©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2026; 32(4): 114420
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.114420
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.114420
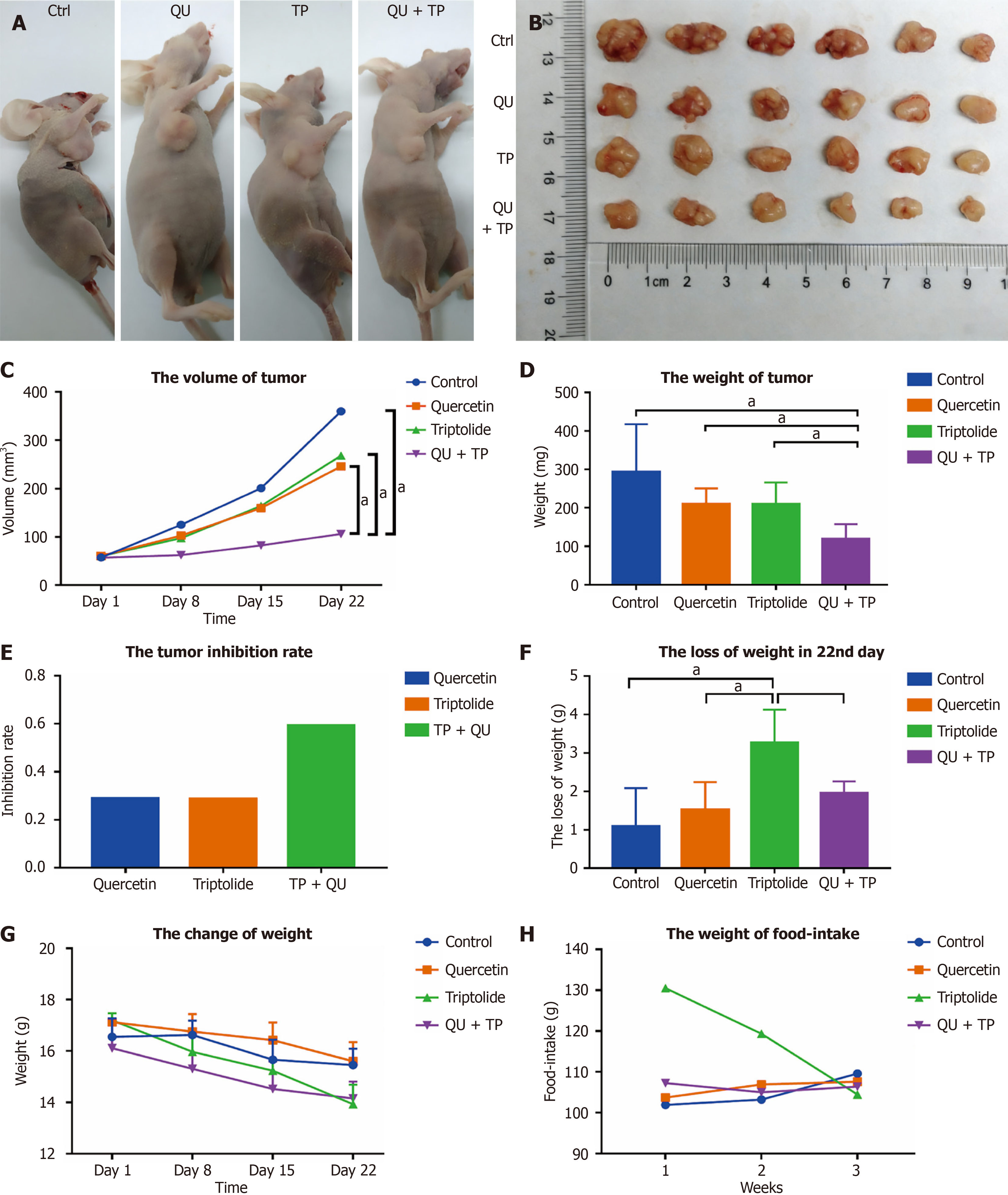
Figure 1 The anti-tumor effect of triptolide and/or quercetin in vivo.
A: The tumor of the nude mice after 21 days’ treatment; B: All tumors stripped from nude mice in the four groups; C: The change of the mean volume of tumor in each group; D: The mean weight in each group after 21 days’ treatment; E: The tumor inhibition rate compared with control group; F: The mean loss of weight in each group after 21 days’ treatment; G: The change of the mean weight of tumor in each group; H: The change of the mean weight of food-intake in each group. TP: Triptolide; QU: Quercetin.
