSIS OF GASTRIC CANCER CELLS
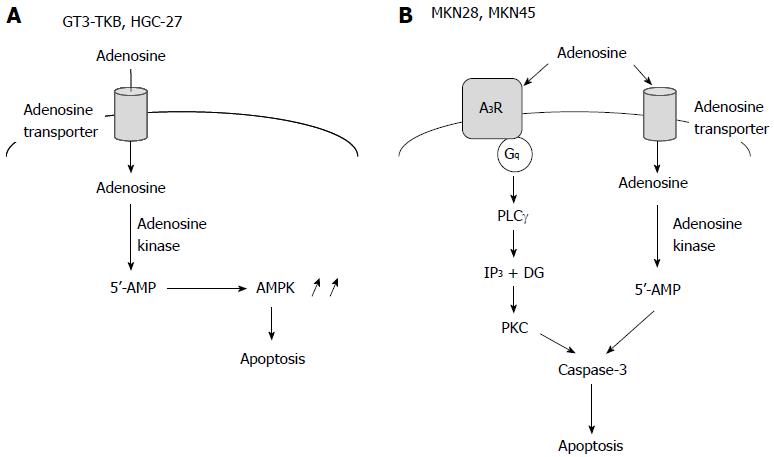
We have found that extracellular adenosine induces apoptosis of the gastric cancer cell lines GT3-TKB[31], MKN28 and MKN45 cells (unpublished data). Adenosine-induced GT3-TKB cell death was significantly inhibited by an inhibitor of the adenosine transporter or an inhibitor of adenosine kinase, while it was not affected by inhibitors of adenosine receptors[31]. This suggested that adenosine transporter-mediated uptake into cells, and adenosine kinase-mediated conversion to AMP, are required for extracellular adenosine-induced apoptosis of GT3-TKB cells. AMPK is activated in response to a cytosolic AMP rise, and therefore, AMPK may execute apoptosis of GT3-TKB cells as a downstream target of AMP (Figure 3A). Extracellular adenosine had no effect on mitochondrial membrane potentials in GT3-TKB cells and adenosine-induced apoptosis was not inhibited by caspase inhibitors[31]. This indicated that extracellular adenosine induces caspase-independent apoptosis of GT3-TKB cells apoptosis through an intrinsic pathway.
Figure 3 Extracellular adenosine-induced apoptosis of gastric cancer cells.
A: The adenosine-induced apoptotic pathway for GT3-TKB and HGC-27 cells; B: The adenosine-induced apoptotic pathway for MKN28 and MKN45 cells. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase.
A study showed that extracellular adenosine causes cell cycle arrest and induces apoptosis of HGC-27 human gastric cancer cells[32]. Adenosine-induced HGC-27 cell apoptosis was inhibited by an inhibitor of the adenosine transporter; however, it was not affected by a broad inhibitor of P1 receptors or a non-selective antagonist of P2 receptors. This supported the involvement of the intrinsic pathway in adenosine-induced apoptosis of gastric cancer cells (Figure 3A).
Extracellular adenosine-induced apoptosis of MKN28 and MKN45 cells was inhibited by an inhibitor of adenosine transporter or an inhibitor of adenosine kinase, although an AMPK activator did not induce apoptosis. This suggested that the intrinsic pathway participates in adenosine-induced apoptosis of MKN28 and MKN45 cells; in other words, intracellularly transported adenosine and converted AMP trigger apoptosis of MKN28 and MKN45 cells (Figure 3B).
Extracellular adenosine-induced apoptosis of MKN28 and MKN45 cells was also inhibited by an inhibitor of the A3 adenosine receptor. This implied that the extrinsic pathway also participates in adenosine-induced apoptosis of MKN28 and MKN45 cells. The A3 adenosine receptor is linked to Gi/Gq proteins involving PKA inhibition and PKC activation[18,19]. Adenosine-induced MKN28 cell apoptosis was abolished by a PKC inhibitor. This indicated that the Gq protein linked to the A3 adenosine receptor is responsible for adenosine-induced apoptosis of MKN28 cells (Figure 3B). Adenosine activated only caspase-3 in both in MKN28 and MKN45 cells, but caspase-4, -8 and -9 were not affected. This suggested that adenosine-induced caspase-3 activation is independent of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress relevant to caspase-4 activation, death receptors relevant to caspase-8 activation or oxidative stress relevant to mitochondrial damage and caspase-9 activation. How extracellular adenosine’s activation of caspase-3 in MKN28 and MKN45 cells remains to be explored.
Extracellular adenosine exhibits a beneficial antitumor effect on a variety of cancer cells including gastric cancer cells. Adenosine is an endogenous substance, and therefore, no or fewer side effects are expected for chemotherapy using adenosine. Thus, adenosine could be developed as a promising drug for gastric cancer chemotherapy. Moreover, the ability of downstream target molecules of adenosine to induce apoptosis of individual gastric cancer cell types, might make them targets for tailor-made chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Especially, specific potential inhibitors and targets of the A3 adenosine receptor and AMP, respectively, could be used therapeutically.
CONCLUSION
Adenosine has the potential to induce apoptosis of gastric cancer cells through diverse intrinsic and extrinsic signaling pathways. The underlying mechanisms vary, depending upon gastric cancer cell types. Understanding the contribution of each downstream target molecule of adenosine to the induction of gastric cancer cell apoptosis, therefore, may aid the establishment of tailor-made chemotherapy for gastric cancer.
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
P- Reviewer: D’Alessandro A S- Editor: Ma YJ L- Editor: Stewart G E- Editor: Wang CH