©The Author(s) 1999.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 15, 1999; 5(2): 147-151
Published online Apr 15, 1999. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v5.i2.147
Published online Apr 15, 1999. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v5.i2.147
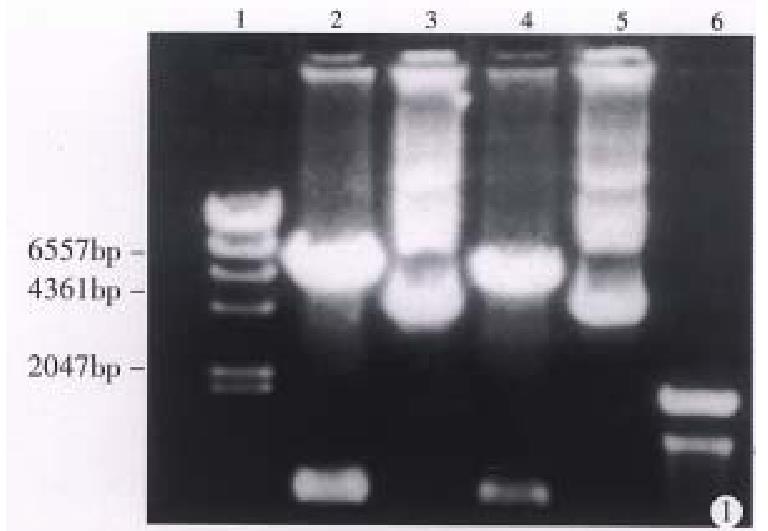
Figure 1 Electrophoretic result of plasmid pLNSXmB7.
After digestion by Hind III, pLNSX-mB7 was cleavaged into two fragments. They represented plasmid DNA and B7 DNA respectively. Lane 1: λ/Hind-III marker; Lane 2, 4: pLNSX-mB7 digested by Hind III; La ne 3, 5: pLNSX-mB7 non-digested; Lane 6: 100bp ladder marker
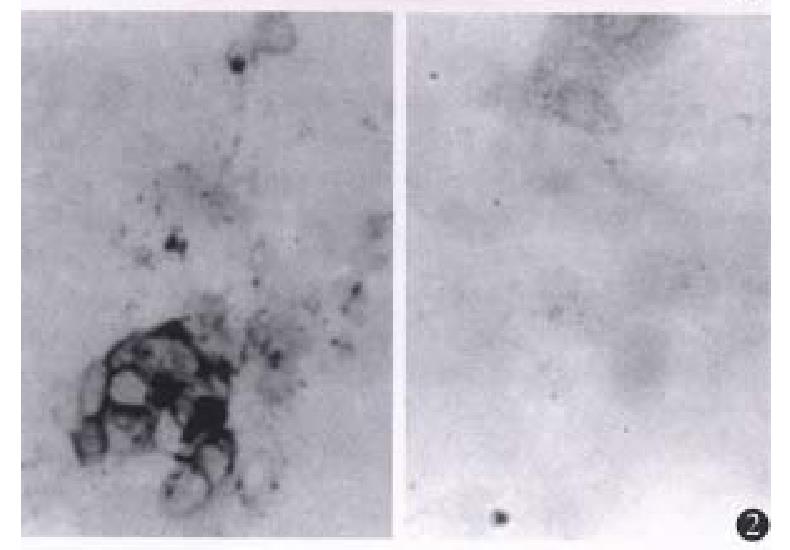
Figure 2 Results of immunohistochemistry.
× 100. The left is the staining of CMT93-B7 cells. Positive staining is mainly located in the cell membrane. The right is the negative staining of wild type CMT93 cells.
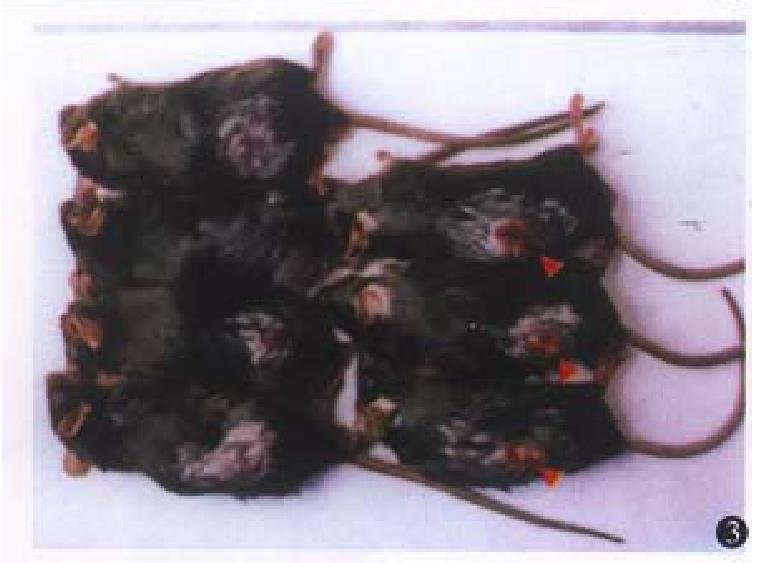
Figure 3 Tumorigenicity of CMT93-B7 (I).
In the left experimental group, all the four mice rejected the tumors completely. In the right control group, one big tumor was found in each mouse. The arrows showed the location of the tu-mors.
