©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2025; 31(25): 107260
Published online Jul 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107260
Published online Jul 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107260
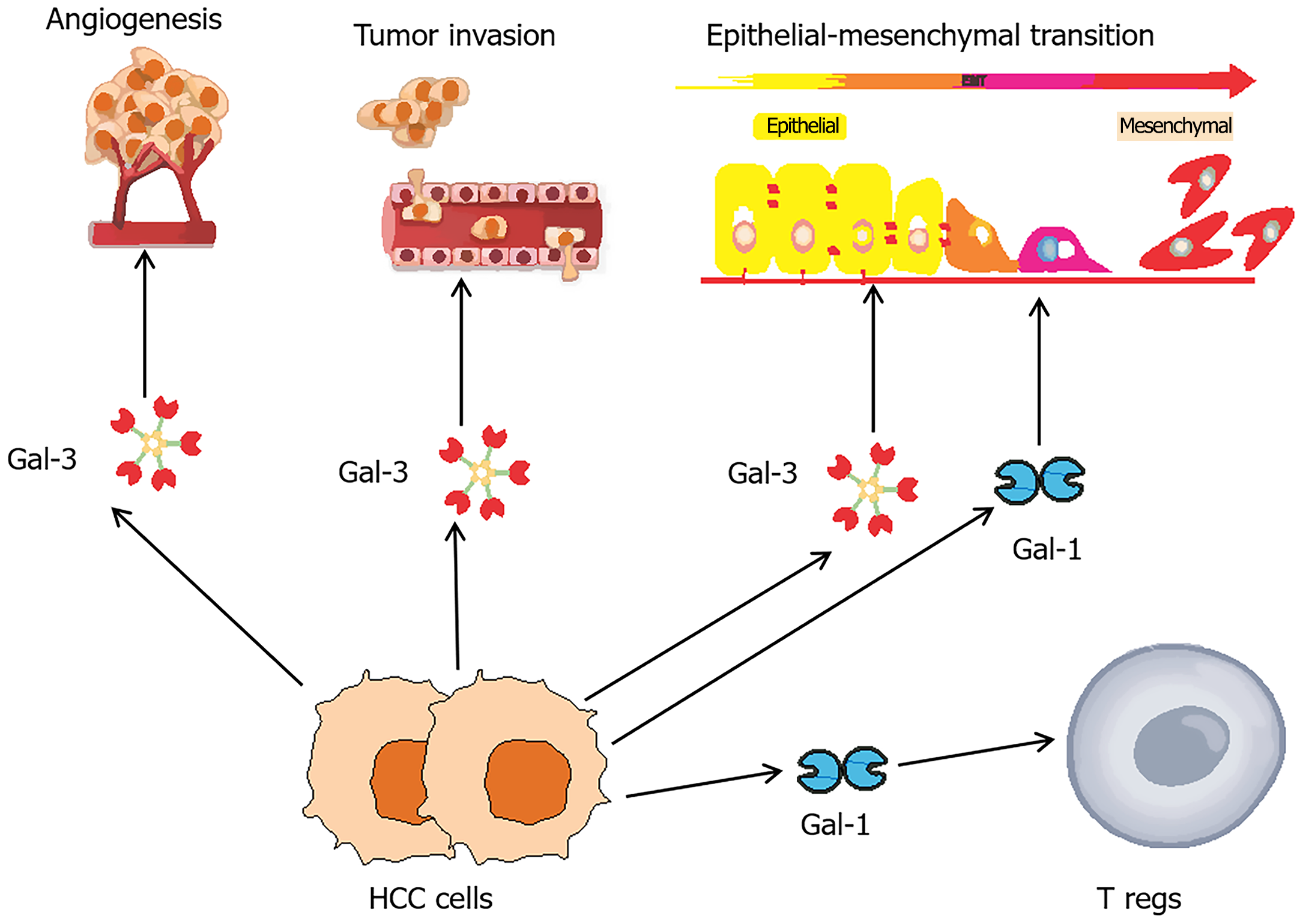
Figure 1 Galectins in key phases of hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis.
Galectins (Gal) play pivotal roles in the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), influencing critical processes such as angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis, and immune modulation. Among these Gal-3 has been extensively studied for its role in promoting angiogenesis and enhancing the invasive and metastatic potential of HCC. Both Gal-1 and Gal-3 are implicated in epithelial-mesenchymal transition, a crucial step in the metastatic progression of HCC. Additionally, HCC cells releasing Gal-1 can modulate the immune microenvironment by stimulating regulatory T cells, leading to immunosuppressive effects and the apoptosis of anti-tumor effector T cells. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Gal: Galectin; Tregs: Regulatory T cells.
- Citation: Gajovic NM, Jovanovic IP, Jocic MV, Stojanovic B, Corovic IF, Todorovic N, Simovic Markovic BJ, Amedei A. Exploring the impact of galectins on liver cancer: From immunopathogenesis to potential targets. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(25): 107260
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i25/107260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107260