©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 15, 2003; 9(2): 351-355
Published online Feb 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i2.351
Published online Feb 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i2.351
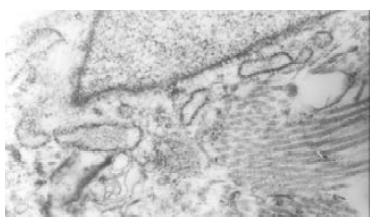
Figure 1 Bile duct fibroblasts of normal rabbit presented shuttle-shaped with abundant rough endoplasmic reticulums (RER), but few mitochondria and microfilament in cytoplasm.
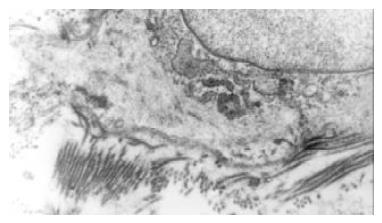
Figure 2 The bile duct fibroblasts of hypercholesterolemic rabbits showed the phenotype of smooth muscle cell.
Rough endoplasmic reticulums (RER) was significantly reduced, but a lot of microfilament bundles or stress fibers appeared in cytoplasm. Dense bodies were scattered within these bundles. Macula densas and discontinuous sarcolemma were found under splasma membrane.
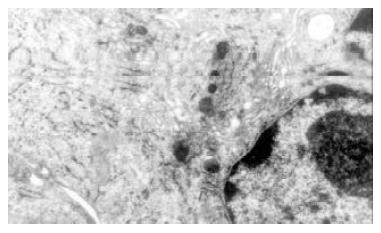
Figure 3 Cultured normal rabbit bile duct fibroblasts characterized typical phenotype of fibroblasts with abundant rough endoplasmic reticulums (RER) and golgi bodies, but few mitochondria and microfilament.
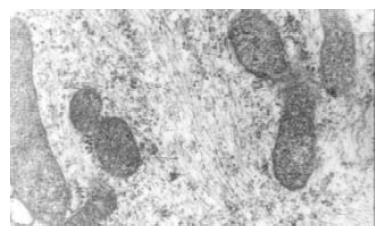
Figure 4 After stimulated by middle concentration cholesterol (0.
6 g/L) for 72 h, the cultured bile duct fibroblasts showed some phenotype of fibroblasts. and there appeared lots of microfilament in cytoplasm, but without dense body. macula densa and discontinuous sarcolemma.
Figure 5 Effects of middle concentration cholesterol (0.
6 g/L) on the cultured bile duct fibroblasts. There were many regular bundles of microfilament that were located along cytoplasmic extension.
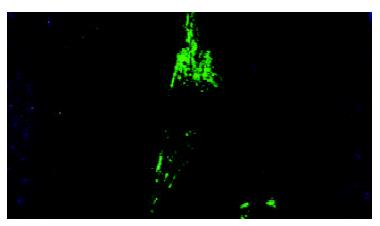
Figure 6 Effects of cholesterol on the α-actin expression of rabbit bile duct fibroblasts.
Note aP < 0.05, versus control and high concentration group (1.2 g/L cholesterol).
- Citation: Chen BY, Wei JG, Wang YC, Wang CM, Yu J, Yang XX. Effects of cholesterol on the phenotype of rabbit bile duct fibroblasts. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(2): 351-355
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i2/351.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i2.351