Published online Sep 15, 1996. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v2.iSuppl1.121
Revised: April 6, 1996
Accepted: July 29, 1996
Published online: September 15, 1996
AIM: A novel mathematical method of characteristic points detection is developed for detecting spikes from GEA (Gastric Electrical Activity) signals.
METHODS: A significant property of wavelet transform is that it well adapted for finding the location and the spatial distribution of singularities. We make use of this for detecting the spikes in GEA by using a quadratic spline wavelet, ψ (t), with compact support and one vanishing moment, which is a first derivative of a smooth function (a cubic spline). The Fourier transform of ψ (t) is given by
Ψ (ω) = iωSac4(ω) = iω [sin(ω/4)]/(ω/4)}4
Now one can find out the wavelet transform W1—SEgg(t) based on
W1—sEgg (t) = IFT[Egg (ω)Ψ (sω)]
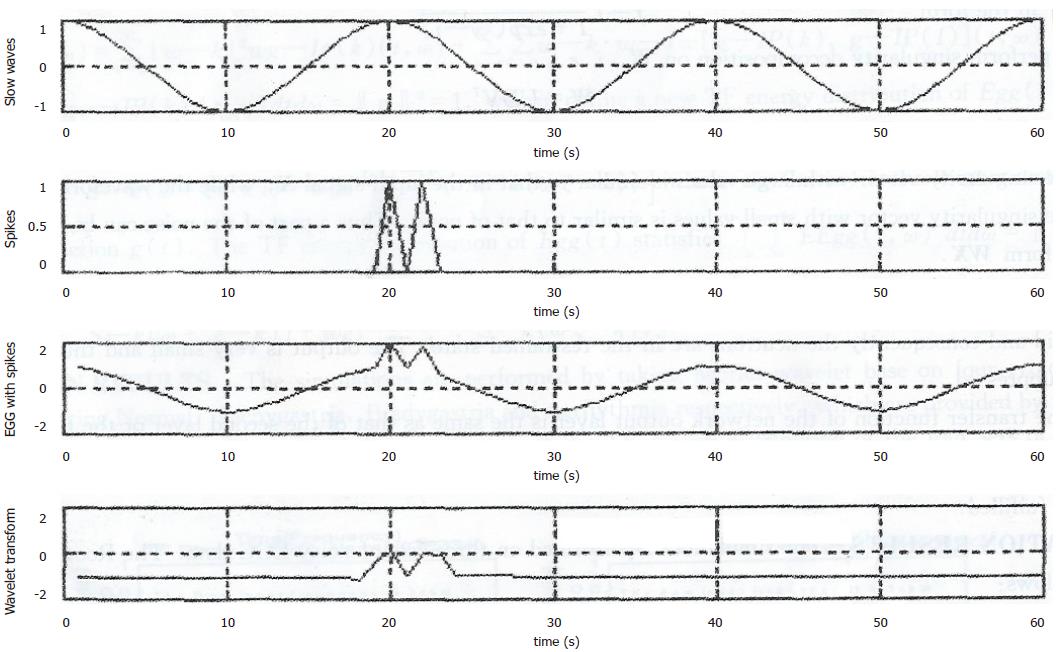
where IFT denotes the inverse Fourier transform. The simulation is done by constructing a GEA signal which is a synthesized wave with 3 cpm slow wave and the spikes imposed on the slow wave. The results are shown in the following Figure 1 where one can clearly see that two spikes are reflected into two local maximas of the wavelet transform |W1—SEgg(t)|. The further work is to investigate the general properties of the singular detection using wavelet transform for developing a robust method used detecting spikes from practical GEA signals.
- Citation: Wang ZS, Li WH, He ZY, Chen JZ, Liang J. Spike detection of gastric electrical activity by wavelet transform. World J Gastroenterol 1996; 2(Suppl1): 121-122
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v2/iSuppl1/121.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v2.iSuppl1.121
The Figure 1.
Original title:
E- Editor: Liu WX