©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2025; 31(27): 108200
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.108200
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.108200
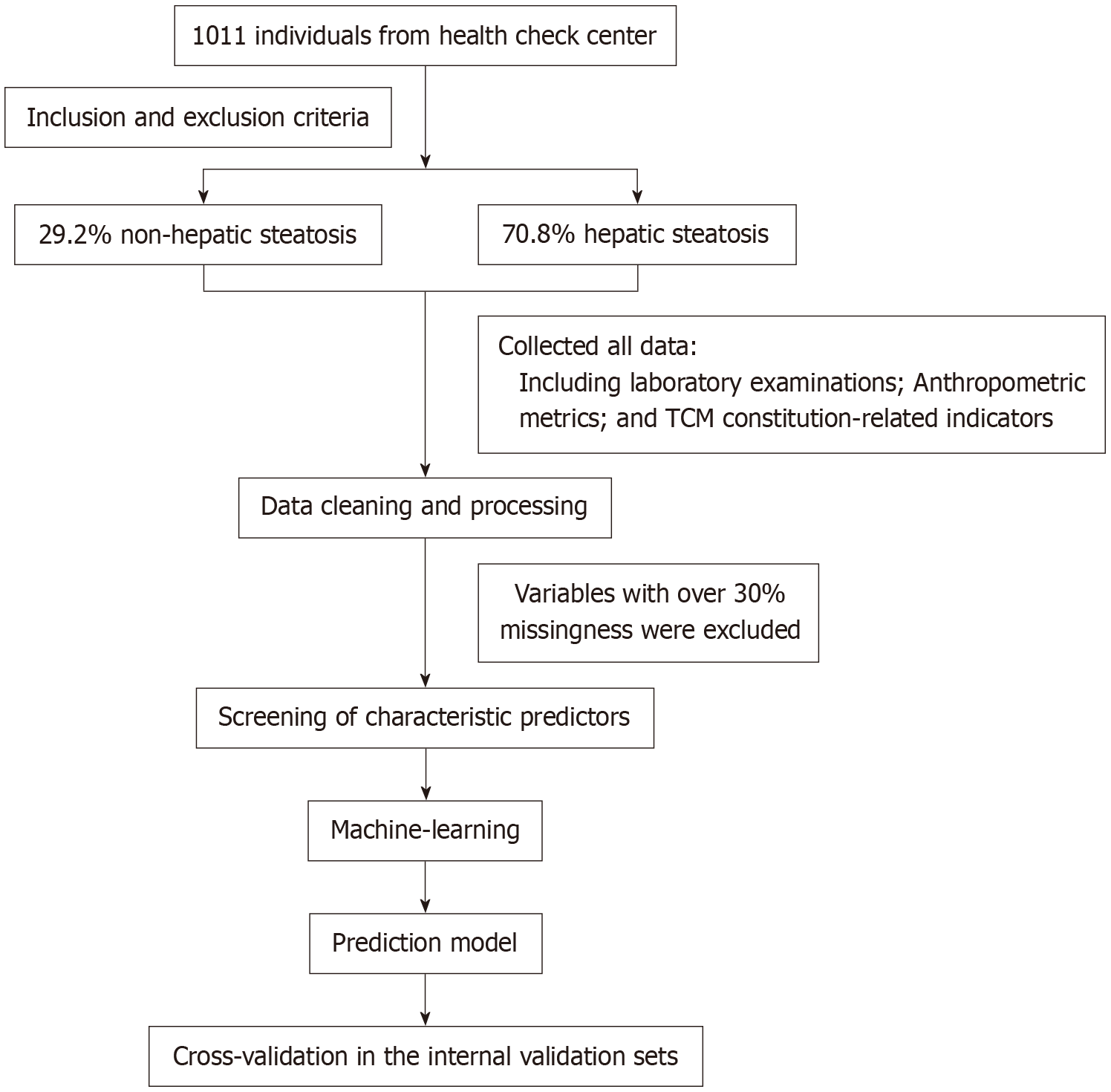
Figure 1 Flow chart of the study design.
