©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2025; 31(32): 108654
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.108654
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.108654
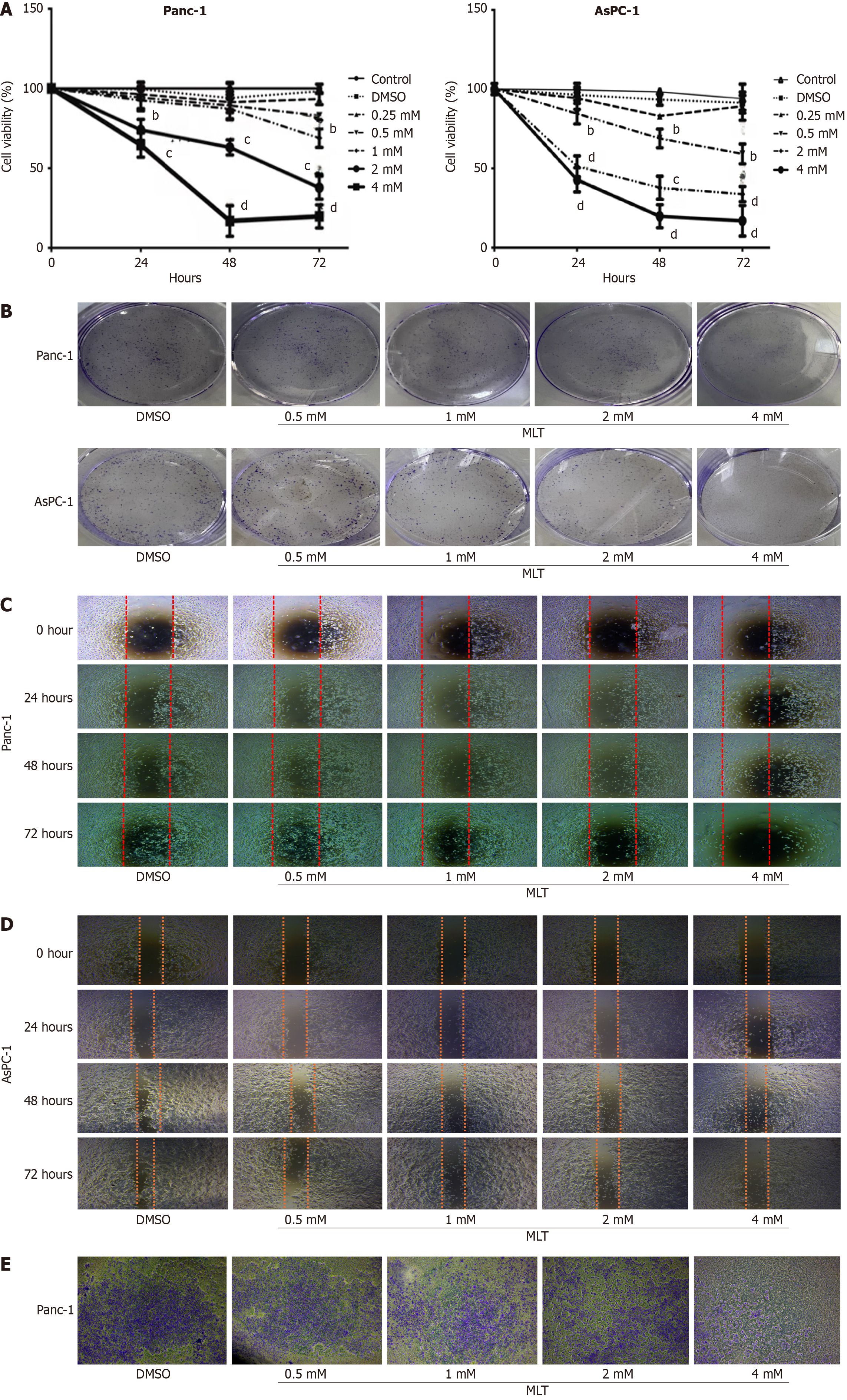
Figure 1 Effects of melatonin on cell viability, colony formation, migration, and invasion in pancreatic cancer.
A: Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells were treated with different melatonin concentrations (0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 mmol/L) or vehicle (0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide) for 0, 24, 48, or 72 hours. Cell viability was assessed using the cell counting kit-8 assay (n = 3); B: Effects of different melatonin concentrations on colony formation in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells; C and D: Scratch assay showing the effects of different melatonin concentrations on the migration of Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells; E: Invasion of Panc-1 cells treated with different melatonin concentrations for 48 hours observed at a magnification of 100 ×. All images show representative images from three independent experiments. MLT: Melatonin; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide. bP < 0.01 vs control, cP < 0.001 vs control, and dP < 0.0001 vs control.
