©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2026; 32(4): 113492
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.113492
Published online Jan 28, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.113492
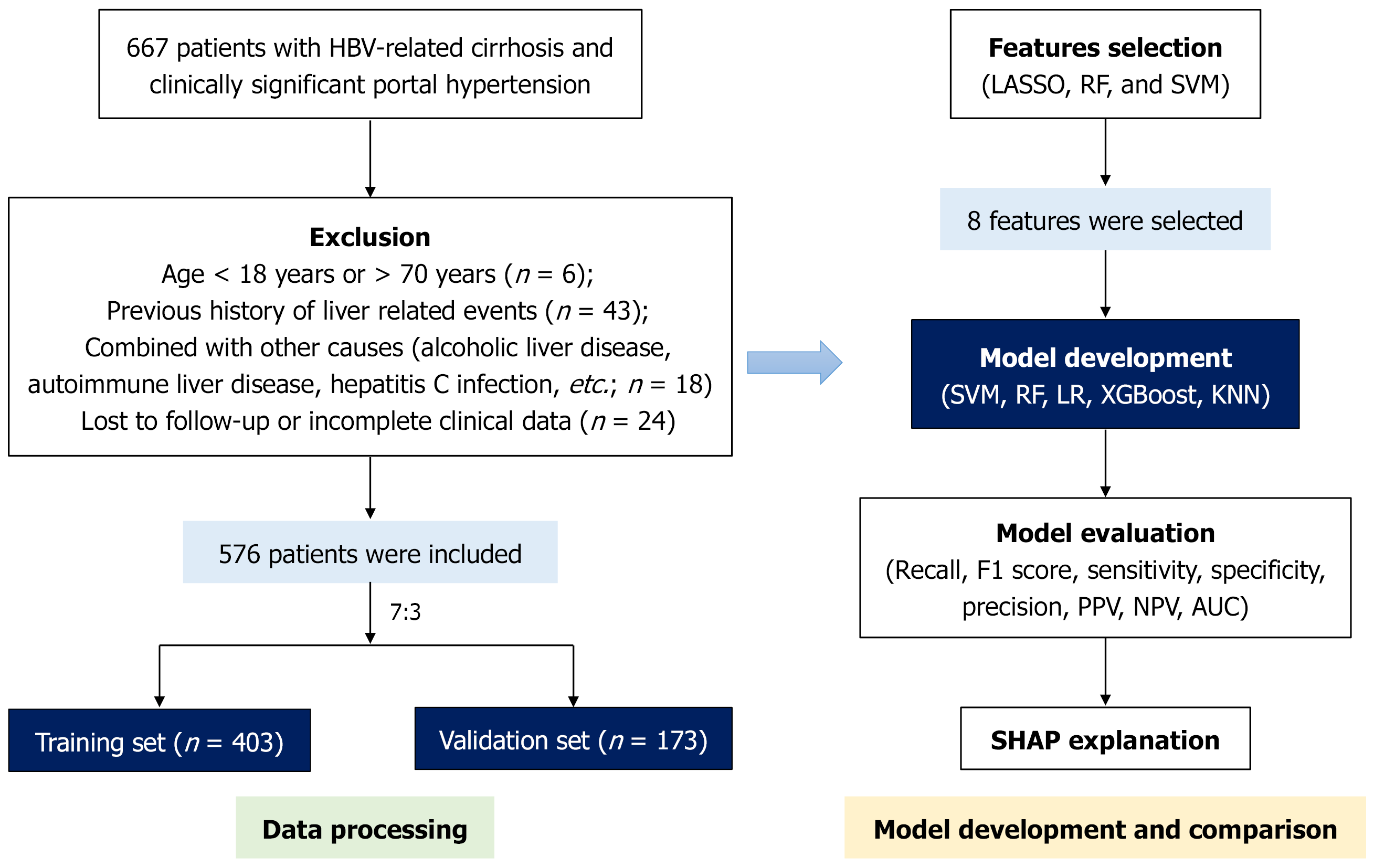
Figure 1 Flowchart.
HBV: Hepatitis B virus; LASSO: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; RF: Random forest; SVM: Support vector machine; LR: Logistic regression; XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting; KNN: K-nearest neighbor; PPV: Positive predictive value; NPV: Negative predictive value; AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations.
