©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2025; 31(38): 112489
Published online Oct 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i38.112489
Published online Oct 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i38.112489
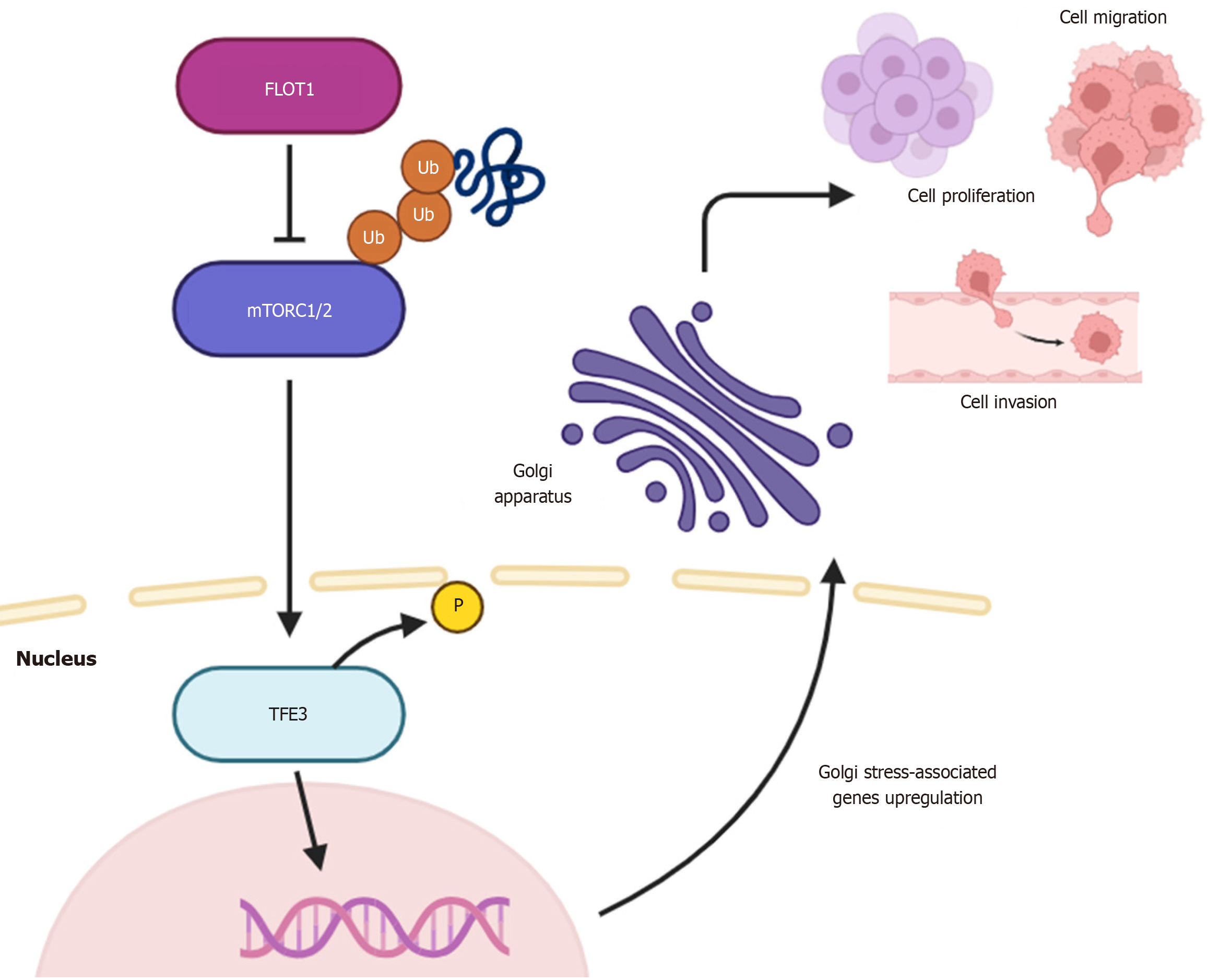
Figure 1 Flotillin-1 proposed mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Flotillin-1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through activation of the Golgi stress response. Flotillin-1 induces ubiquitination and inhibition of mechanistic target of rapamycin complexes 1 and 2, facilitating transcription factor E3 dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation. Once in the nucleus, transcription factor E3 activates the transcription of Golgi stress-associated genes, thereby enhancing hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. FLOT1: Flotillin-1; mTORC1/2: Mechanistic target of rapamycin complexes 1 and 2; TFE3: Transcription factor E3; Ub: Ubiquitin.
- Citation: Mazziotta C, Rotondo JC. Unraveling the role of flotillin-1 in driving hepatocellular carcinoma progression through transcription factor E3-mediated Golgi stress response. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(38): 112489
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i38/112489.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i38.112489