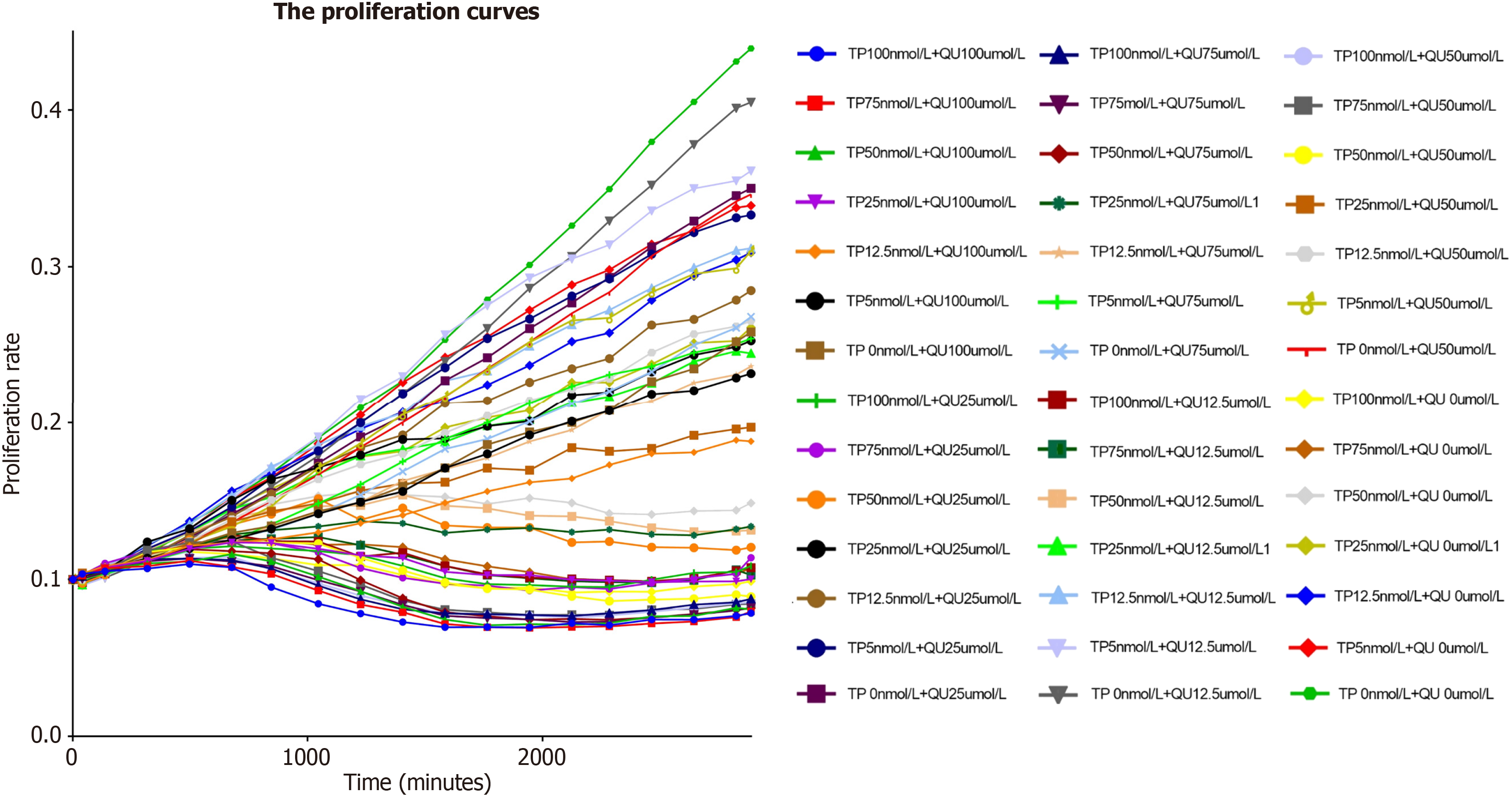
Figure 2 The proliferation curves of different dose combinations between quercetin and triptolide using IncuCyteZOOM 2015A.
The combination of various doses was added to the cells and they were cultured in IncuCyteZOOM 2015A. We took pictures of each group every 3 hours. Then the software could change them into data of proliferation. TP: Triptolide; QU: Quercetin.
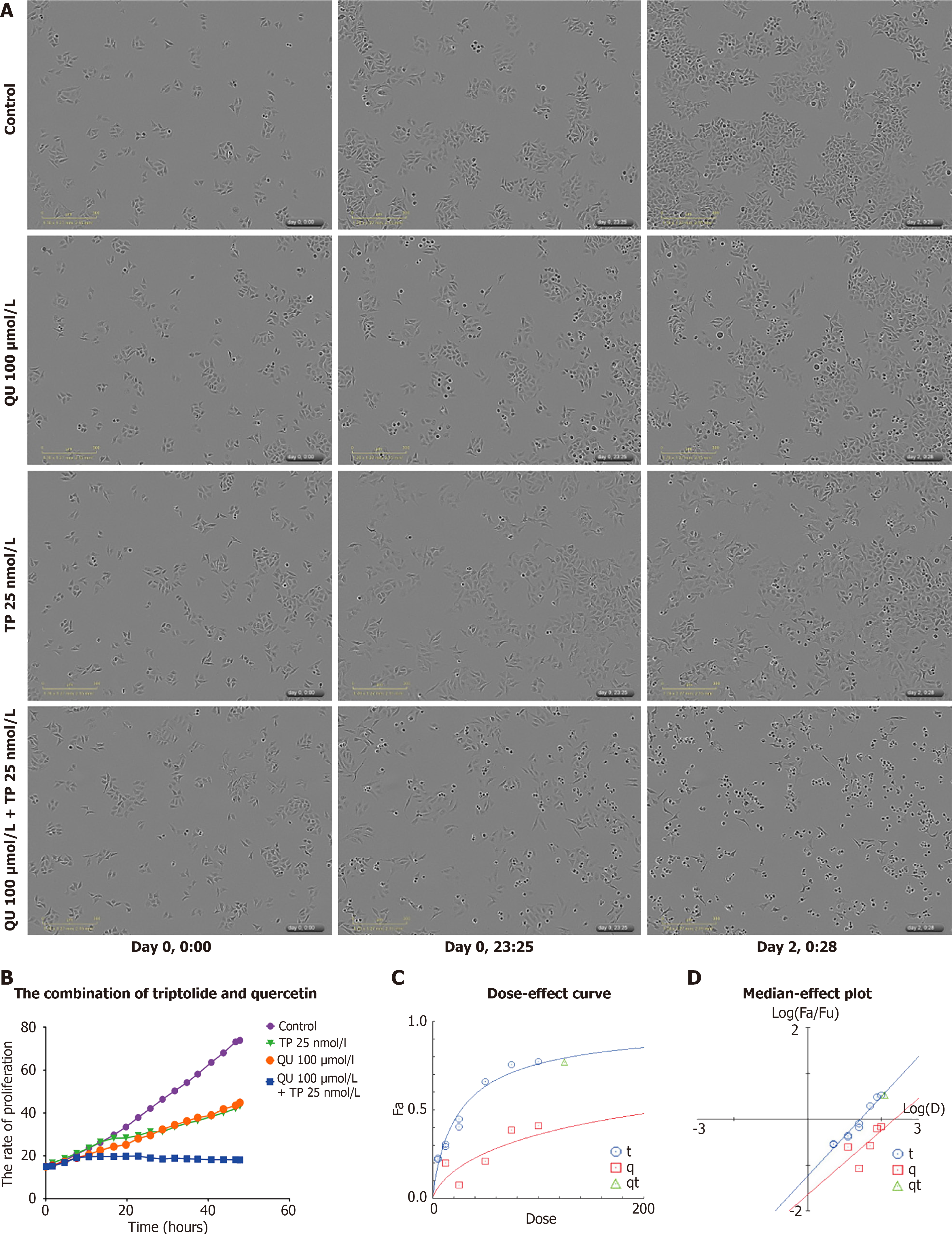
Figure 3 The combination of 25 nmol/L triptolide with 100 μmol/L quercetin.