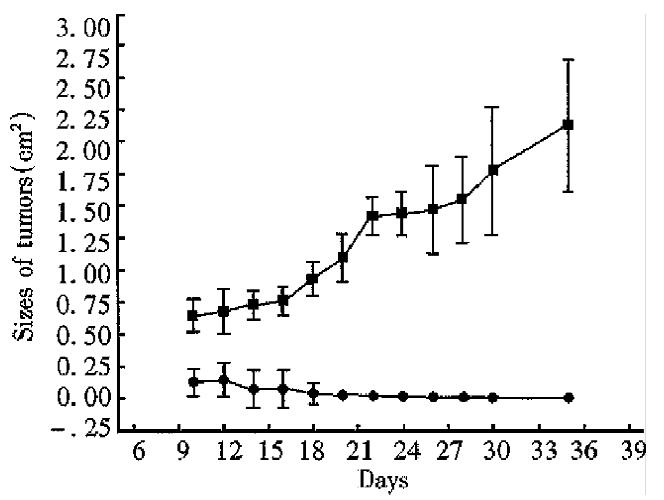
Figure 4 Tumorigenicity of CMT93-B7(II).
■The tumors in control mice injected wild type CMT93 grew progressively (n = 3). ●The tumors in experimental mice inoculated CMT93-B7 vanished gradually (n = 4, P < 0.01 compared with control group).
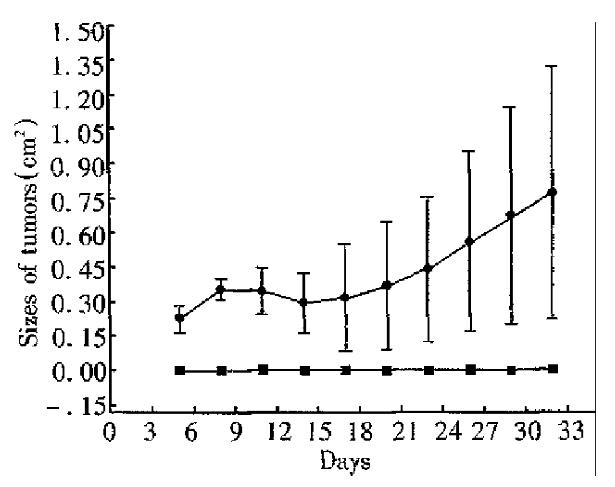
Figure 5 Protective immunity.
■In control group, four native mice injected 2.5 × 106 wild type CMT93 cells, one mouse’s tumor vanished. Three mice’s tumor grew progressively. ●In experimental group, four mice primed with CMT93-B7 were rechallenged with 2.5 × 106 wild type CMT93 cell, and no tumors were found. (P < 0.05 compared with control group).
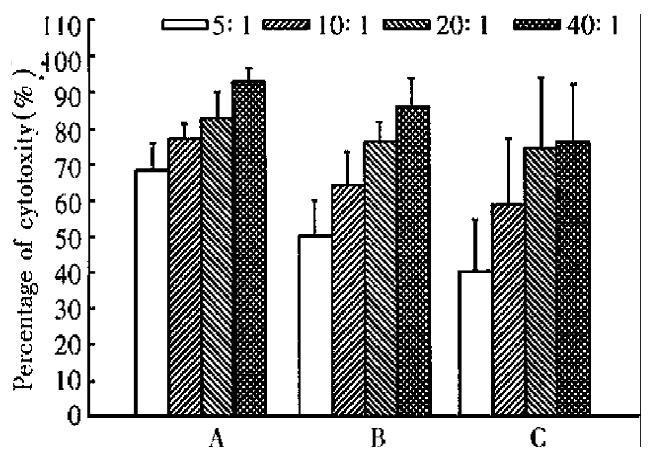
Figure 6 Cytotoxicity of abdominal cavity infiltrating lymphocytes (ACIL) against tumor cells.
A: Cytotoxicity of CMT93-B7 induced ACIL against CMT93-B7 tumor cells, n = 4. B: Cytotoxicity of CMT93-B7 induced ACIL against CMT93 wild type tumor cells, n = 4. C: Cytotoxicity of CMT93 induced ACIL against CMT93 wild type tumor cells, n = 4. By paired Student's t test: A is different from B significantly, P < 0.05; B is different from C significantly, P < 0.05.
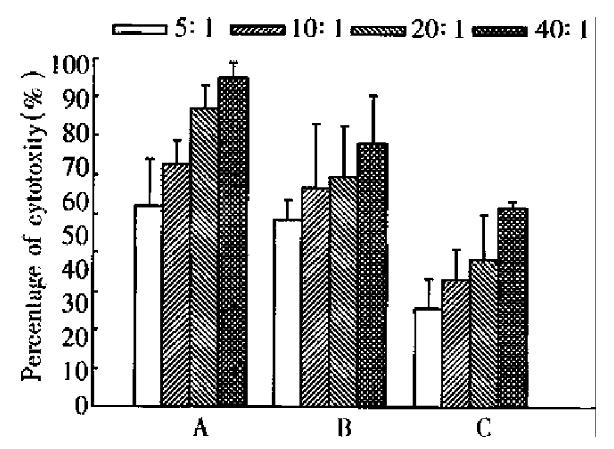
Figure 7 Cytotoxicity of spleen cells against tumor cells.
A: Cytotoxicity of CMT93-B7 induced spleen cells against CMT93-B7 tumor cells, n = 4. B: Cytotoxicity of CMT93-B7 induced spleen cells against CMT-93 wild type tumor cells, n = 4. C: Cytotoxicity of CMT93 induced spleen cells against CMT93 wild type tumor cells, n = 4. By paired Student’s t test: A is different from B significantly, P < 0.05; B is different from C significantly, P < 0.01.
-
Citation: Hu JY, Wang S, Zhu JG, Zhou GH, Sun QB. Expression of B
7 costimulation molecules by colorectal cancer cells reducestumorigenicity and induces anti-tumor immunity. World J Gastroenterol 1999; 5(2): 147-151 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v5/i2/147.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v5.i2.147