©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 2002; 8(4): 712-717
Published online Aug 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.712
Published online Aug 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.712
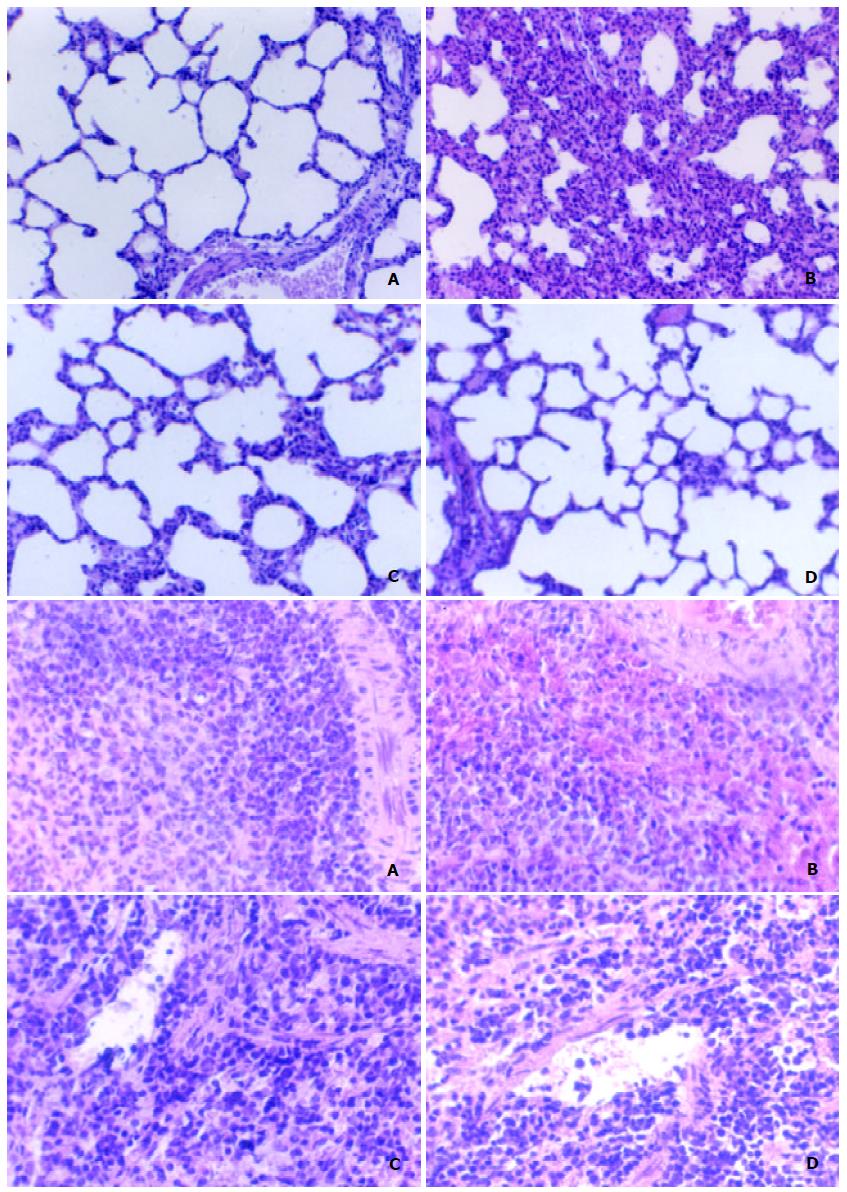
Figure 1 CCK-8 alleviated pulmonary (upper, × 100) and spleen (lower, × 200) structural injury 6 h after LPS administration.
A. Control group; B. LPS group; C. CCK-8 + LPS group; D. CCK-8 group. Plate depicts a representative field from one of three rats.
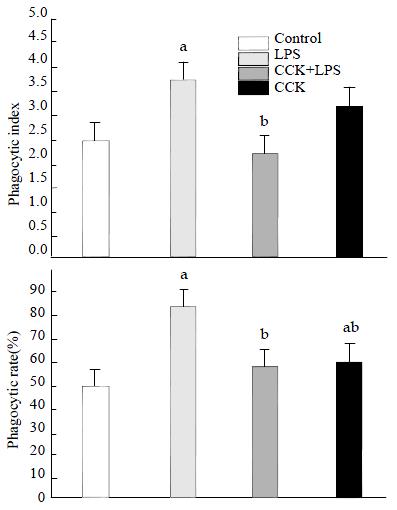
Figure 2 Effect of CCK-8 on LPS-induced increase of phagocytic capacity of Candida albicans by alveolar macrophages isolated 2 h after LPS administration.
aP < 0.05 vs Control, bP < 0.01 vs LPS.
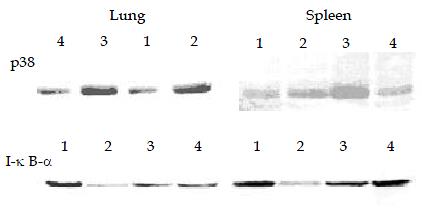
Figure 3 p38 MAPK (A) was activated by LPS and enhanced by CCK-8 in rat lung (left) or spleen (right) using Western blotting.
Degradation of IκB-α in lung and spleen following LPS administration was observed and pre-administration of CCK-8 could reduce its degradation. These figures are representative of three different experiments.1. Normal control, 2 LPS (8 mg•kg⁻¹), 3. CCK-8 (40 μg•kg⁻¹) + LPS, 4. CCK-8.
- Citation: Meng AH, Ling YL, Zhang XP, Zhang JL. Anti-inflammatory effect of cholecystokinin and its signal transduction mechanism in endotoxic shock rat. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(4): 712-717
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i4/712.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.712