©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 15, 2002; 8(6): 1094-1097
Published online Dec 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.1094
Published online Dec 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.1094
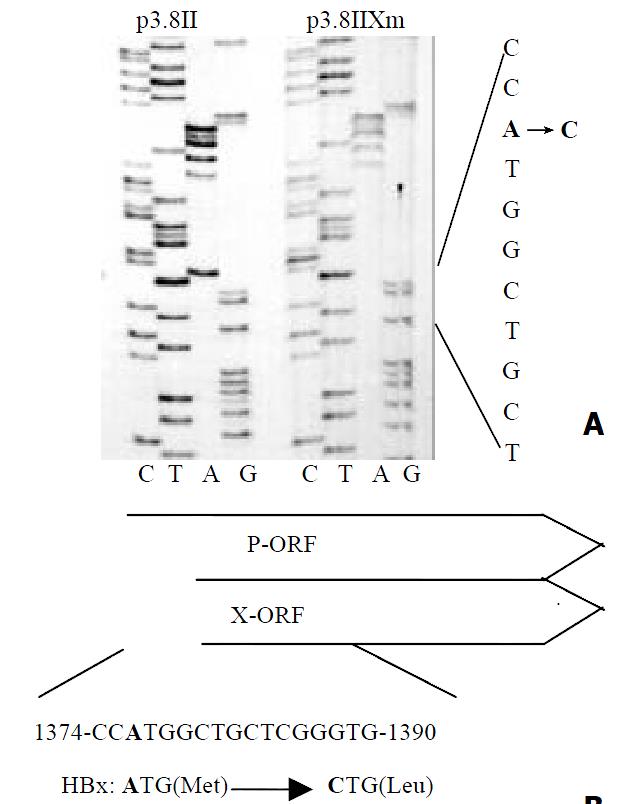
Figure 1 Partial DNA sequences of p3.
8II and p3.8IIXm is indicated in the left panel (A). The point mutation A→C re-sults in the amino acid changes in the ORF of HBV polymerase (P) and X protein(X) (B).
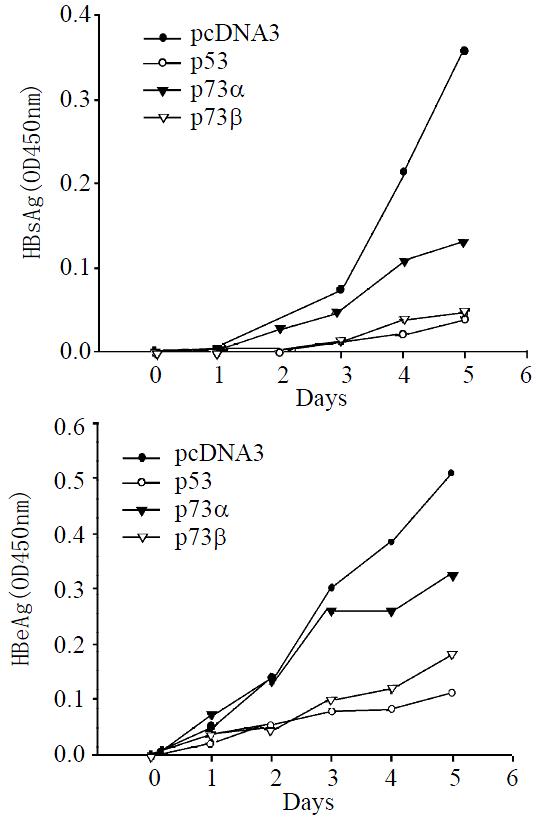
Figure 2 Time course of HBV antigen expression.
HepG2 cells were transiently transfected with X-minus p3.8IIXm, and cotransfected with pcDNA3, p53, p73α, or p73β individually. Culture medium were harvested at certain days, and detected by ELISA kit.