A: The sequence pictures of the combination of 100 μmol/L quercetin and 25 nmol/L triptolide in 48 hours in the same point by live cell workstation (IncuCyteZOOM 2015A); B: The proliferation curve for 25 nmol/L triptolide combined with 100 μmol/L quercetin in 48 hours; C: The combination index for the combination of 25 nmol/L triptolide with 100 μmol/L quercetin calculated by CompuSyn. TP: Triptolide; QU: Quercetin.
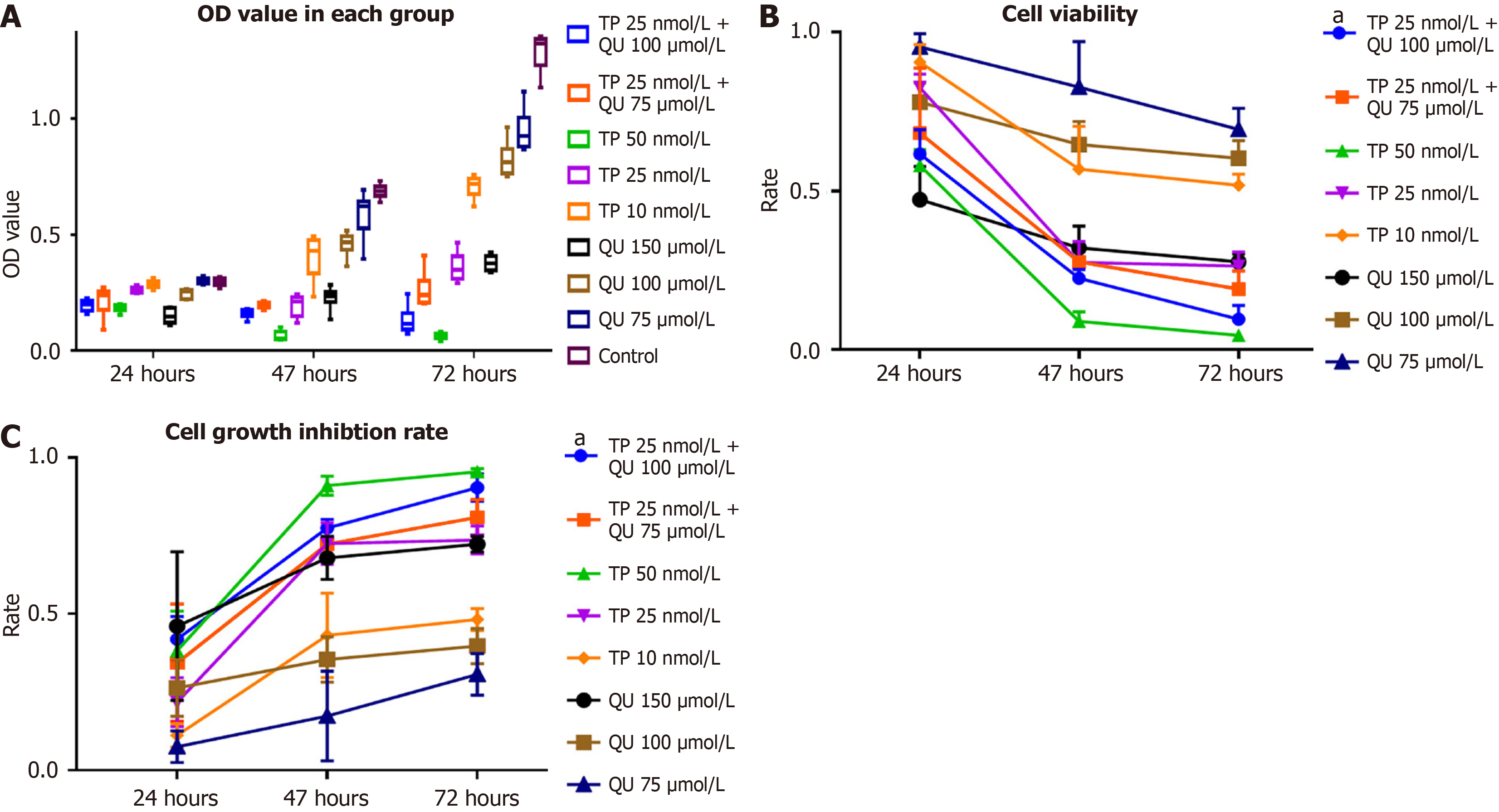
Figure 4 Combinational anti-tumor effect of triptolide and quercetin in HepG2 cell line compared with single drug tested by CCK-8.
HepG2 cell cells were treated with 25 nmol/L triptolide alone or combined with 75 μmol/L or 100 μmol/L quercetin for 24 hours, 48 hours, 72 hours treatment. A: The OD value determined by CCK-8 assay in 24 hours, 48 hours, 72 hours treatment; B: Cell viability ratio in each group; C: Cell growth inhibition ratio in each group. The tests were performed at least three independent parallel experiments. All of the data were expressed by mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 compared to other groups excluded triptolide 50 nmol/L group. TP: Triptolide; QU: Quercetin.
