©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2025; 31(23): 105076
Published online Jun 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.105076
Published online Jun 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.105076
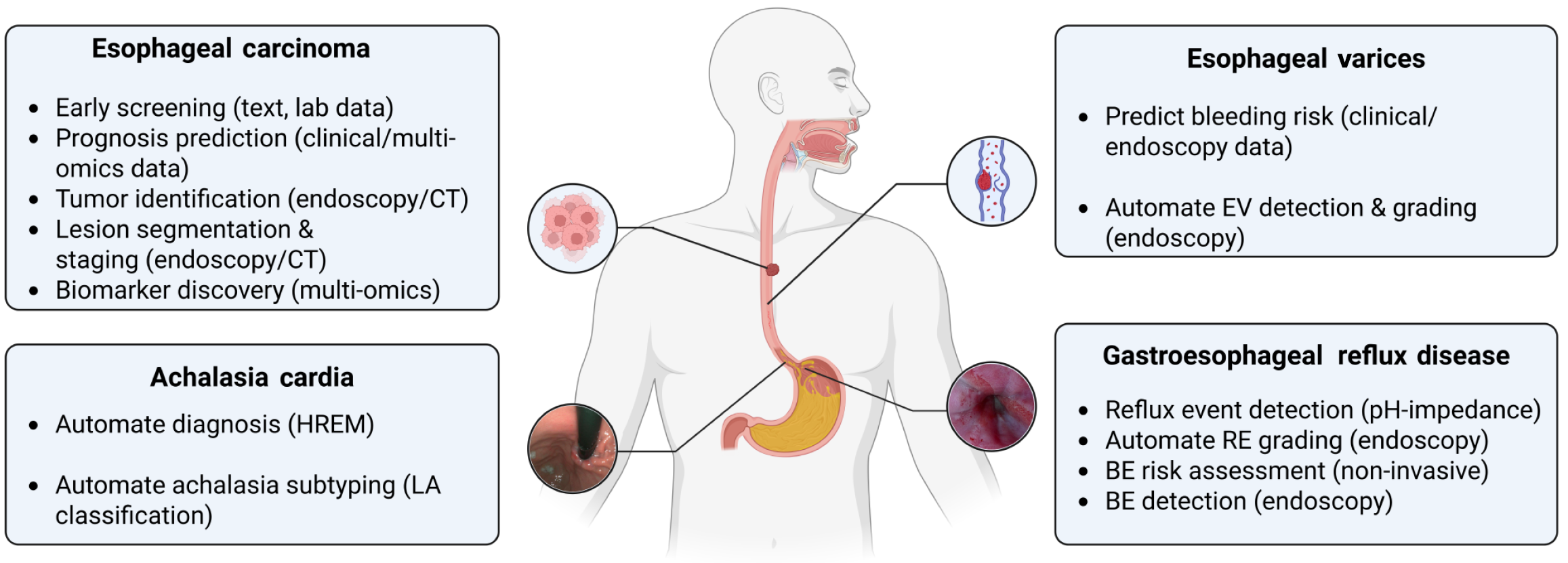
Figure 1 Overview of machine learning applications in major esophageal disorders.
CT: Computed tomography; HREM: High-resolution esophageal manometry; BE: Barrett’ s esophagus; EV: Esophageal varices; RE: Reflux esophagitis.