TCM: Traditional Chinese medicine.
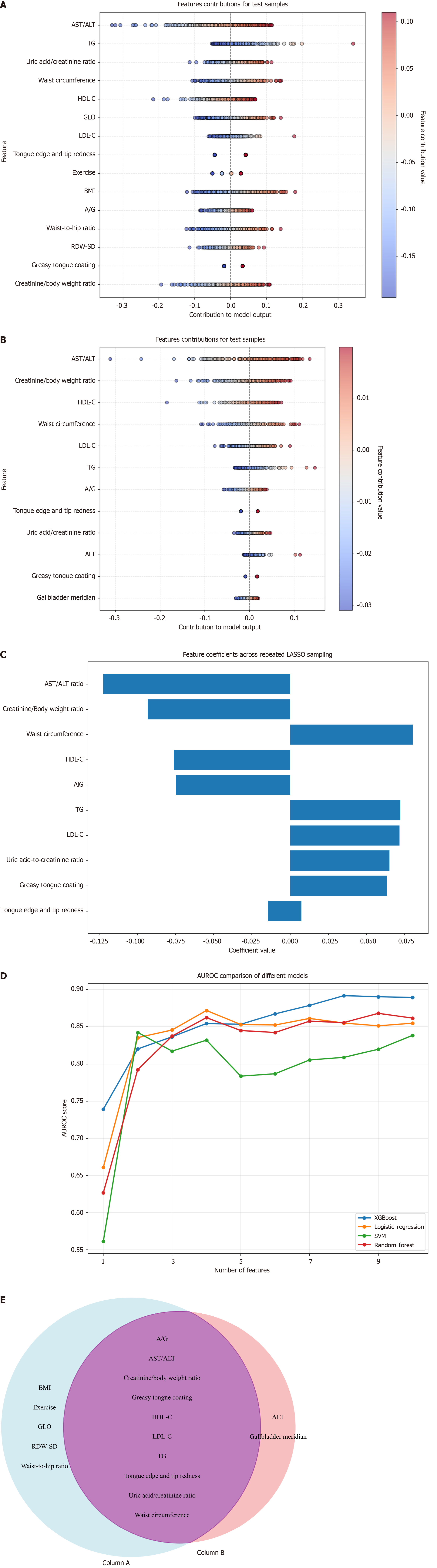
Figure 2 Perform feature selection using LASSO and recursive feature elimination.
A: Characteristic indicators screening based on recursive feature elimination (RFE); B: Characteristic indicators screening based on LASSO; C: Feature importance values following LASSO selection; D: Contribution of each feature to the model's inference outcomes; E: Characteristics of RFE combined with LASSO. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG: Triglyceride; BMI: Body mass index; A/G: Albumin/globulin; RDW: Red Cell Distribution Width; AUROC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic; SVM: Support Vector Machine; GLO: Globulin.