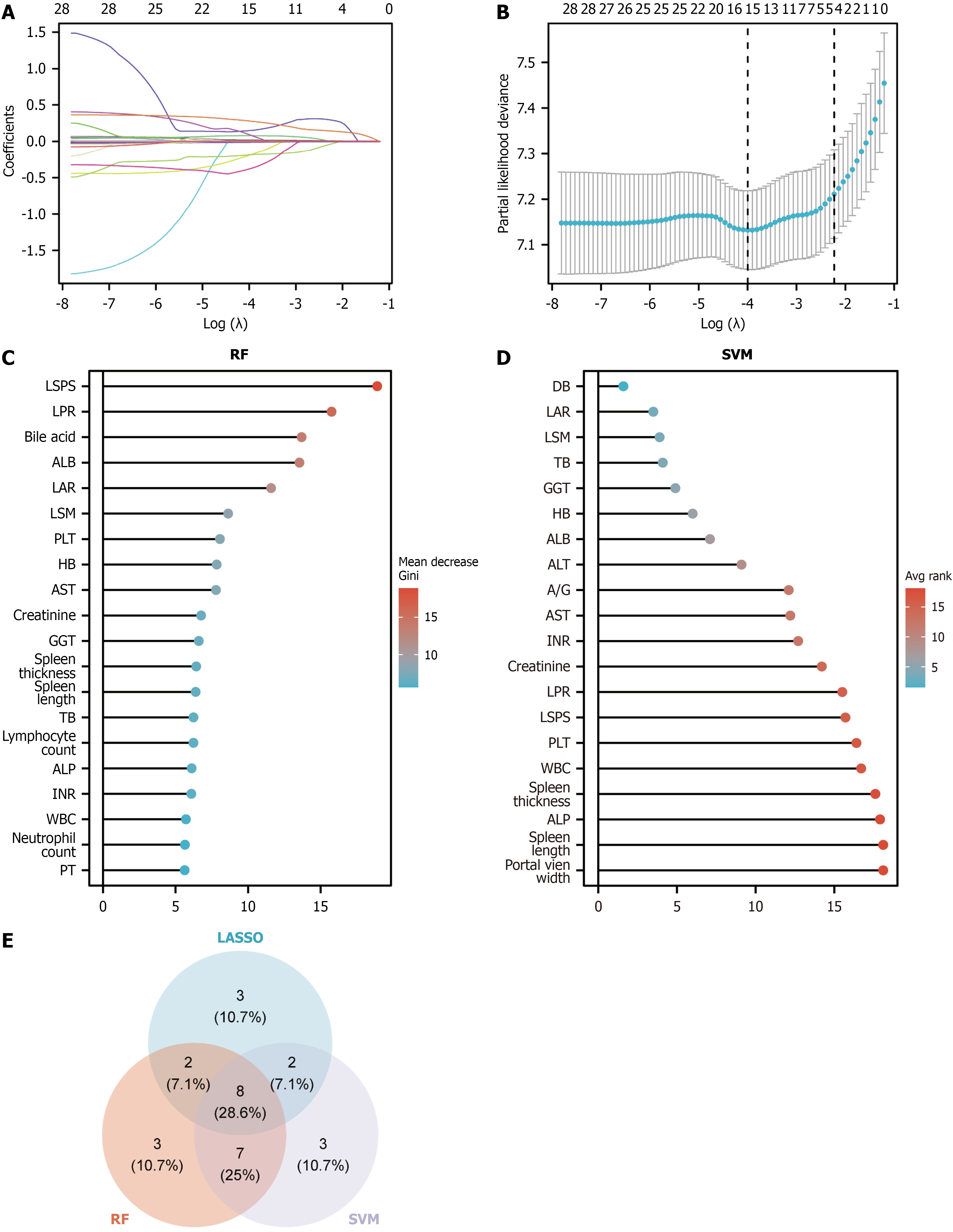
Figure 2 Feature selection.