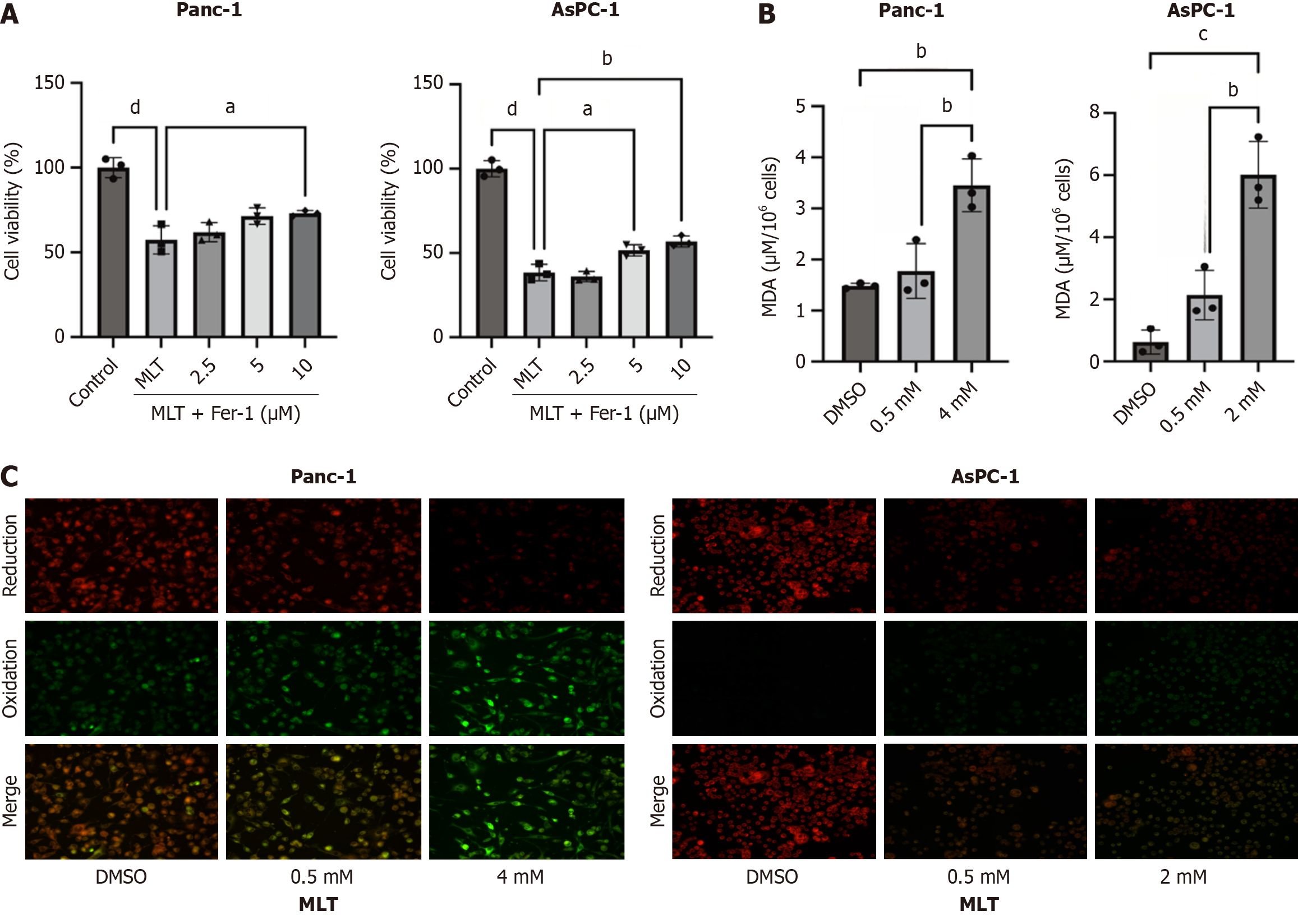
Figure 2 Melatonin promotes ferroptosis in human pancreatic cancer cell lines Panc-1 and AsPC-1.
