©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2026; 32(1): 114558
Published online Jan 7, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i1.114558
Published online Jan 7, 2026. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v32.i1.114558
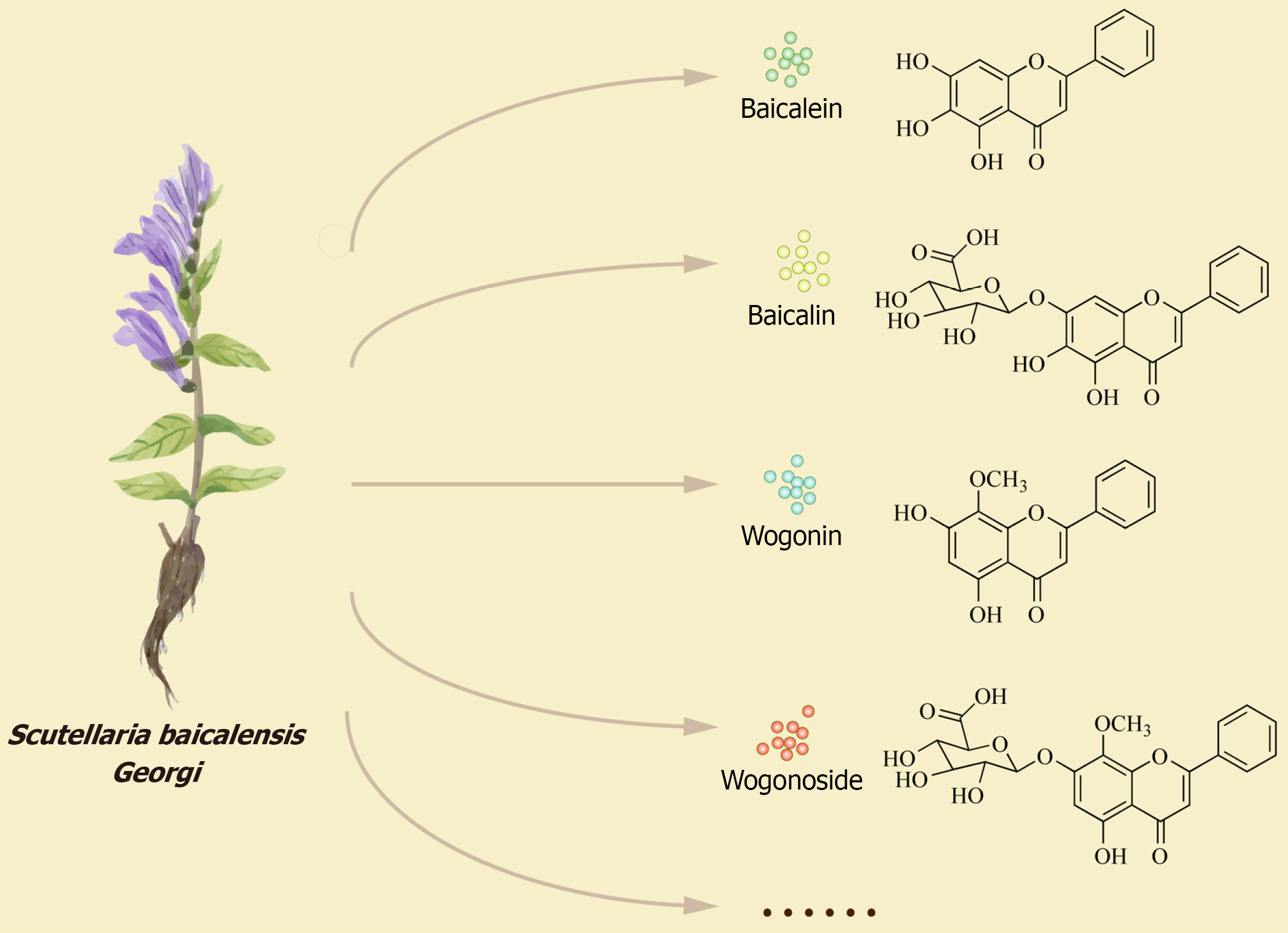
Figure 1 The important active ingredients of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (Huangqin).
Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (Huangqin), the dried root of Scutellaria L. (family Labiaceae), contains 132 compounds. Among these, baicalein, baicalin, wogonin, and wogonoside are recognized as the principal active components responsible for its anti-inflammatory effects.
