©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2025; 31(39): 111323
Published online Oct 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i39.111323
Published online Oct 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i39.111323
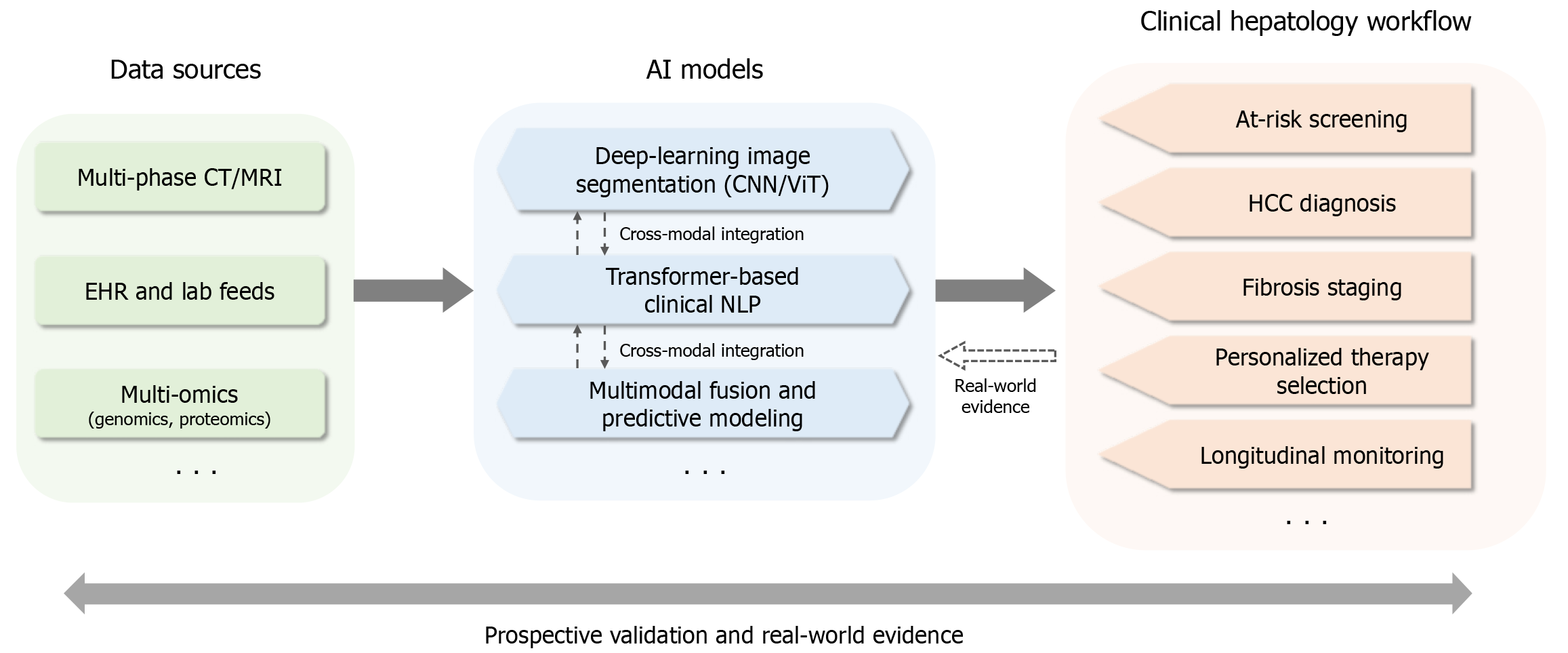
Figure 1 A conceptual framework showing the interaction between artificial intelligence models and clinical workflows in hepatology.
Real-time processes contents patient monitoring, early warning, and real-time clinical decision support. Offline processes include model training and validation, medical image analysis, omics data analysis, and electronic health record analysis. CT: Computerized tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; EHR: Electronic health record; AI: Artificial intelligence; CNN: Convolutional neural network; ViT: Vision transformer; NLP: Natural language processing; HCC: Hepa
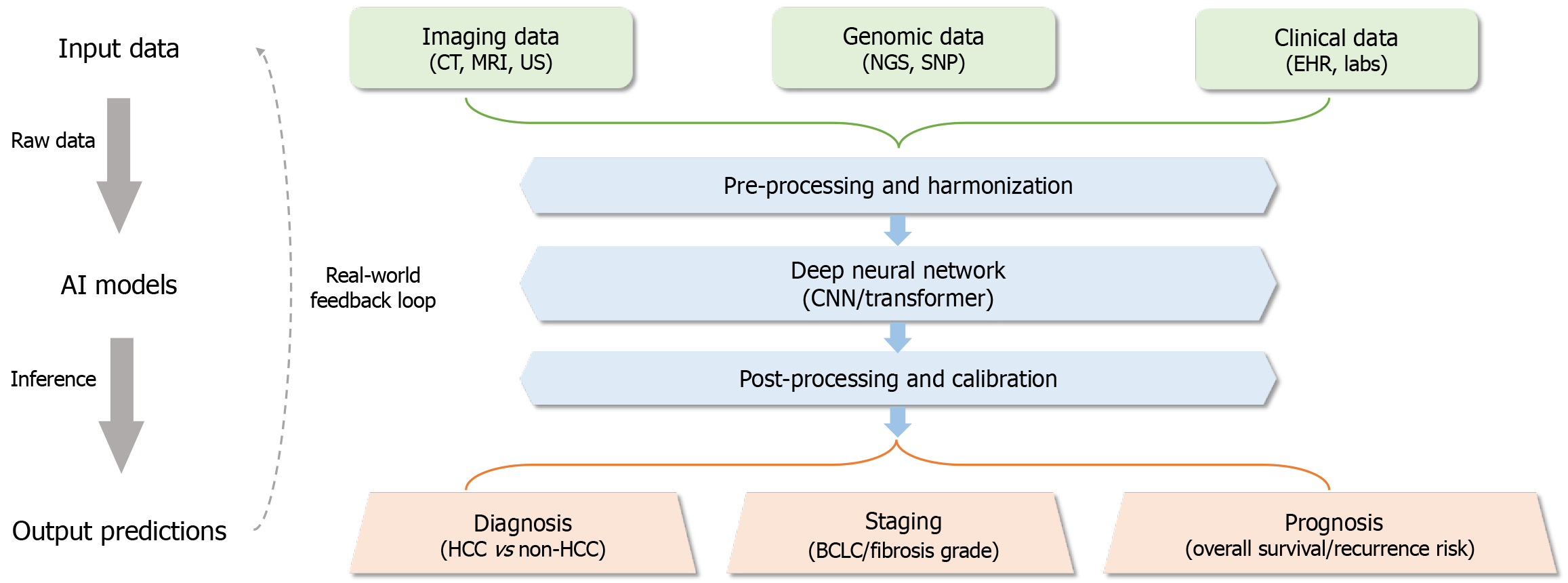
Figure 2 A figure showing artificial intelligence-assisted diagnostic pipeline.
Data preprocessing step includes radiomics, natural language processing and data integration. Feature extraction step includes convolutional neural network and machine learning algorithms. Prediction step includes classification, forecasting and assessment. Feedback step contents issuing early warnings, providing real-time decision