A: Pancreatic cancer cells Panc-1 and AsPC-1 were treated with melatonin and different concentrations of the ferroptosis inhibitor ferrostatin-1. Cell viability was assessed using the cell counting kit-8 assay (n = 3); B: Malondialdehyde levels in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells treated with different melatonin concentrations were measured using a commercial assay kit (n = 3); C: Lipid reactive oxygen species levels in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells treated with different melatonin concentrations were detected in situ using the C11-BODIPY 581/591 fluorescent probe (n = 3). MLT: Melatonin; Fer-1: Ferrostatin-1; MDA: Malondialdehyde; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, and dP < 0.0001.
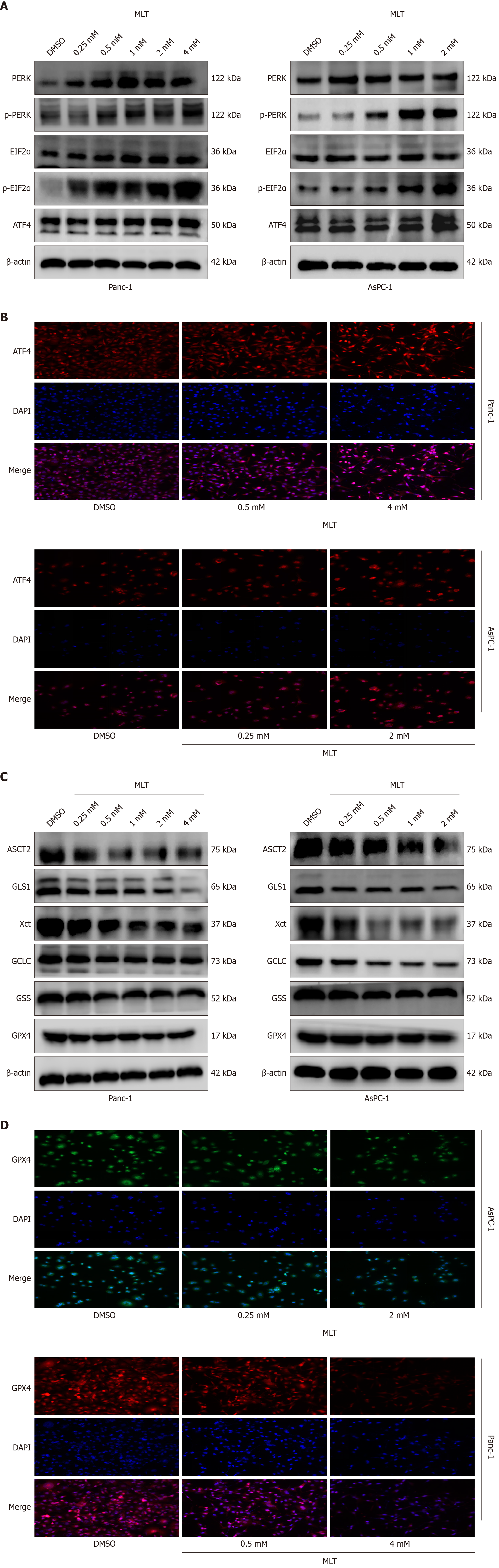
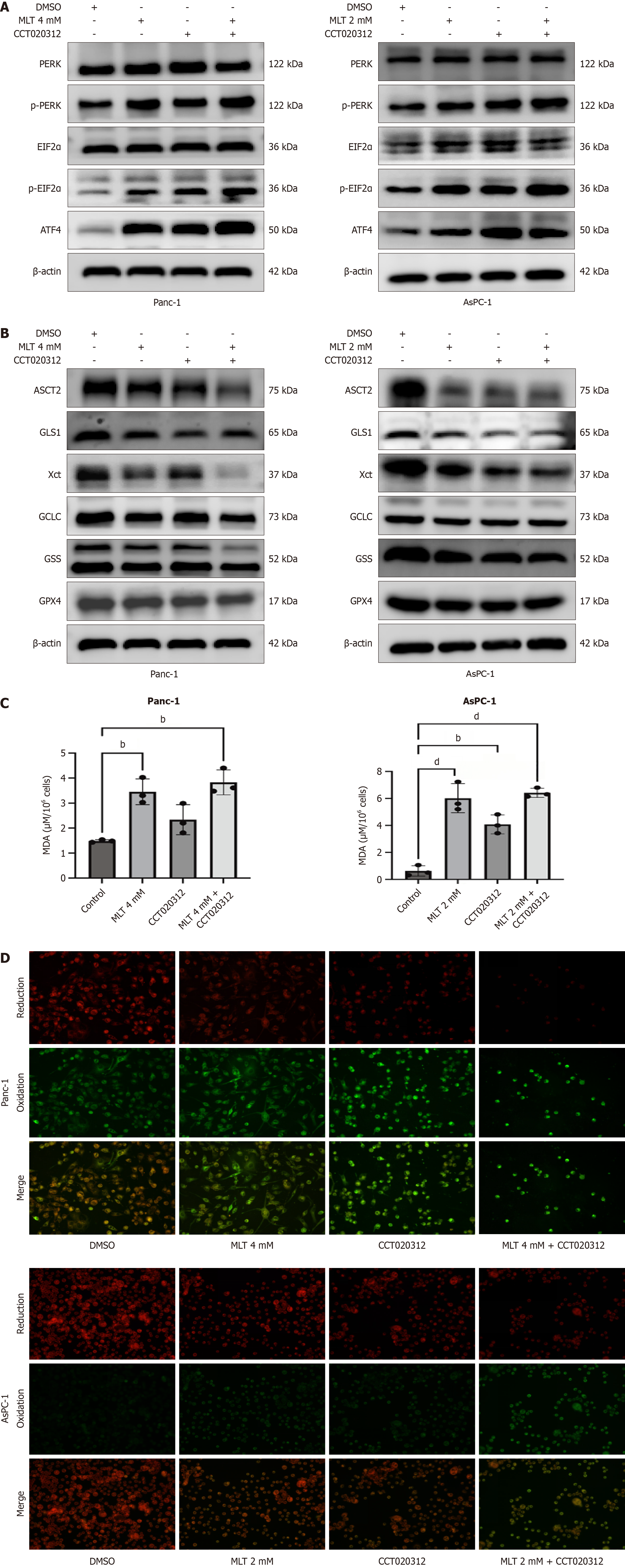
Figure 3 Effects of melatonin on endoplasmic reticulum stress and glutamine metabolism pathways in human pancreatic cancer.
A: The expression levels of protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase-eukaryotic initiation factor 2α-activating transcription factor 4 axis proteins in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells treated with different melatonin concentrations were measured using western blotting (n = 3); B: The expression of activating transcription factor 4 in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells treated with different melatonin concentrations was assessed using immunofluorescence; C: The expression levels of glutamine metabolism-related proteins (alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 2, glutaminase 1, X-cysteine transporter, glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit, glutathione synthetase, and glutathione peroxidase 4) in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells treated with different melatonin