©The Author(s) 1999.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 15, 1999; 5(2): 138-142
Published online Apr 15, 1999. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v5.i2.138
Published online Apr 15, 1999. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v5.i2.138
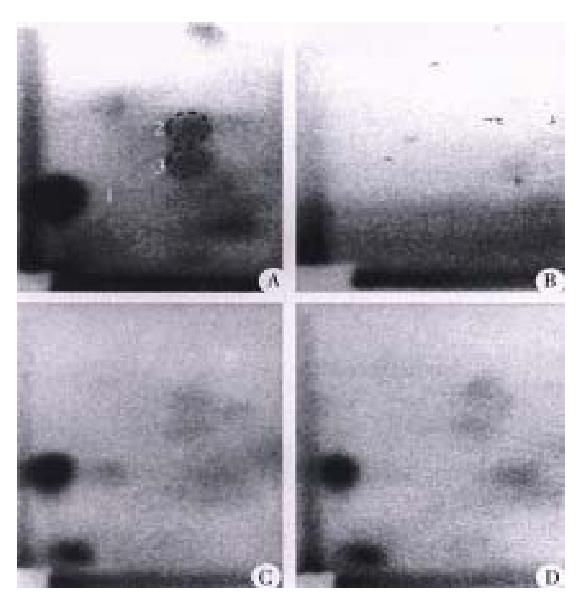
Figure 1 Autoradiograms of PhIP-DNA adducts analyzed by 32P-postlabeling.
(A) N-Hydroxy-PhIP modified calf thymus DNA; (B) colon DNA from control rats without PhIP treatment; (C) colon DNA from rats given 10 mg/kg PhIP an d control diet; (D) colon DNA from rats given 10 mg/kg PhIP after 10 days on the diet containing 20% (w/w) Chinese cabbage.
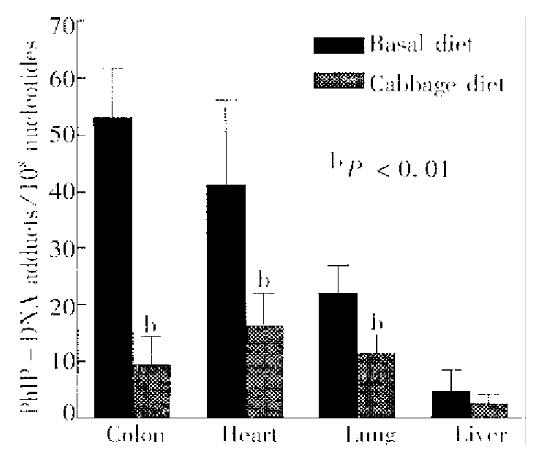
Figure 2 PhIP-DNA adduct levels in tissues of rats given PhIP (10 mg/kg) with or without pretreatment with Chinese cabbage for 10 days.
Values shown are -x±s from 5 rats/group. Asterisk-designates a response significantly different from control at P < 0. 01 with ANOVA.
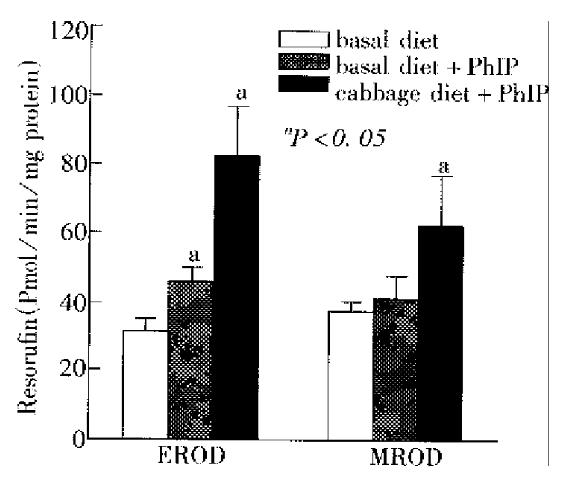
Figure 3 Activity of 7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase (EROD) and methoxyresorufin O-demethylase (MROD) in hepatic microsomes from rats received different treatments.
Activity values shown are the -x±s from three experiments, each from 5 individual microsome samples. Asterisk-designates a response significantly different from control at P < 0.05 with ANOVA.
-
Citation: Tan W, Lin DX, Xiao Y, Ff K, Chen JS. Chemoprevention of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenyli-midazo [4, 5-
b ] pyridine-induced carcinogen-DNA adducts by Chinese cabbage in rats. World J Gastroenterol 1999; 5(2): 138-142 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v5/i2/138.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v5.i2.138