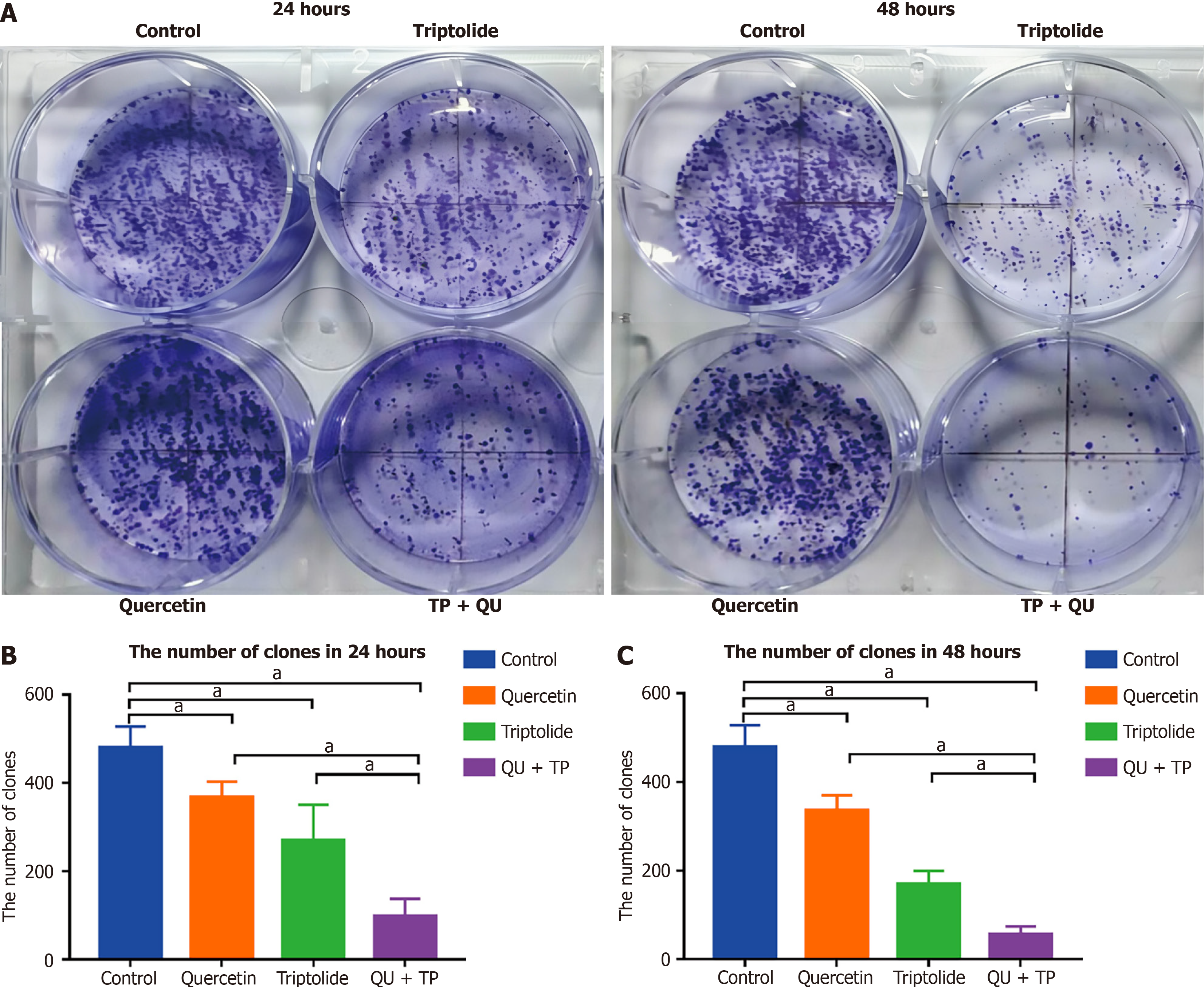
Figure 5 The colony formation of triptolide and/or quercetin in HepG2 cell line.
A: The photos of HepG2 cell line’s colonies with 1000 seeding cell number that treated with 25 nmol/L triptolide and/or 100 μmol/L quercetin for 24 hours; B: The photos of HepG2 cell line’s colonies with 1000 seeding cell number that treated with 25 nmol/L triptolide and/or 100 μmol/L quercetin for 48 hours; C: Quantitative representation of the colonies of HepG2 cells. Compared to the control group, the colony formations in treated groups were decreased and the combinational group was lowest. Meanwhile, the colony formation decreased as time goes on in each