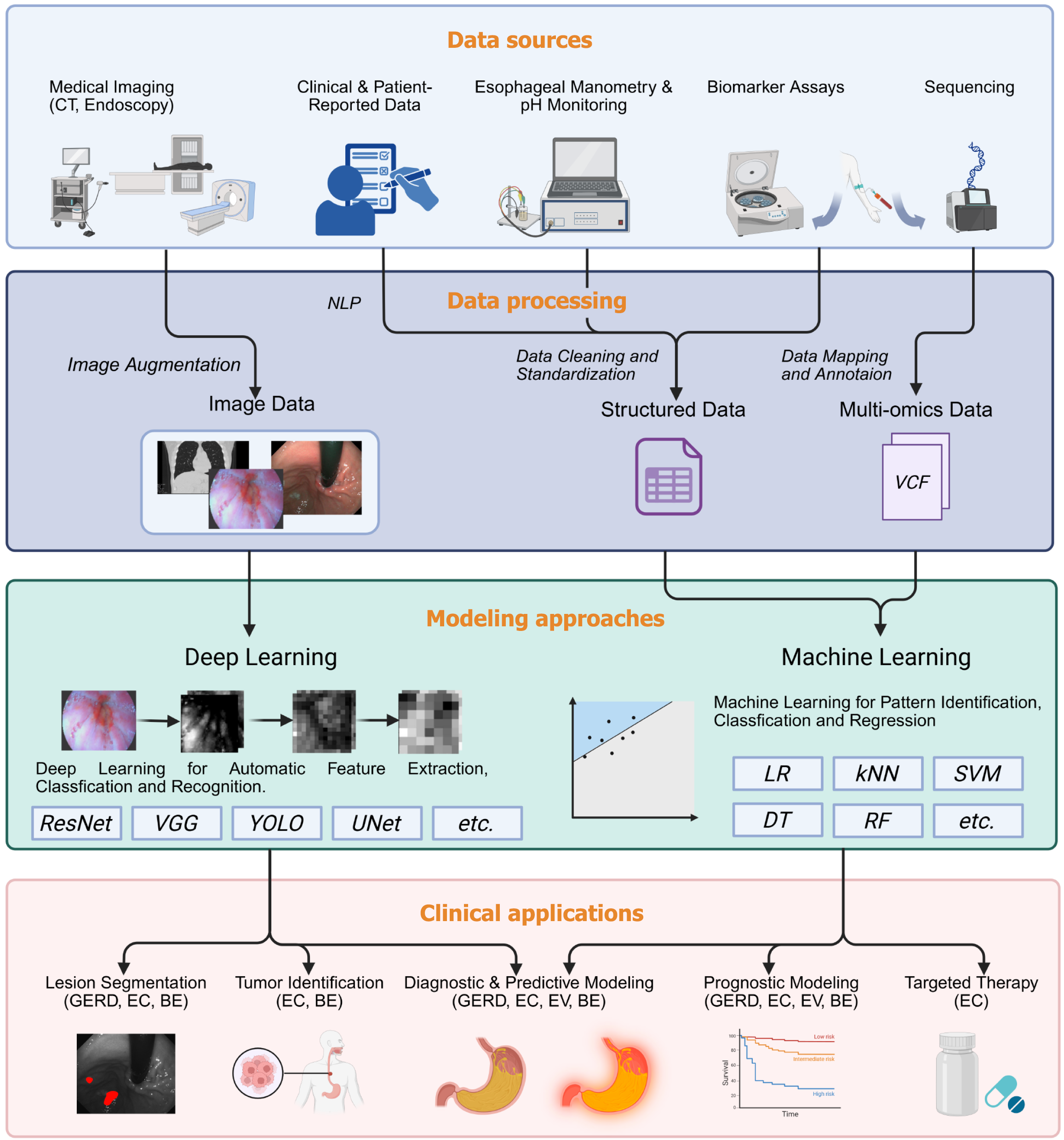
Figure 2 Integrated data-drive modeling pipeline for esophageal disorders leveraging deep learning and machine learning for improved diagnosis and prognosis.
CT: Computed tomography; NLP: Natural language processing; VCF: Variant call format; VGG: Visual geometry group network; YOLO: You only look once; UNet: U-shaped convolutional network; ResNet: Residual neural network; kNN: K-nearest neighbors; LR: Logistic regression; SVM: Support vector machine; RF: Random forest; DT: Decision tree; GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; BE: Barrett’s esophagus; EC: Esophageal carcinoma; EV: Esophageal varices.