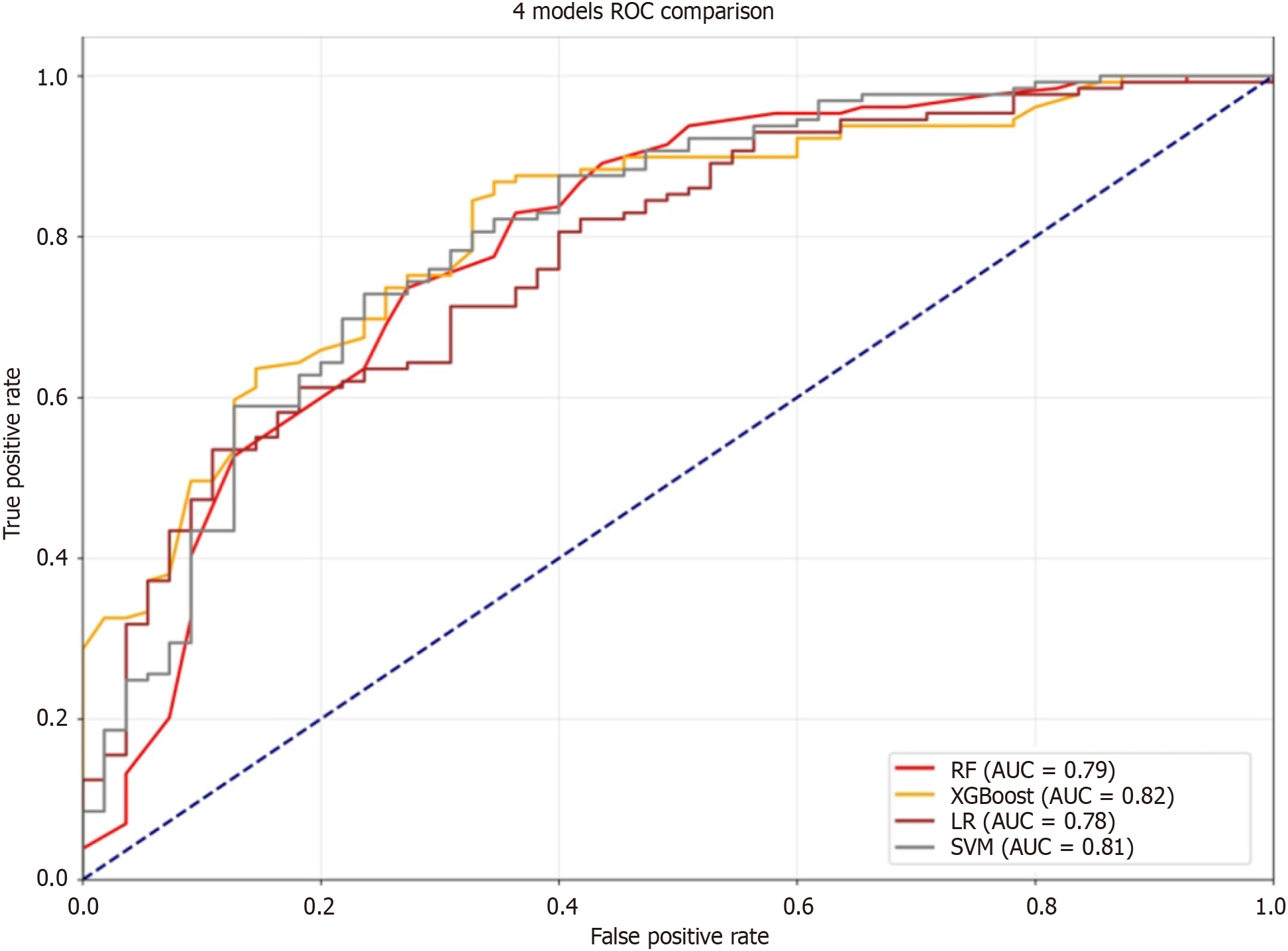
Figure 3 Performance of machine learning models to predict hepatic steatosis.
Receiver operating characteristic curves of the four performing machine learning models. RF: Random Forest; LR: Logistic regression; SVM: Support Vector Machine; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; AUC: Area under the curve.