A: Curve showing the change in variable coefficients for different λ values in least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression; B: Curve showing the relationship between partial likelihood deviation and log(λ); C: Feature importance ranking calculated by the random forest (RF) algorithm; D: Feature importance ranking evaluated by the support vector machine (SVM) algorithm; E: Intersection Venn diagram of features screened by LASSO, RF, and SVM. LSPS: Liver stiffness-spleen diameter-to-platelet ratio score; LPR: Liver stiffness measurement-to-platelet ratio; ALB: Albumin; LAR: Liver stiffness measurement-to-albumin ratio; LSM: Liver stiffness measurement; PLT: Platelet; HB: Hemoglobin; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; GGT: Gamma-glutamyltransferase; TB: Total bilirubin; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; INR: International normalized ratio; WBC: White blood cell; PT: Prothrombin time; DB: Direct bilirubin; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; A/G: Albumin/globulin ratio; LASSO: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator.
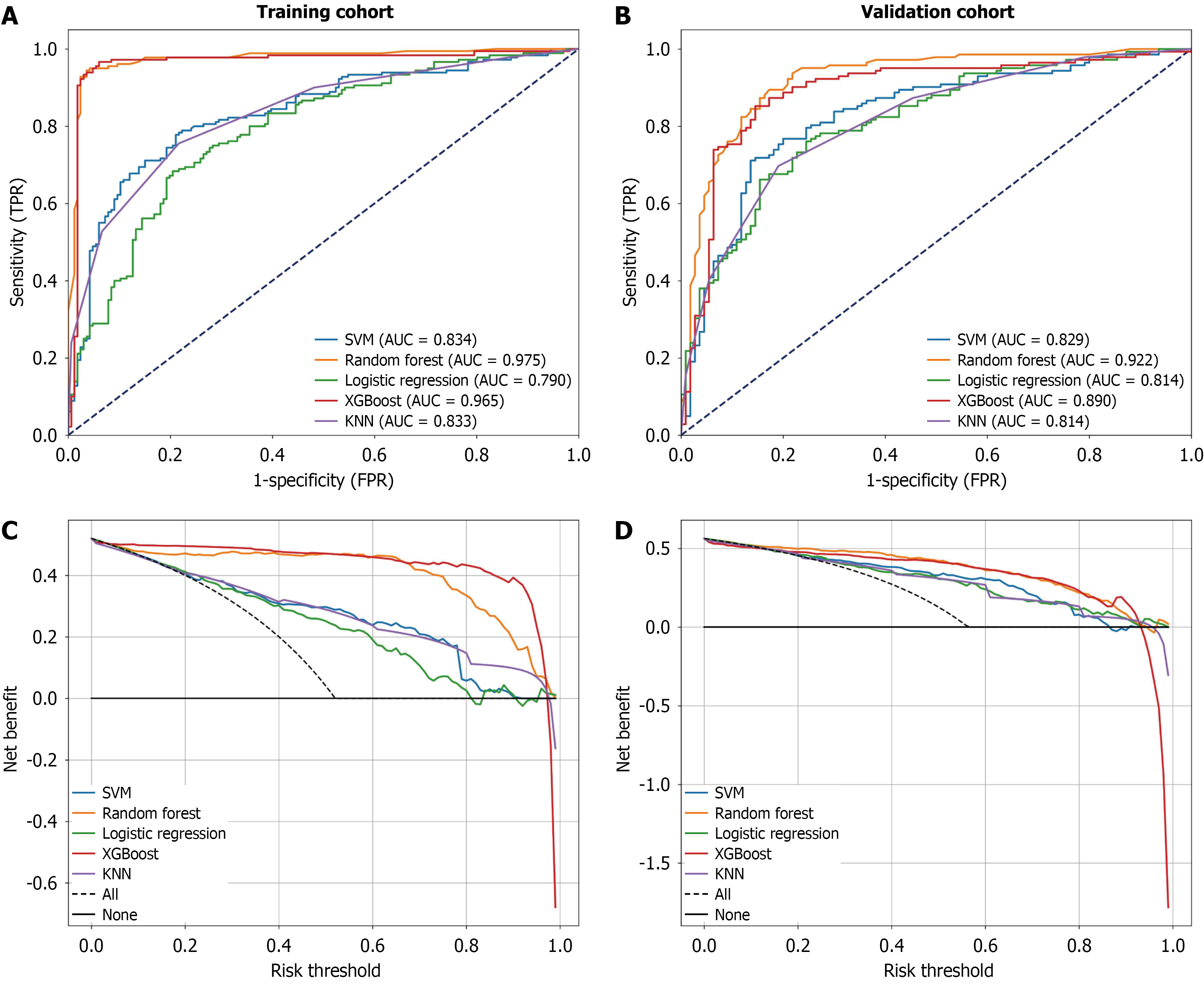
Figure 3 Predictive performance of five machine learning models.
