©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 2003; 9(8): 1791-1794
Published online Aug 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1791
Published online Aug 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1791
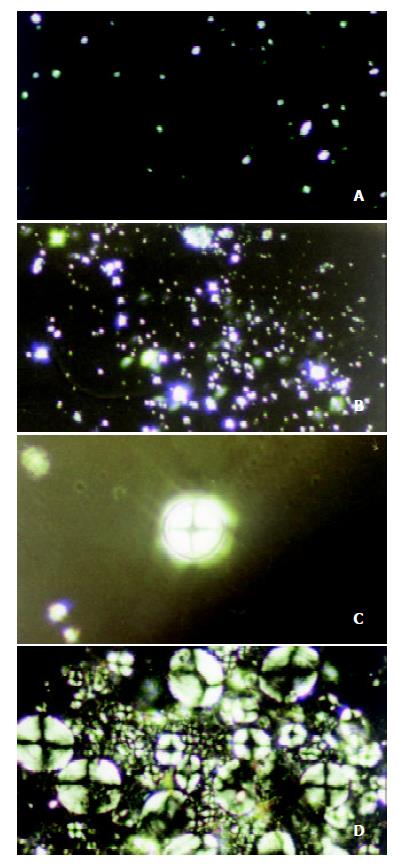
Figure 1 Malta cross showed in bile liquid crystals in gallbladders of guinea pigs in the control group: (a) Small and scattered crosses (10 days, ×400).
(b) The crosses gradually grew in size and number (25 days, ×400). (c) Single big crosses (25 days, ×400). (d) Densely distributed crosses (60 days, ×400).
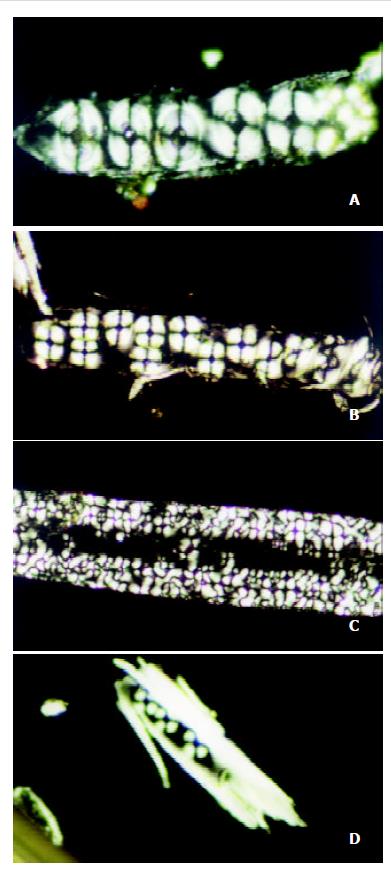
Figure 2 Malta cross shown in bile liquid crystals in gallblad ders of guinea pigs in the stone-causing group: (a) The cross merged into strings (10 days, ×400).
(b) Gradually growing strings of the cross (25 days, ×200). (c) Strings of the cross in phase-changing (60 days, ×400). (d) Stone crystals nucleated by strings of the cross (60 days, ×200).
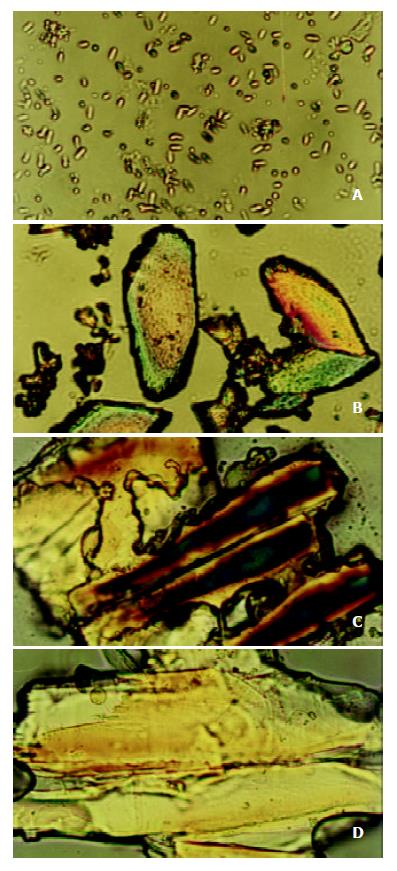
Figure 3 Gallbladder stone crystals in bile of the stone-caus-ing group.
- Citation: Yang HM, Wu J, Li JY, Gu L, Zhou MF. Role of nucleation of bile liquid crystal in gallstone formation. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(8): 1791-1794
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i8/1791.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i8.1791