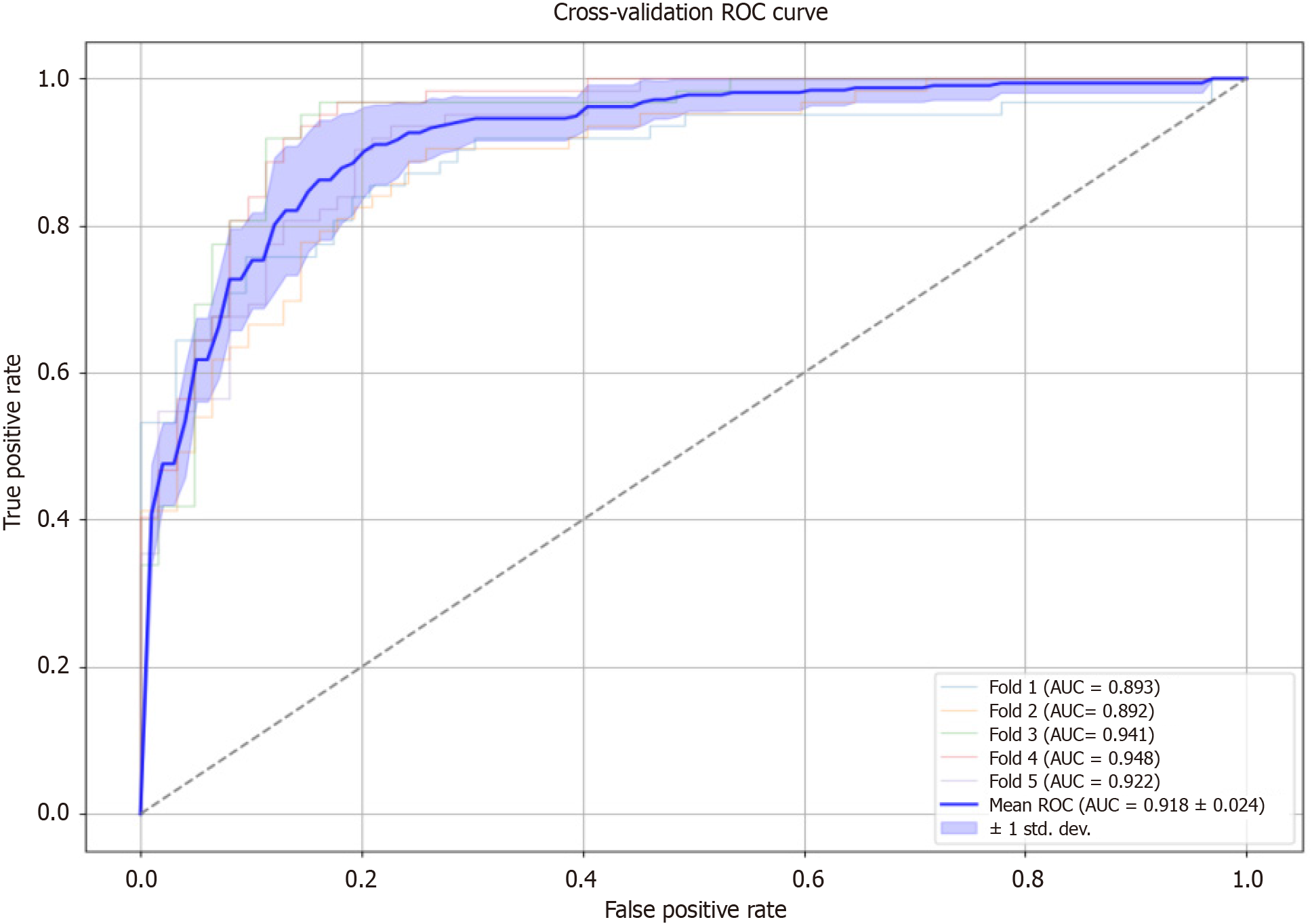
Figure 4 Cross-validation receiver operating characteristic curve.
The receiver operating characteristic curves for XGBoost model evaluated through five-fold cross-validation. The X-axis represents the false positive rate, and the Y-axis represents the true positive rate. Area under the curve is a measure of the model's overall performance, with higher values indicating better discrimination.
