Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2003; 9(6): 1182-1186
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1182
Published online Jun 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1182
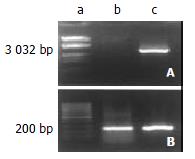
Figure 1 RT-PCR assay of ezrin mRNA.
The expression of ezrin mRNA was significantly increased in SHEEMT compared with that in SHEEIMM cells. A. Ezrin; B. GAPDH: a. Marker; b. SHEEIMM; c. SHEEMT.
Figure 2 Western blot analysis of ezrin protein expression.
The ezrin protein was exhibited as a band of 81-kDa segment, whose expression was up-regulated in SHEEMT compared with that in SHEEIMM cells. Lane a: SHEEIMM; lane b: SHEEMT.
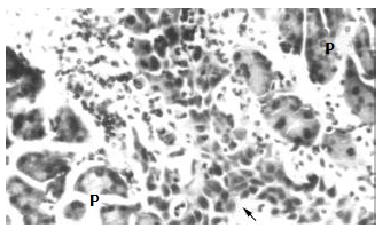
Figure 3 The inoculated SHEEMT cells (arrow) invaded into the parenchyma of pancreas (P) (HE, × 200).
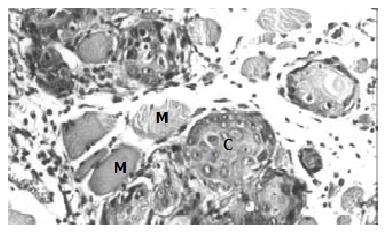
Figure 4 Tumor formation in subcutaneous tissue inoculated with SHEEMT cells (C), the latter was also shown to invade and destroy nearby muscle fibers (M).
(HE, × 200).
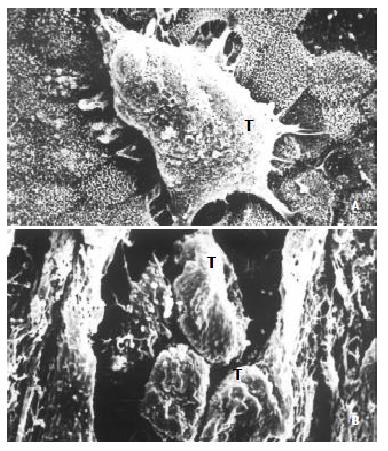
Figure 5 The invasiveness of inoculated SHEEMT cells on amniotic epithelium was demonstrated by scanning electron microscopy.
A. A cluster of SHEEMT cells (T) grew on the amniotic epithelial surface (bar, 5 μ); B. On the cutting surface, SHEEMT cells (T) were observed invading into the amnion stroma (bar, 50 μ).
- Citation: Shen ZY, Xu LY, Chen MH, Li EM, Li JT, Wu XY, Zeng Y. Upregulated expression of Ezrin and invasive phenotype in malignantly transformed esophageal epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(6): 1182-1186
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i6/1182.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1182