©The Author(s) 2001.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2001; 7(5): 685-689
Published online Oct 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i5.685
Published online Oct 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i5.685
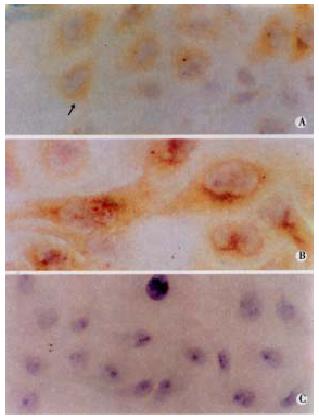
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical detection of HCV-encoded protein in infected 7721 cells.
Positive reaction (yellow) with anti-NS3 (A) and anti-CP10 (B) in 7721 cells, were scattered in the lobules (SP method, original magnification, A × 200, B × 400). Lack of staining with the same antibody in uninfected 7721 cells processed at the same times and 7721 incubated with oormal serum (C).
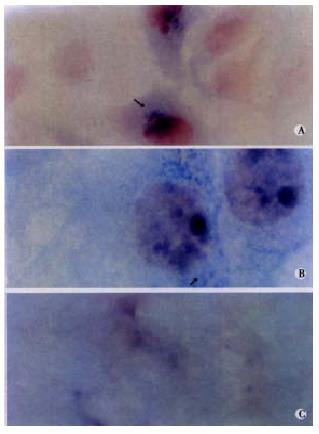
Figure 2 Detection of minus-strand of HCV RNA in cells using in situ hybridization.
Positive reaction (blue) was mainly present with cytoplasm (A, original magnification, × 400). Higher magnification showed the positive cells looked morhologically normal (B, original magnification, × 1000). No signal in uninfected cells (C).
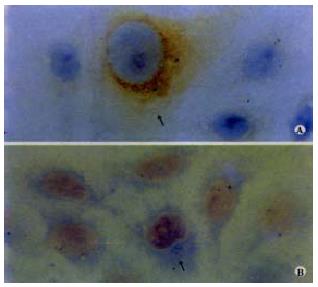
Figure 3 Cell-free transmission of HCV in cell culture.
HCV transmission to fresh/uninfected 7721 was carried out by using the supernatant of culture medium derived from HCV-infected cell culture. The presence of minus-strand of HCV RNA and NS 3 antigen in cells was detected by in situ hybridization (A, original magnification, × 400) and immunohistochem istry (B, original magnification, × 400), respectively.
- Citation: Song ZQ, Hao F, Min F, Ma QY, Liu GD. Hepatitis C virus infection of human hepatoma cell line 7721 in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7(5): 685-689
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v7/i5/685.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v7.i5.685