support, enabling personalized treatment plans, providing objective evidence and non-invasive, efficient tools for clinical decision-making. AI: Artificial intelligence; CT: Computerized tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; US: Ultrasonography; NGS: Next-generation sequencing; SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphism; EHR: Electronic health records; CNN: Convolutional neural network; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; BCLC: Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer.
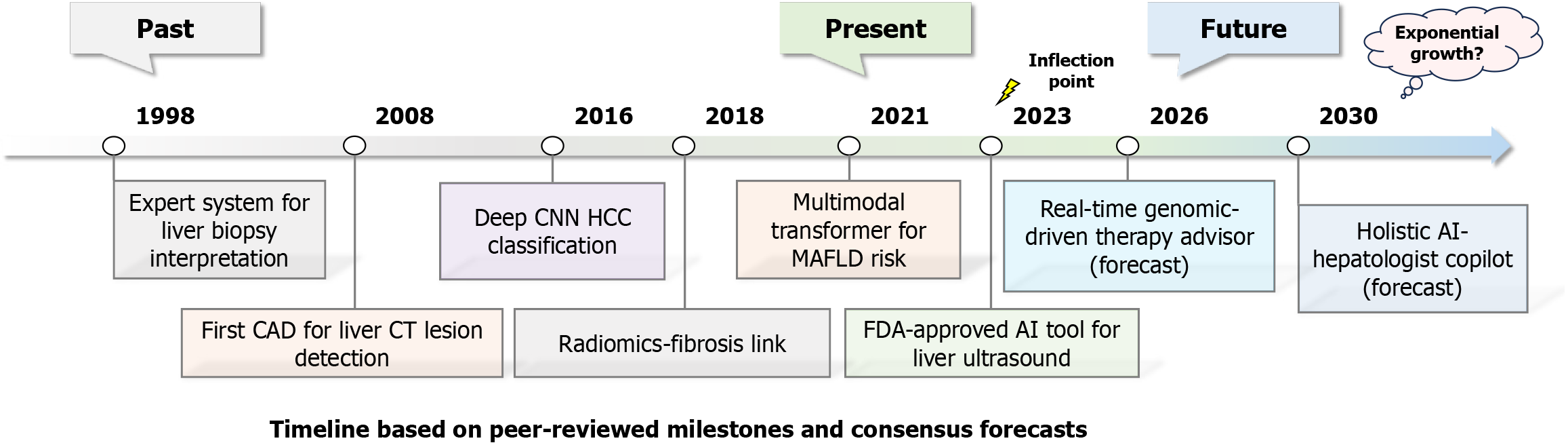
Figure 3 A timeline outlining historical evolution and future projections of artificial intelligence in liver medicine.
CAD: Computer-aided diagnosis; CT: Computed tomography; CNN: Convolutional neural network; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; MAFLD: Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease; FDA: Food and Drug Administration; AI: Artificial intelligence.
- Citation: Zheng Y, Li H, Wang R, Jiang CS, Zhao YT. Multi-model applications and cutting-edge advancements of artificial intelligence in hepatology in the era of precision medicine. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(39): 111323
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i39/111323.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i39.111323