A: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves in the training cohort; B: ROC curves in the validation cohort; C: Decision curve analysis in the training cohort; D: Decision curve analysis in the validation cohort. TPR: True positive rate; FPR: False positive rate; XGBoost: Extreme gradient boosting; SVM: Support vector machine; AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; KNN: K-nearest neighbor.
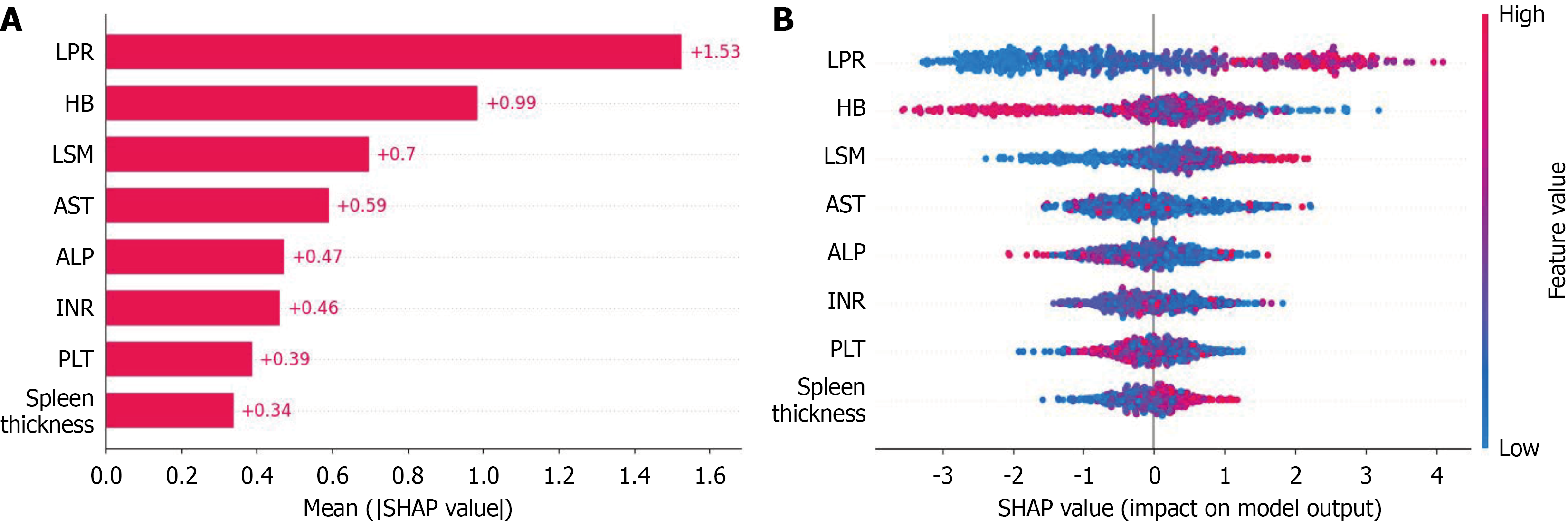
Figure 4 Model interpretability analysis based on SHapley Additive exPlanations.
A: Feature importance ranking; B: SHapley Additive exPlanations value distribution. LPR: Liver stiffness measurement-to-platelet ratio; HB: Hemoglobin; LSM: Liver stiffness measurement; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; INR: International normalized ratio; PLT: Platelet; SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations.