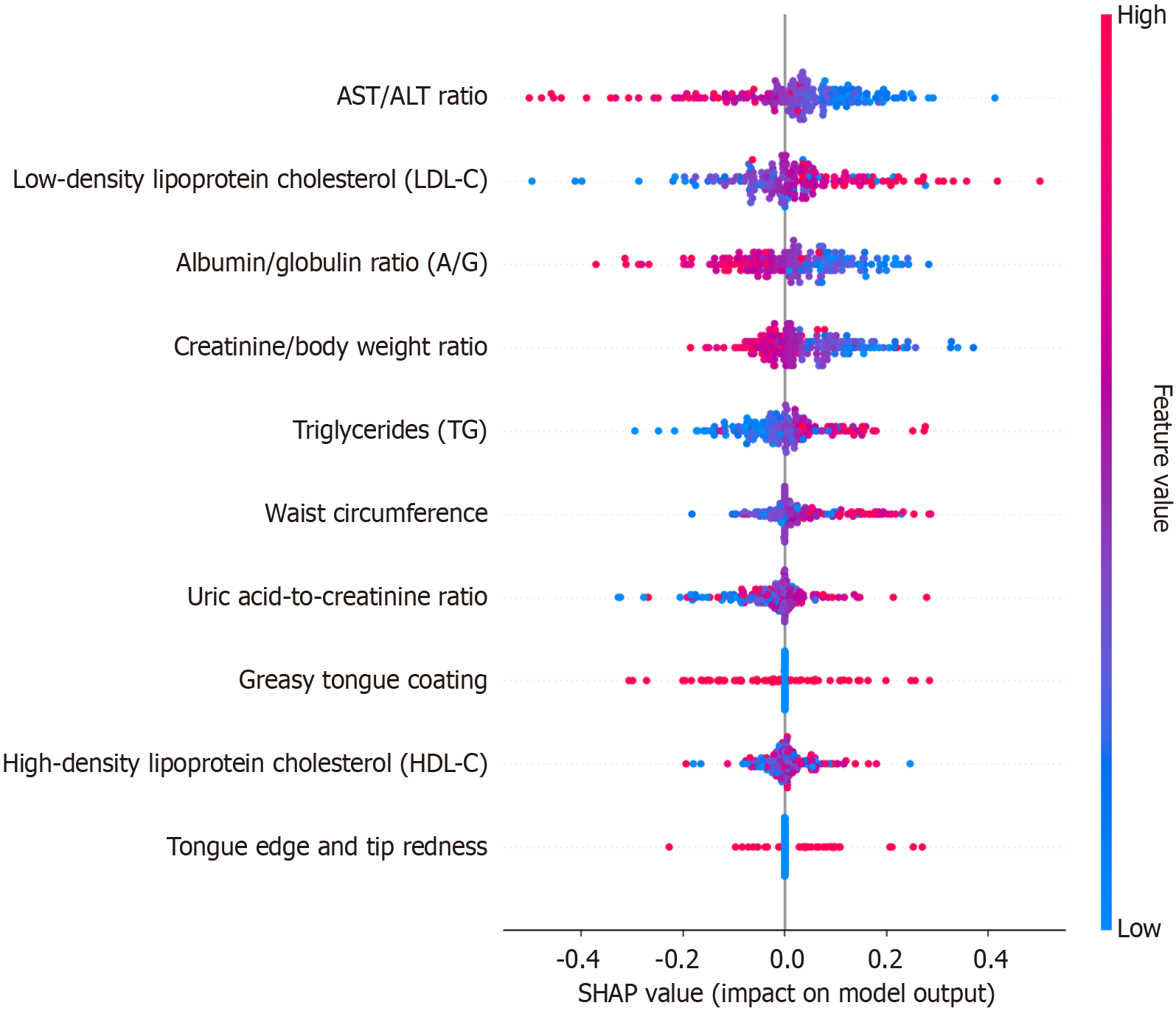
Figure 5 SHAP summary dot plot.
The probability of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease development increases with the SHAP value of a feature. A dot is made for SHAP value in the model for each single patient, so each patient has one dot on the line for each feature. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG: Triglyceride; A/G: Albumin/globulin.
- Citation: Tian Y, Zhou HY, Liu ML, Ruan Y, Yan ZX, Hu XH, Du J. Machine learning-based identification of biochemical markers to predict hepatic steatosis in patients at high metabolic risk. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(27): 108200
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i27/108200.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.108200