Copyright
©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 2002; 8(4): 624-630
Published online Aug 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.624
Published online Aug 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.624
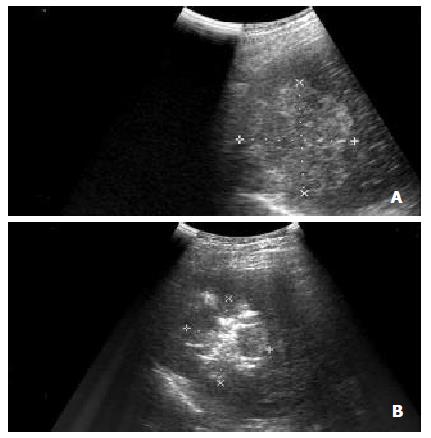
Figure 1 (A) Intercostal oblique sonogram shows a 5.
7 cm diameter nodular HCC in segment 8. (B) The RF electrode has been placed in the lesion, and the electrode tip is recognizable as an echogenic area in the tumor. Sonogram obtained after several minutes of energy deposition shows a hyperechoic patch around the electrode tip.
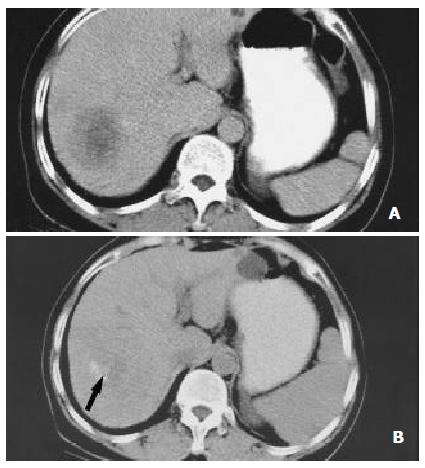
Figure 2 Nearly complete necrosis in a large HCC located in segment 7 and treated with RF therapy in a 57-year-old colorectal cancer liver metastases.
(A) CT scan obtained prior to therapy demonstrates a large, 5.3 cm nodules. (B) CT scan obtained 6 mo after RF therapy shows nearly complete tumor necrosis. A small hypervascularized area of viable neoplastic tissue (arrow) remains at the posteromedial aspect of the tumor.
- Citation: Jiang HC, Liu LX, Piao DX, Xu J, Zheng M, Zhu AL, Qi SY, Zhang WH, Wu LF. Clinical short-term results of radiofrequency ablation in liver cancers. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(4): 624-630
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i4/624.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.624