drug groups. Data was presented as means ± SE of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05. TP: Triptolide; QU: Quercetin.
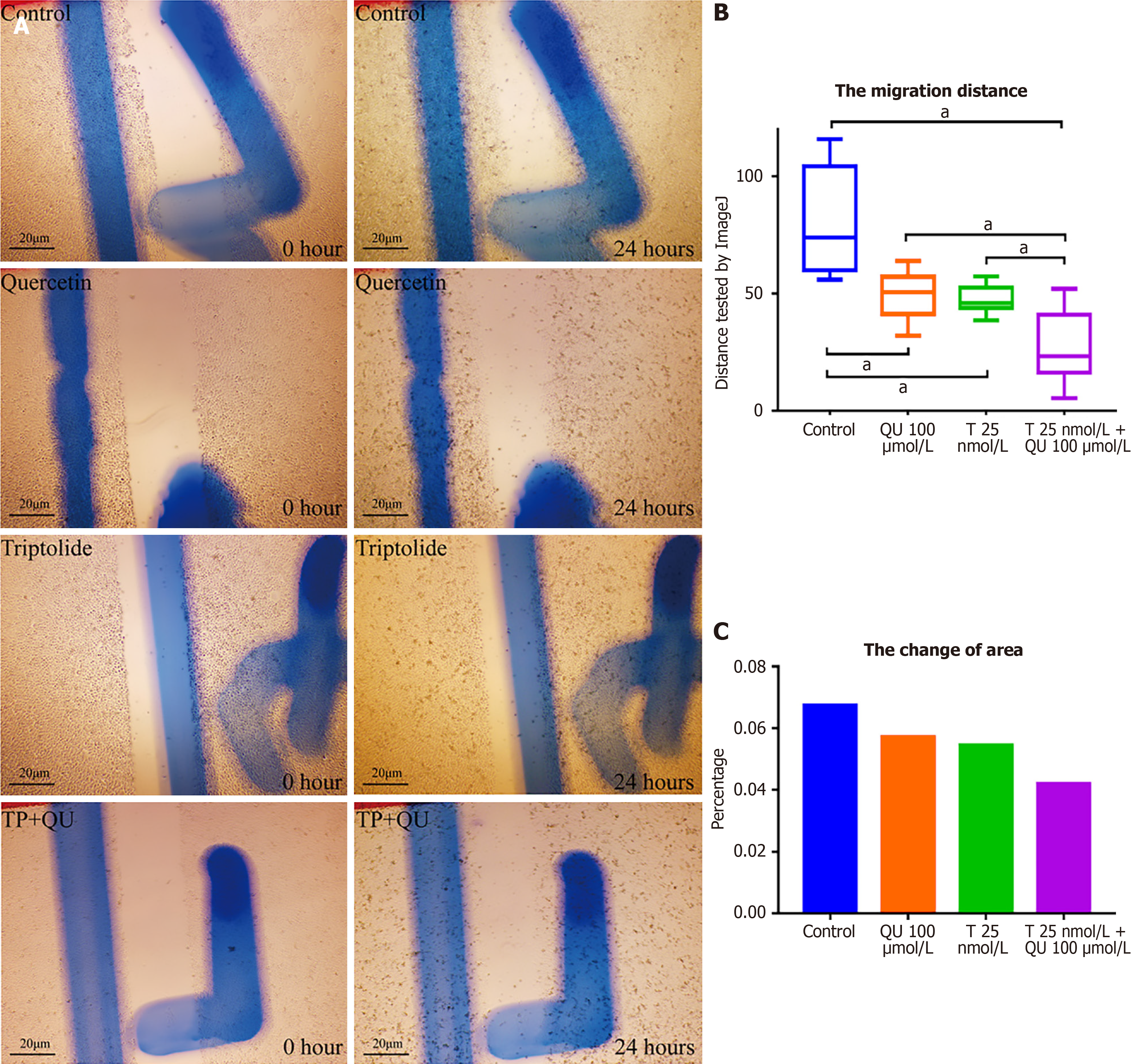
Figure 6 Combinational effect of triptolide and quercetin in migration tested by wound-healing assay.
A: The migrational pictures for four groups after 24 hours treatment; B: Migrational distance for each group after 24 hours tested by ImageJ; C: Area of migration for each group after 24 hours tested by ImageJ. Data was presented as means ± SE. aP < 0.05. TP: Triptolide; QU: Quercetin.
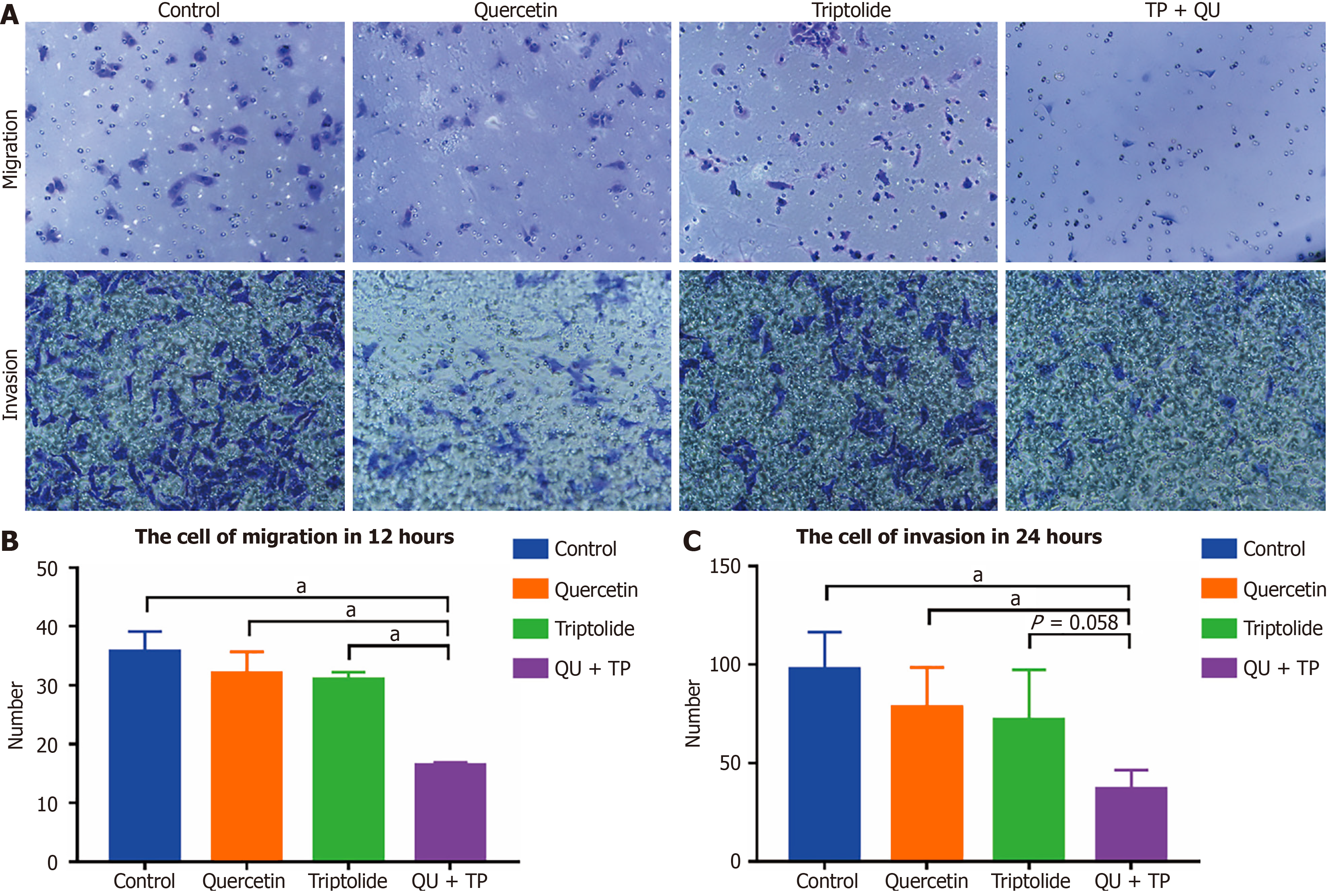
Figure 7 The migration and invasion of HepG2 tested by Transwell in each group.
