©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2026; 32(4): 114842
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.114842
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.114842
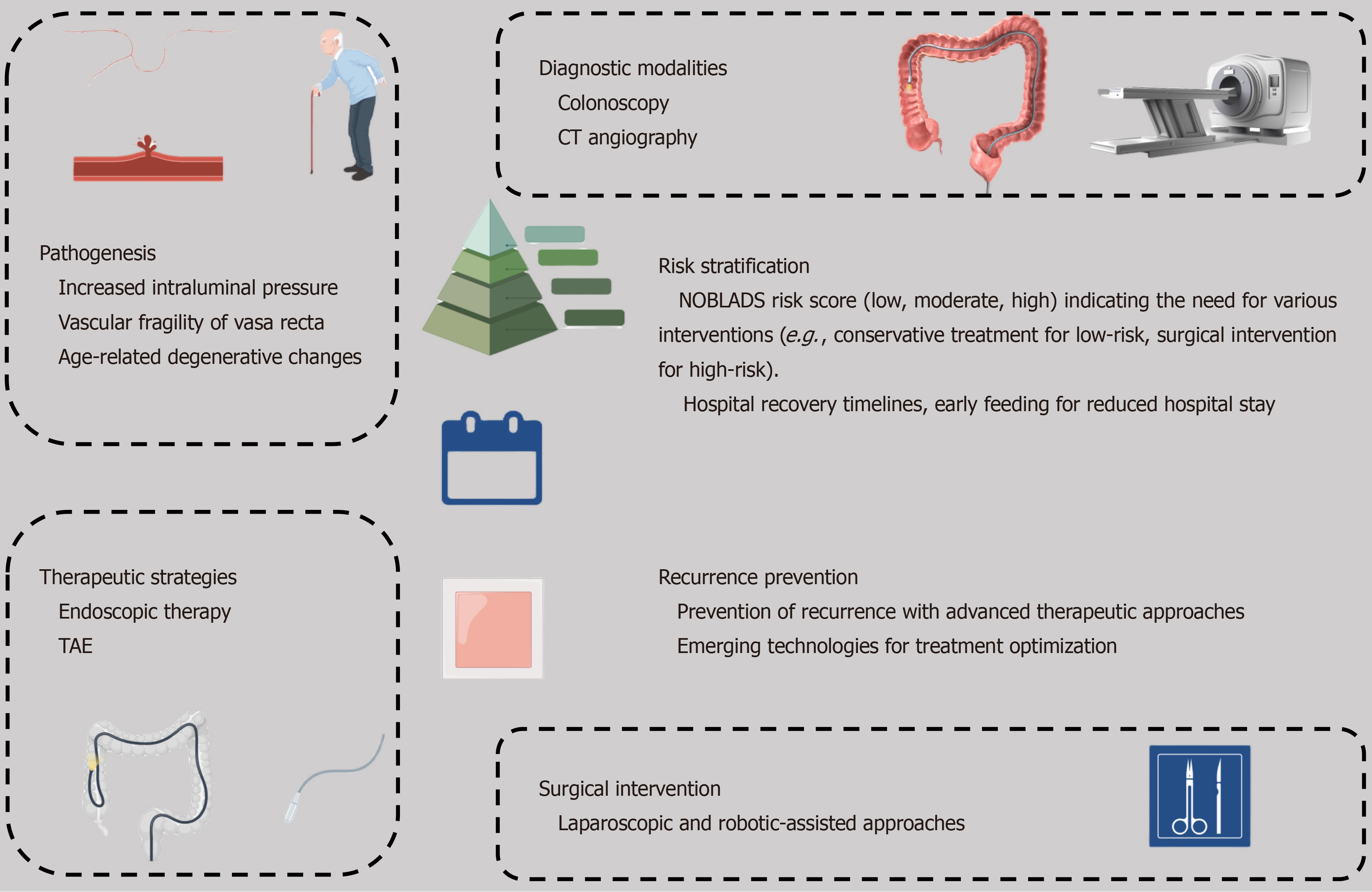
Figure 1 The multifactorial pathogenesis of colonic diverticular hemorrhage, including increased intraluminal pressure, vascular fragility of the vasa recta, and age-related structural changes of the colonic wall.
Diagnostic approaches are summarized, with colonoscopy serving as the first-line tool for direct visualization and therapy, complemented by computed tomography angiography for precise localization of active bleeding. Therapeutic strategies include endoscopic treatments such as band ligation and clipping, transcatheter arterial embolization for refractory bleeding, and surgical resection for complicated or persistent cases. The central role of risk stratification models (e.g., NOBLADS score) in guiding treatment decisions is highlighted, along with emerging measures for recurrence prevention, such as early feeding protocols and biomaterial patch therapy. TAE: Transcatheter arterial embolization; CT: Computed tomography.
- Citation: Hui YQ, Wang ZX, Wang CX, Tong C. Colonic diverticular hemorrhage: Etiology, diagnostic challenges, and evolving therapeutic strategies. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(4): 114842
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i4/114842.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.114842