©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 15, 2003; 9(9): 2021-2024
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2021
Published online Sep 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2021
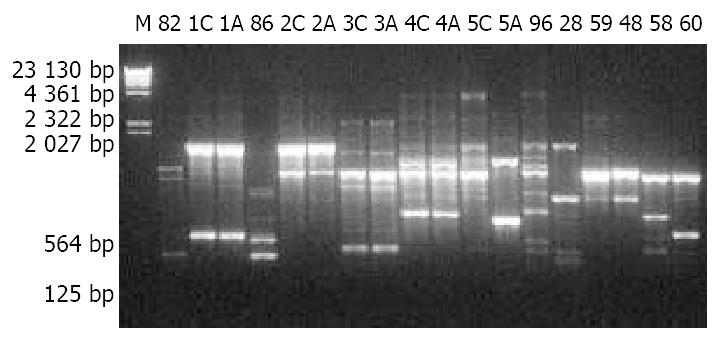
Figure 1 10 g/L agarose gel electrophoresis of RAPD products of H pylori isolates.
M: λDNA Hind III markers; 82, 86, 96, 28, 59, 48, 59 and 60: Designations of H pylori isolates; A: Antrum; C: Cardia.
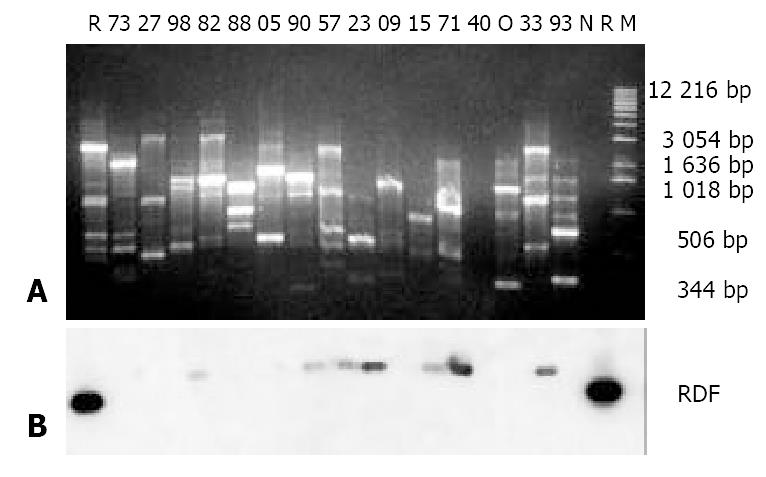
Figure 2 Results of agarose gel electrophoresis of RAPD products (A) and Southern blotting (B).
A: 10 g/L agarose gel elec-trophoresis of RAPD products of H pylori isolates; M: 1 Kb DNA ladder; 73, 27, 98, 82, 88, 05, 90, 57, 23, 09, 15, 71, 40, 33 and 93: Designations of the H pylori isolates; N: H pylori reference strain NCTC11637; R: 1 ng RDF loaded in the well; O: Template blank control; B: Southern blotting results using the RDF as a probe, the dark blots on either side of Picture B corresponding to the 1 ng RDF in the agarose gel in Picture A.
-
Citation: Han FC, Ng HC, Ho B. Stability of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprinting in genotyping clinical isolates of
Helicobacter pylori . World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(9): 2021-2024 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i9/2021.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2021