A: The picture of migration and invasion. The migration and invasion of HepG2 showed best result in the group of 25 nmol/L triptolide combined 100 μmol/L quercetin; B: The numbers of migrational cell. It showed the combinational group had statistically significant difference compared with other groups after 12 hours treatment; C: The numbers of invasional cell. The combinational group had statistically significant difference compared with control group and quercetin group after 24 hours treatment, meanwhile the P value is low compared to triptolide (P = 0.058). The tests were performed at least three independent parallel experiments. Data was presented as means ± SE of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05. TP: Triptolide; QU: Quercetin.
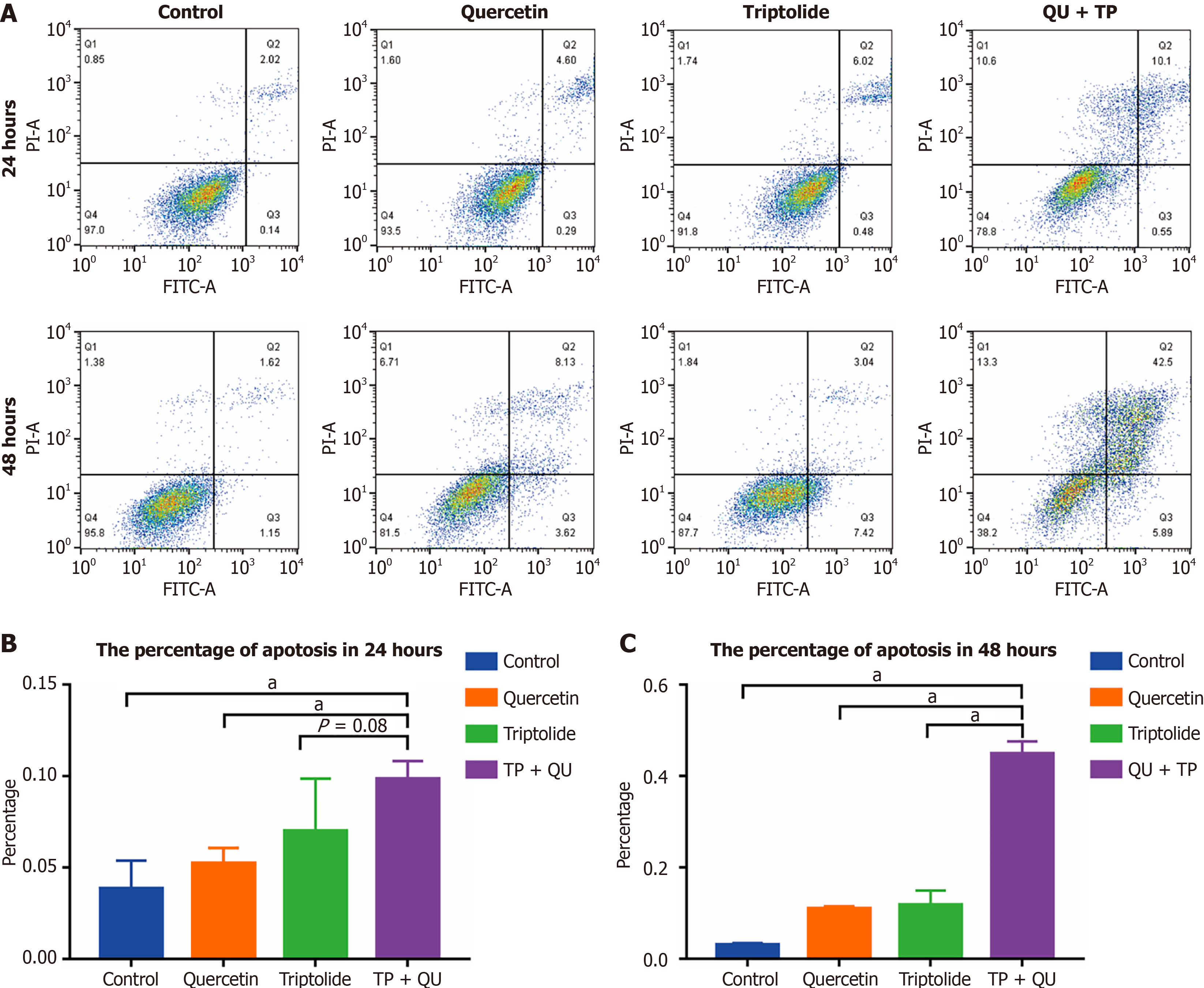
Figure 8 Apoptotic effects of triptolide and/or quercetin in HepG2 cell line by fluorescence activated cell sorter analysis.
A: Annexin V-FITC/PI was performed to measure the apoptosis and then deal with FlwoJo 10. The pictures showed the treated cells in the four quadrants; B and C: The percentage of apoptotic cells in difference phases in 24 hours or 48 hours. Percentages of negative represent viable cells, annexin V-positive represent early apoptotic cells, PI-positive represent necrotic cells, or annexin V and PI double-positive represent late apoptotic cells. The tests were performed at least three independent parallel experiments. Data was presented as means ± SE of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05. TP: Triptolide; QU: Quercetin.
