Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 15, 2003; 9(4): 829-832
Published online Apr 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i4.829
Published online Apr 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i4.829
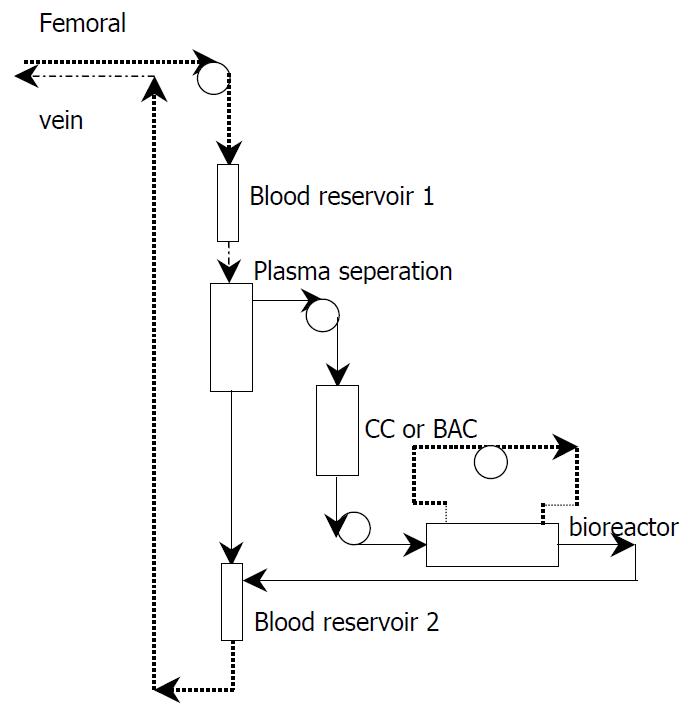
Figure 1 The constructed bioartificial liver.
CC: charcoal column. BAC: bilirubin absorption column.
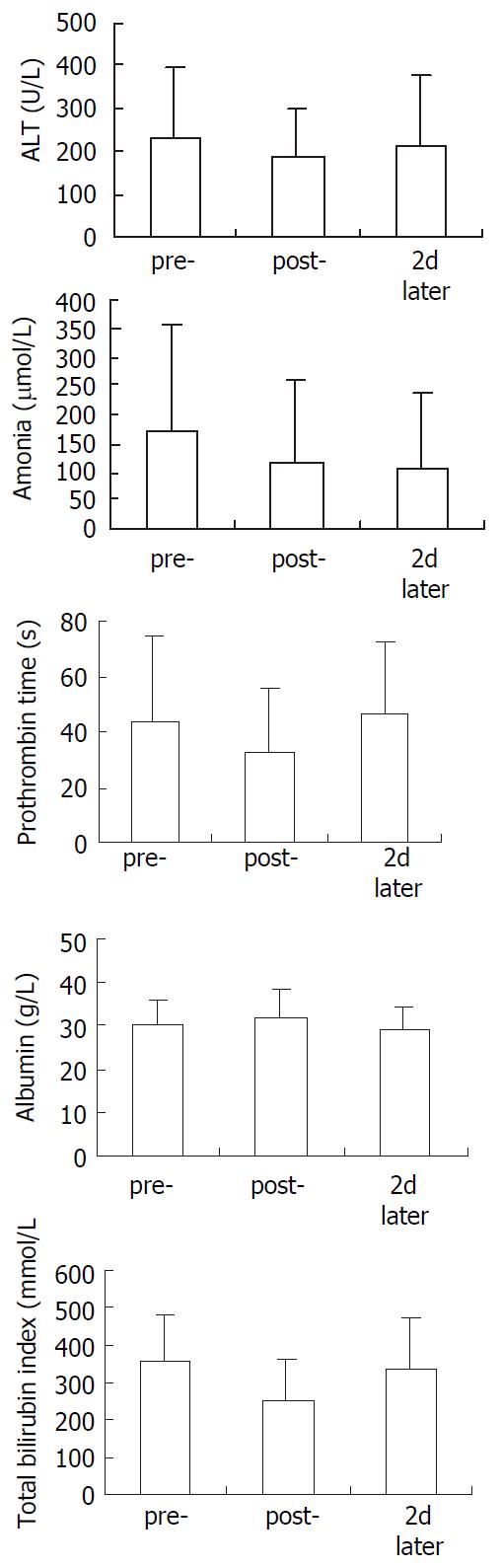
Figure 2 Change of ALT, ammonia, prothrombin time, albu-min and total bilirubin index in 12 patients.
Compared with pre-, ammonia, prothrombin time and total bilirubin index showed significant decreace in post-. 2 d later, only ammo-nia showed significant lowing. pre-: pre-treatment, post-: post-treatment, 2 d later: 2 d after the treatment. Paired T test was used to test the difference.
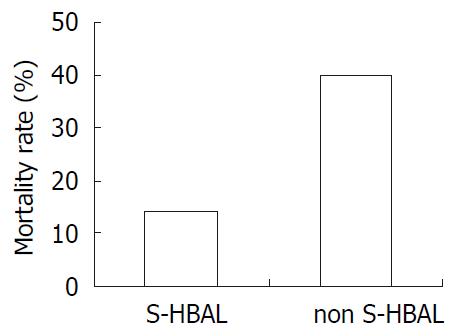
Figure 3 The mortality rate of simultaneous HBAL and non-simultaneous HBAL.
Significant difference was found between this two groups (P < 0.05).
- Citation: Ding YT, Qiu YD, Chen Z, Xu QX, Zhang HY, Tang Q, Yu DC. The development of a new bioartificial liver and its application in 12 acute liver failure patients. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(4): 829-832
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i4/829.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i4.829