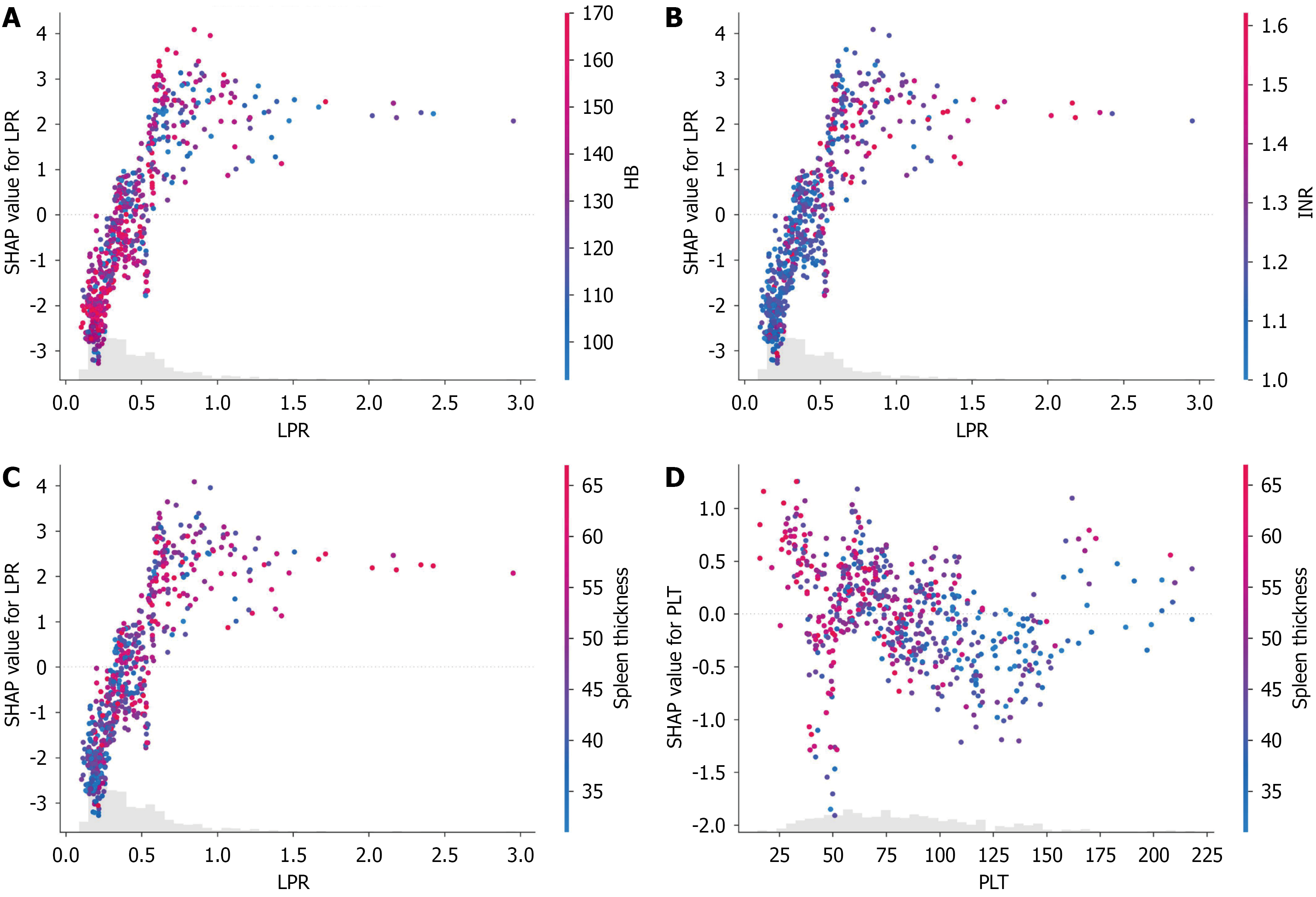
Figure 5 Feature interaction analysis based on SHapley Additive exPlanations.
A: Interaction between liver stiffness measurement-to-platelet ratio (LPR) and hemoglobin; B: Interaction between LPR and international normalized ratio; C: Interaction between LPR and spleen thickness; D: Interaction between platelet and spleen thickness. LPR: Liver stiffness measurement-to-platelet ratio; HB: Hemoglobin; INR: International normalized ratio; PLT: Platelet; SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations.
- Citation: Li YQ, Li ZJ, Li YQ, Feng Y, Wang XB. Machine learning-based prediction models for liver-related events in patients with hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and clinically significant portal hypertension. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(4): 113492
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i4/113492.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i4.113492