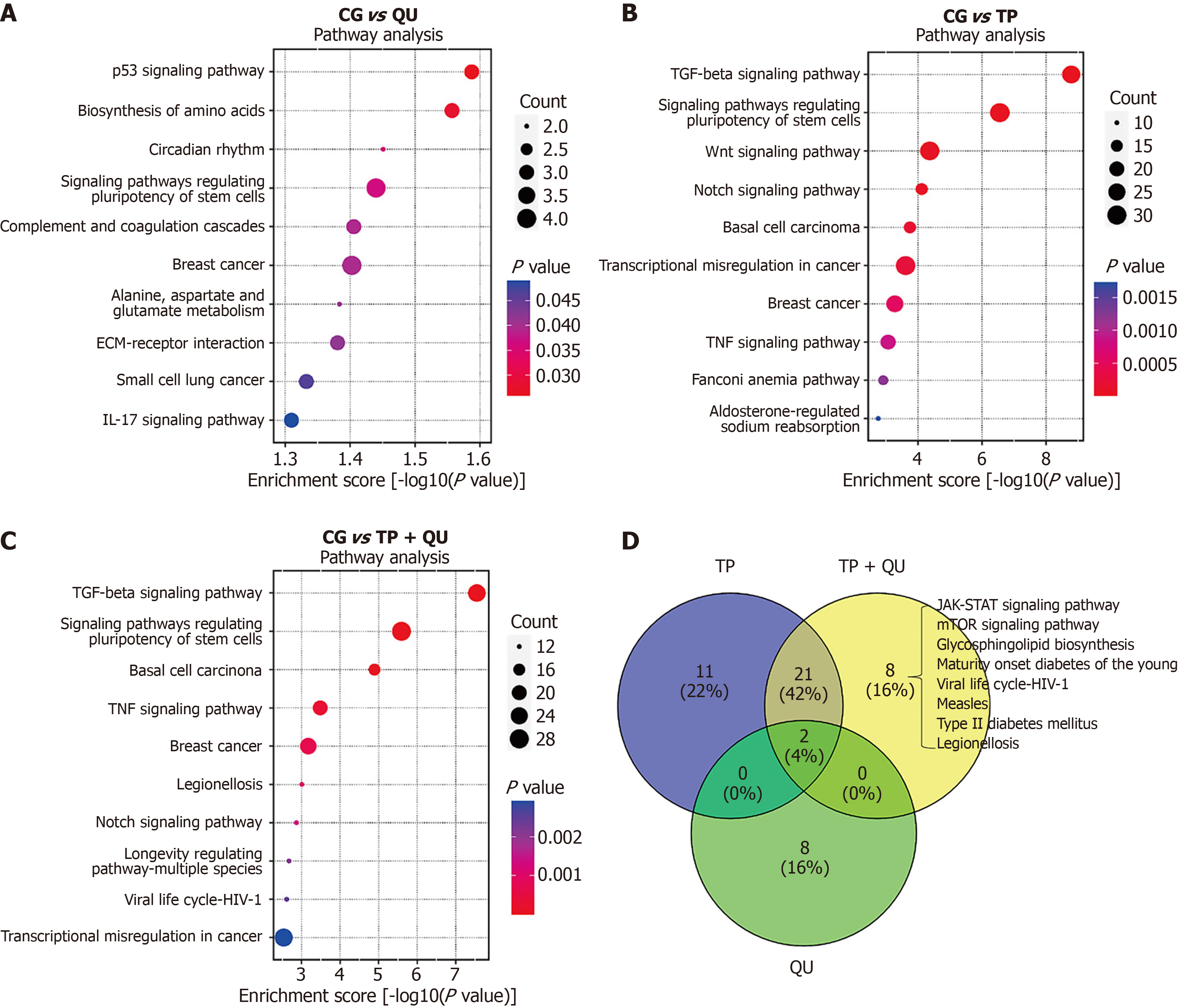
Figure 9 Pathway functional analysis by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes compared with control group based on RNA sequencing.
A: The top ten signaling pathways with the greatest statistical difference for control group compared with quercetin; B: The top ten signaling pathways with the greatest statistical difference for control group compared with triptolide; C: The top ten signaling pathways with the greatest statistical difference for control group compared with triptolide + quercetin; D: The Venn diagram of signaling pathways for three different drug interventions groups compared with control group. TP: Triptolide; QU: Quercetin.
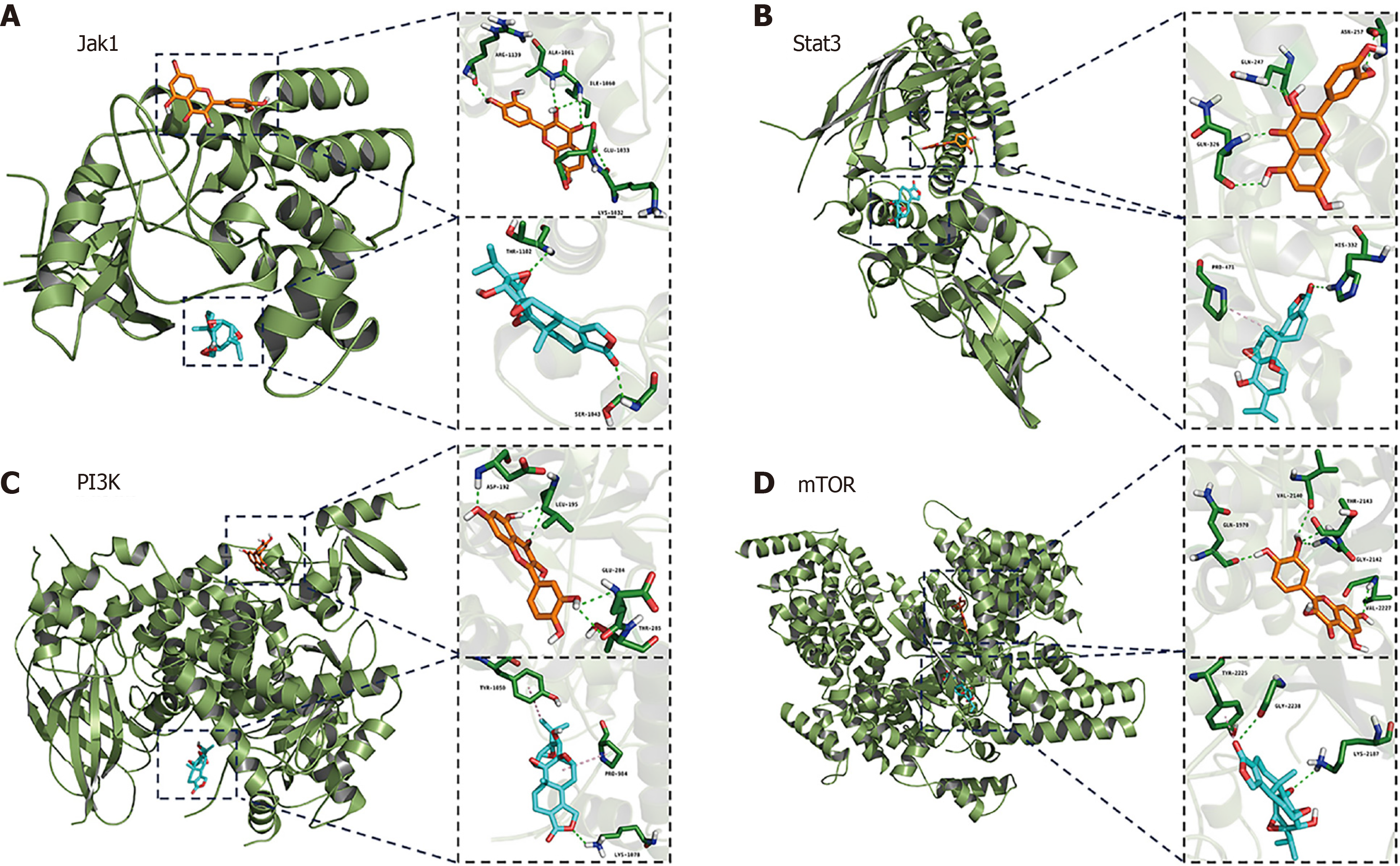
Figure 10 Molecular docking analysis of the two molecules with targets.