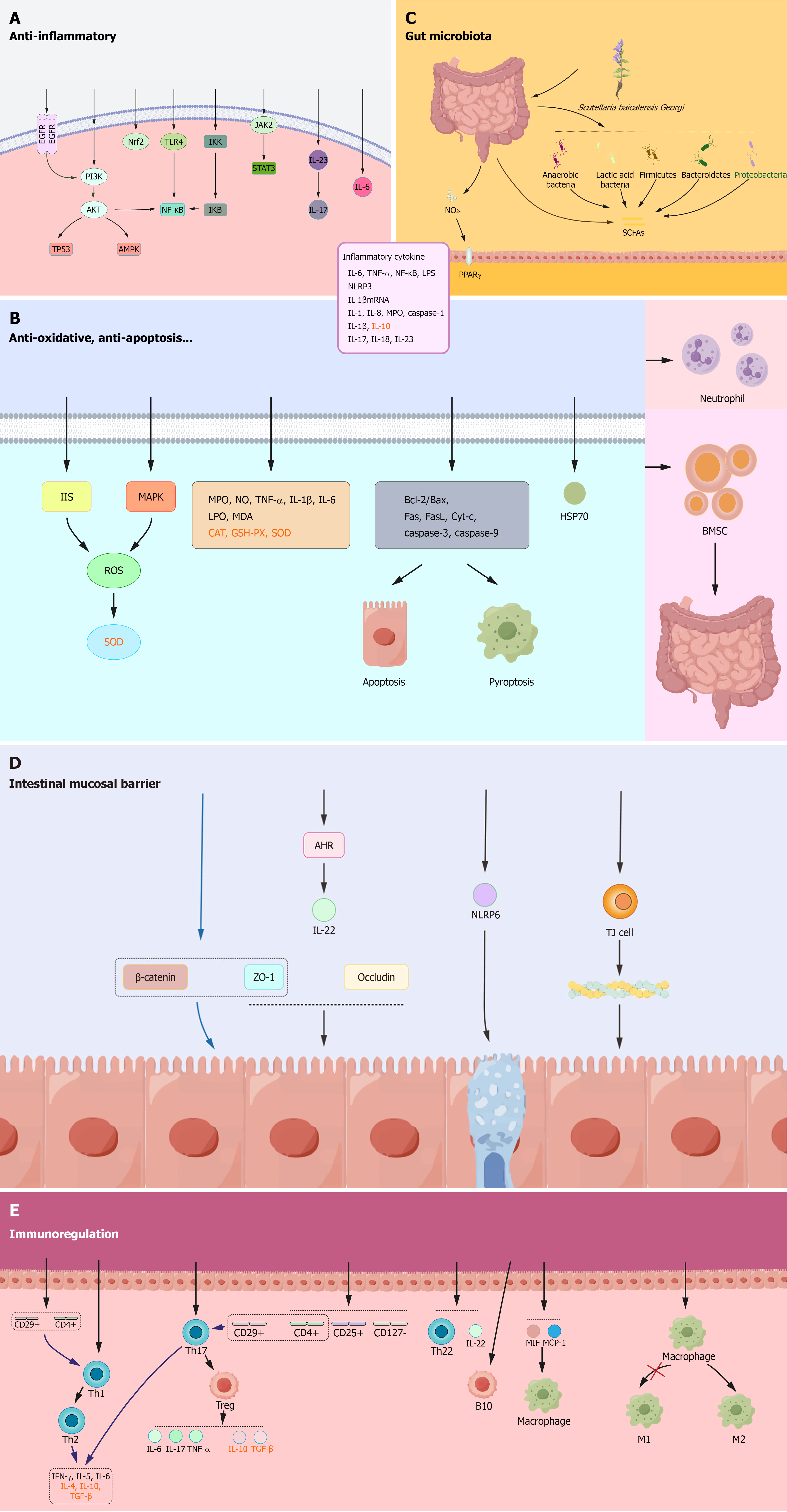
Figure 2 The mechanism of action of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (Huangqin) on ulcerative colitis.
A: Anti-inflammatory effects, including inhibition of inflammatory signaling pathways [epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/nuclear factor-κB, EGFR/PI3K/AKT/tumor protein 53, and EGFR/PI3K/AKT/mitogen-activated protein kinase] and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines [tumor necrosis factor-α, in
- Citation: Ding Y, Wang CY, Pan YT, Wang YJ, Zhao AG, Wen HZ. Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi as a potential therapeutic drug intervention in ulcerative colitis: Mechanisms of action and clinical trials. World J Gastroenterol 2026; 32(1): 114558
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v32/i1/114558.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v32.i1.114558