concentrations were measured through western blotting (n = 3); D: The expression of glutathione peroxidase 4 in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells treated with different concentrations of melatonin was analyzed using immunofluorescence. MLT: Melatonin; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; PERK: Protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; p-PERK: Phosphorylated-protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; ElF2α: Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; p-ElF2α: Phosphorylated-eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; ATF4: Activating transcription factor 4; ASCT2: Alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 2; GLS1: Glutaminase 1; Xct: X-cysteine transporter; GCLC: Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GSS: Glutathione synthetase; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4.
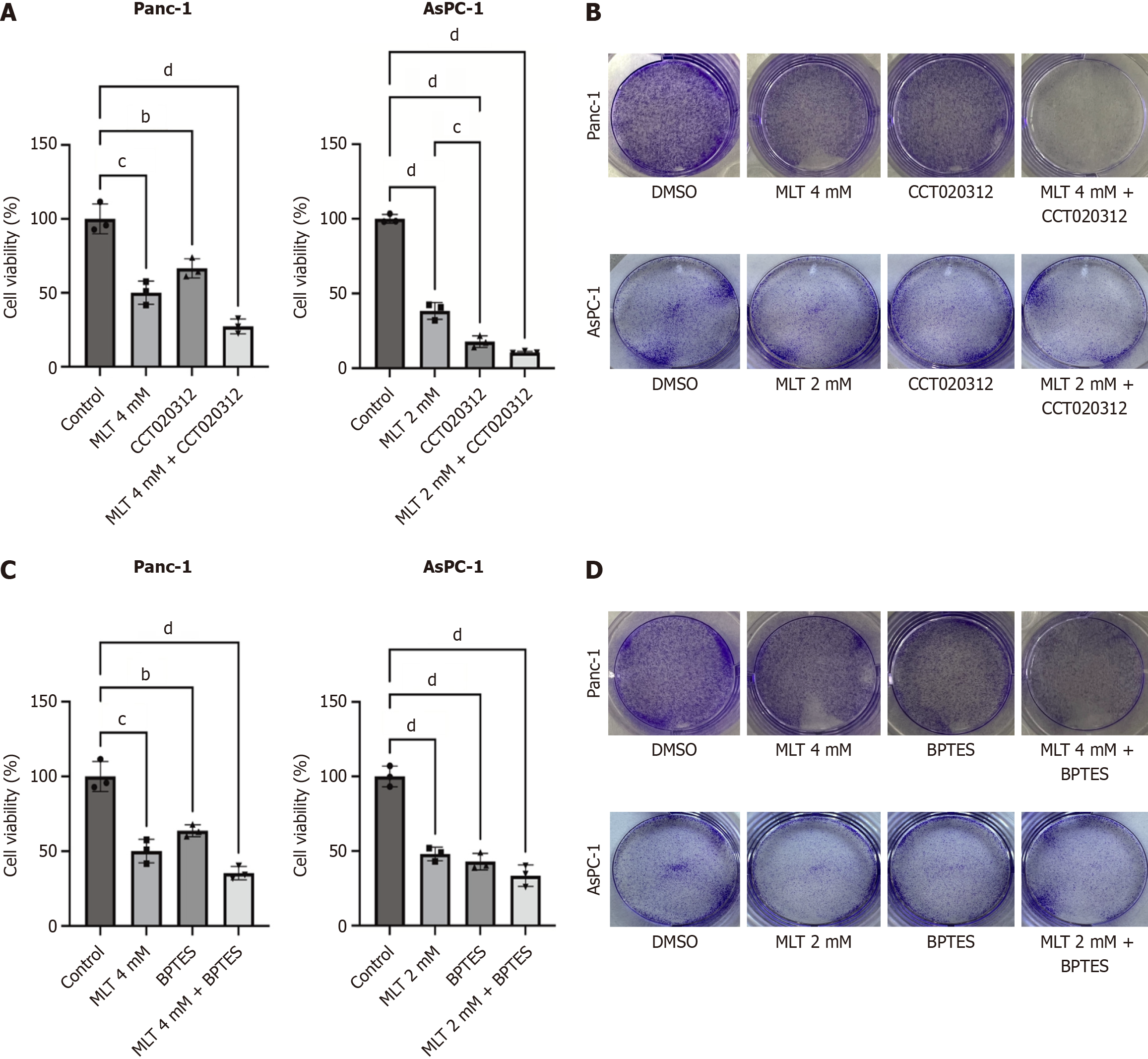
Figure 4 Melatonin + CCT020312 or BPTES enhances anticancer effects and reduces Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cell viability.
A: Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells were treated with high melatonin concentrations combined with the protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase agonist CCT020312 for 24 hours, and cell viability was assessed using the cell counting kit-8 assay (n = 3); B: Colony formation assay showing the effect of combined treatment of melatonin and CCT020312; C: Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells were treated with high melatonin concentrations combined with the glutaminase 1 inhibitor BPTES for 24 hours, and cell viability was assessed using the cell counting kit-8 assay (n = 3); D: Colony formation assay showing the effect of combined treatment of melatonin and BPTES. MLT: Melatonin; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, and dP < 0.0001.
Figure 5 Melatonin + CCT020312 exacerbates activating transcription factor 4-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and increases ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.
A: The expression levels of protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK)-eukaryotic initiation factor 2α-activating transcription factor 4 axis proteins in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells treated with high melatonin concentrations combined with the PERK agonist CCT020312 for 24 hours were analyzed using western blotting (n = 3); B: The expression levels of glutamine metabolism-related proteins in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells treated with high melatonin concentrations combined with the PERK agonist CCT020312 for 24 hours were analyzed using western blotting (n = 3); C: Malondialdehyde levels in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells were measured using a commercial assay kit (n = 3); D: Lipid reactive oxygen species levels in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells were detected in situ using a reactive oxygen species assay kit. MLT: Melatonin; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; PERK: Protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; p-PERK: Phosphorylated-protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; ElF2α: Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; p-ElF2α: Phosphorylated-eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; ATF4: Activating transcription factor 4; ASCT2: Alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 2; GLS1: Glutaminase 1; Xct: X-cysteine transporter; GCLC: Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GSS: Glutathione synthetase; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4. bP < 0.01, and dP < 0.0001.