A: Quercetin and triptolide (TP) docked with Janus kinase 1; B: Quercetin and TP docked with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; C: Quercetin and TP docked with phosphoinositide 3-kinase; D: Quercetin and TP docked with mammalian target of rapamycin. Jak1: Janus kinase 1; Stat3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin.
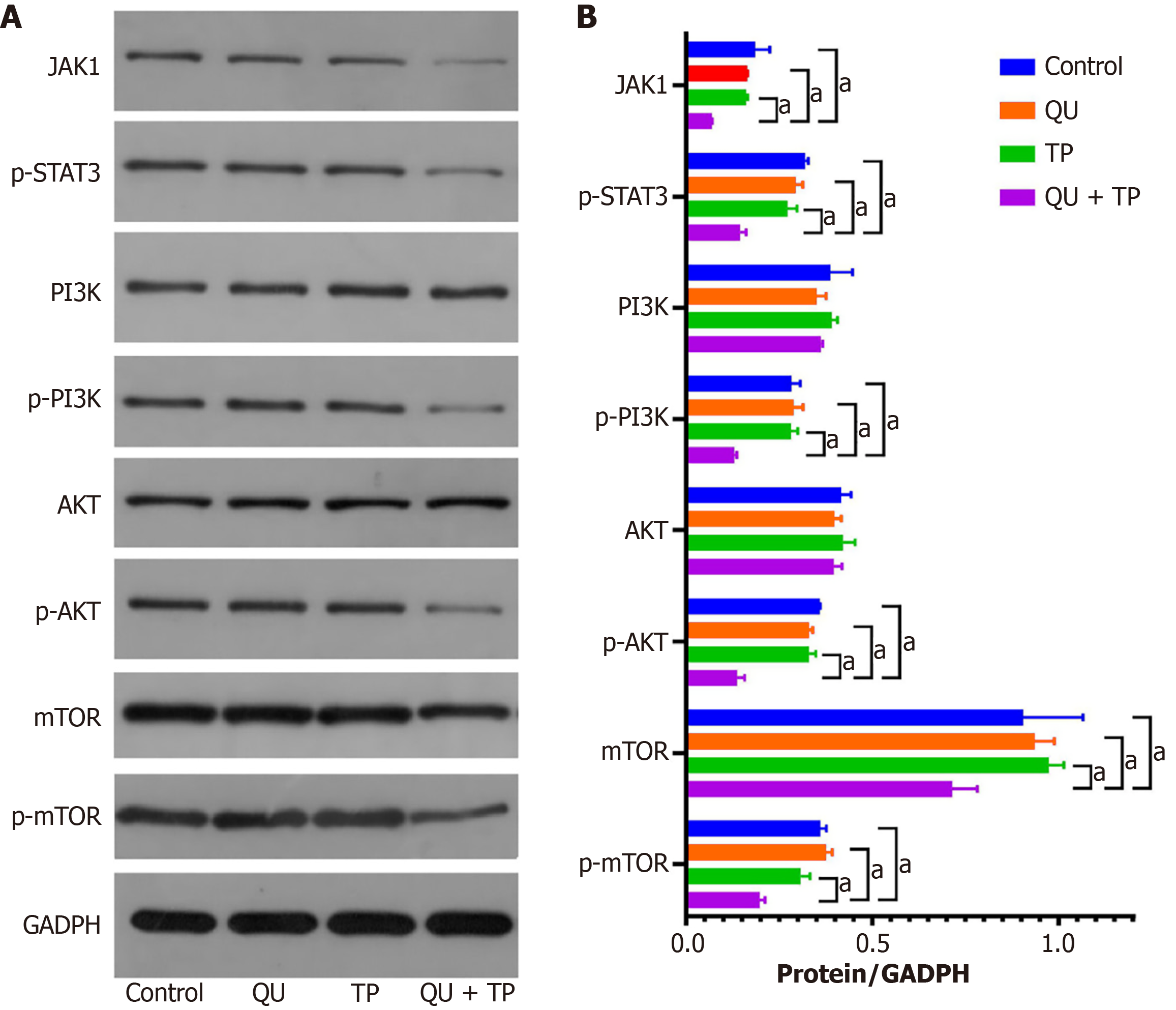
Figure 11 The expression level of related mechanism protein.
A: Western blots showing the levels of Janus kinase 1, p-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, p-phosphoinositide 3-kinase, protein kinase B, p-protein kinase B, mammalian target of rapamycin, and p-mammalian target of rapamycin; B: The expression of each protein normalized by β-actin according to grey value. aP < 0.05. TP: Triptolide; QU: Quercetin; Jak1: Janus kinase 1; Stat3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin.
- Citation: Tong HX, Zhang JL, Nie WY, Jiang LJ, Hu JQ, Lu T. Synergistic anti-hepatoma effect of triptolide and quercetin via co-inhibition and interaction with Janus kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin signal pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(4): 114420
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i4/114420.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.114420