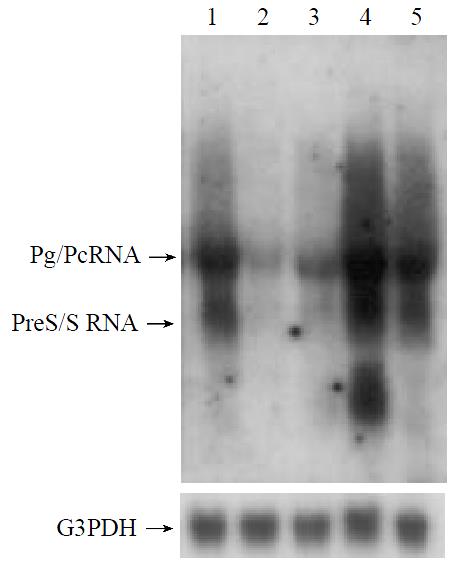
Figure 3 Northern blotting analysis of HBV viral transcripts, including pregenomic/precore RNA and preS/S RNA.
HepG2 cells were transiently transfected with p3.8IIXm, and also with the expression plasmids. Lane 1 represents pcDNA3, lane 2, p53, lane 3, p73β, lane 4, pHBX and lane 5, p73α respecitively. Total cellular RNA were extacted and α-32p-dCTP labeled 3.2 kb HBV DNA or G3PDH used as probe.
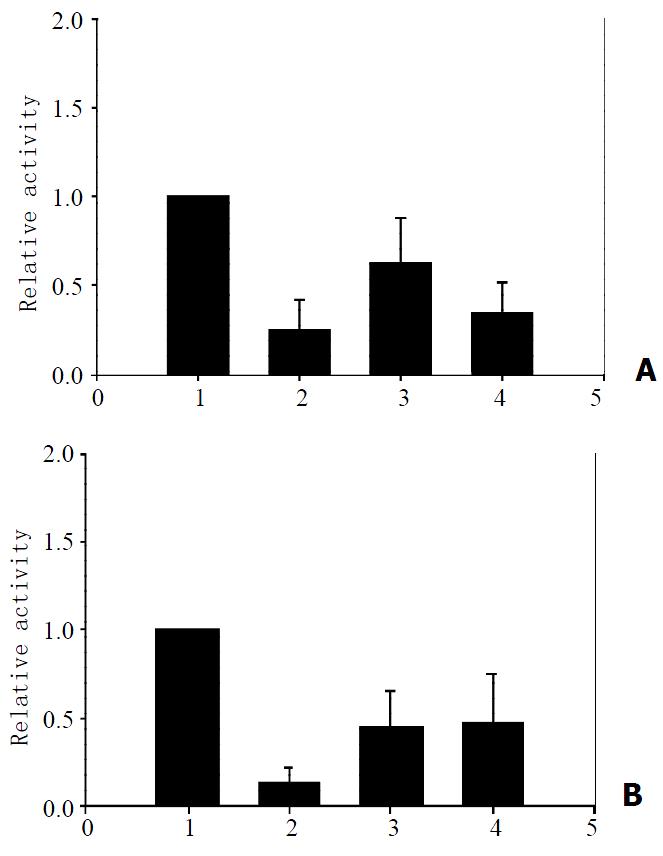
Figure 4 Effects of p73α and p73β on the regulatory sequences of hepatitis B virus.
HepG2 cells were transfected with expres-sion plasmids, pcDNA3(1), p53(2), p73α (3), and p73β (4). In each case, 1 μg of reporter plasmids, pENI/XpLuc, containing the enhancer I/X promoter (A) and pENII/CpLuc, containing enhancer II/core promoter (B), were individually cotransfected. 42 hours after transfection, the cells were harvested and luciferase activity was determined. The value obtained with reporters alone was arbitrarily set to 100%, and the other values were normal-ized accordingly. The column heights reflect the average of at least three independent experiments.
- Citation: Xu ZH, Zhao MJ, Li TP. p73β inhibits transcriptional activities of enhancer I and X promoter in hepatitis B virus more efficiently than p73α. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(6): 1094-1097
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i6/1094.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.1094