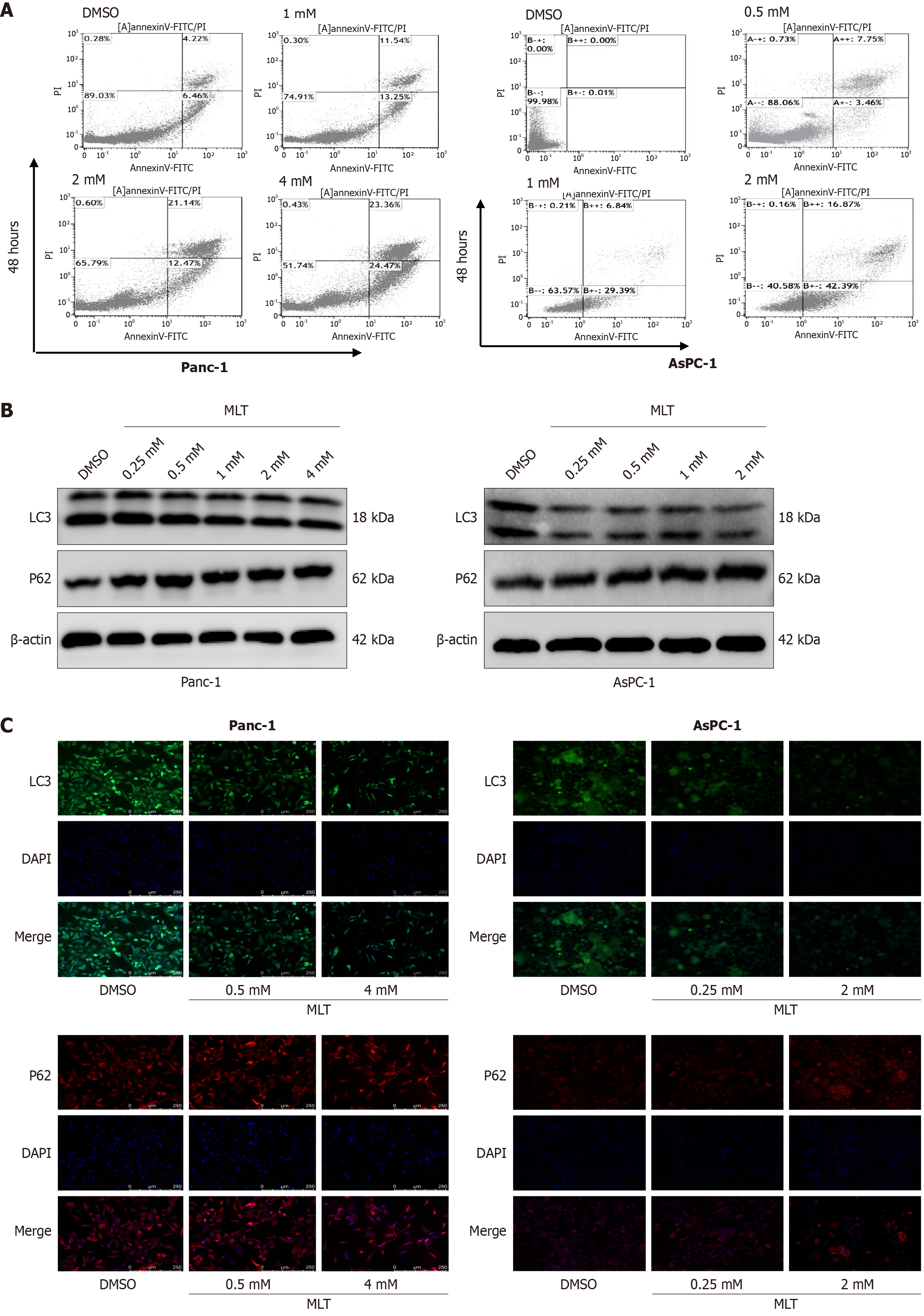
Figure 6 Effects of melatonin on apoptosis and autophagy in human pancreatic cancer cells Panc-1 and AsPC-1.
A: Apoptosis in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells after 48 hours of melatonin treatment was detected using annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate/propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry; B: The expression levels of sequestosome-1 and microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 proteins in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells treated with different melatonin concentrations for 24 hours were measured using western blotting (n = 3); C: The expression of sequestosome-1 and microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 in Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells treated with different melatonin concentrations was measured using immunofluorescence. MLT: Melatonin; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; PI: Propidium iodide; LC3: Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3; P62: Sequestosome-1.
- Citation: Zhao Q, Zhang H, Wu HM, Yang QY, Zhao H, Kang L, Lv XY. Melatonin-induced ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells by stimulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibiting alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 2-driven glutamine metabolism. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(32): 108654
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i32/108654.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i32.108654