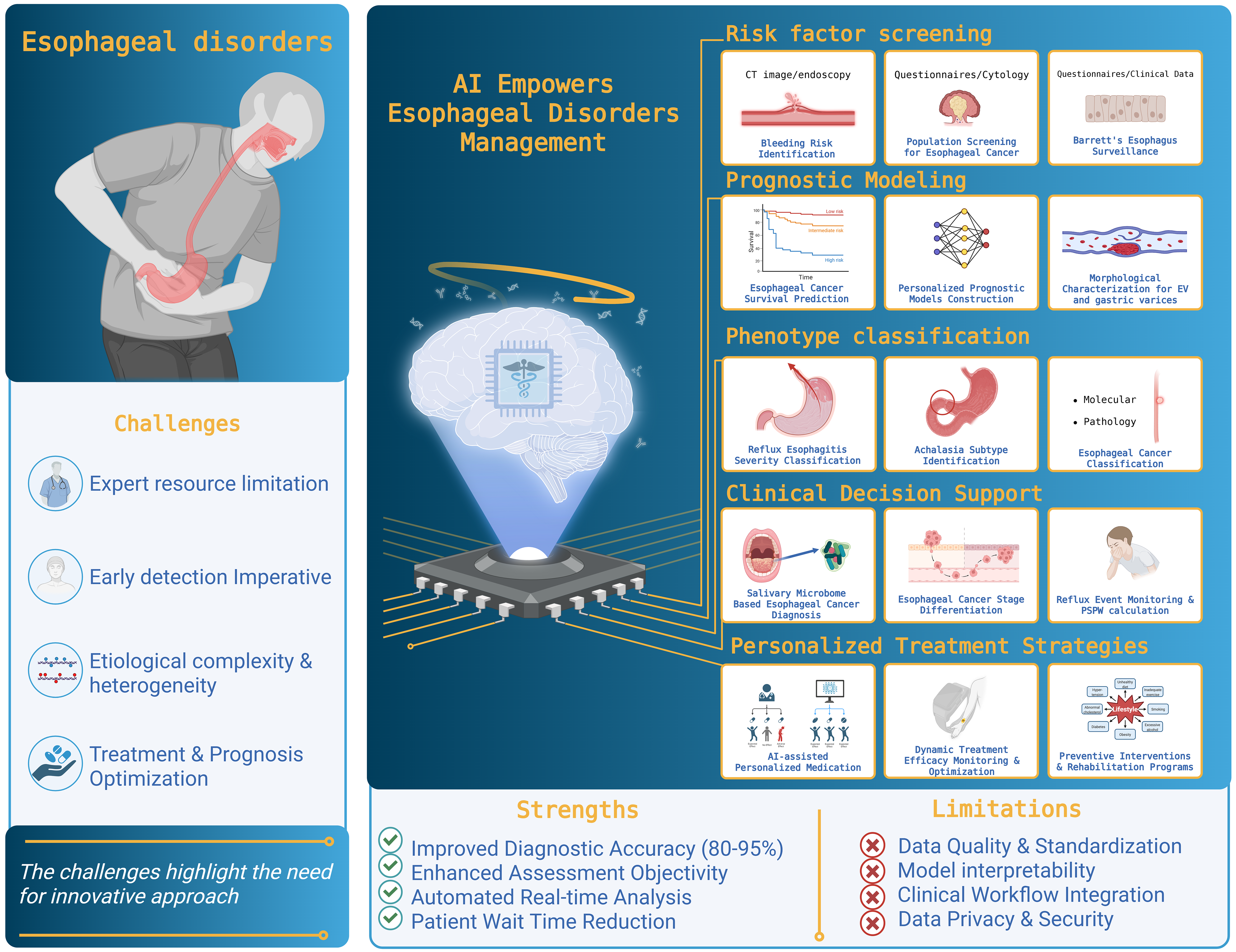
Figure 3 Conceptual overview of artificial intelligence-driven applications in esophageal disorder management focusing on risk factor screening, prognostic modeling, phenotype classification, clinical decision support, and personalized treatment planning.
AI: Artificial intelligence; CT: Computed tomography; EV: Esophageal varices; PSPW: Post-reflux swallow-induced peristaltic wave.
- Citation: Liu SW, Li P, Li XQ, Wang Q, Duan JY, Chen J, Li RH, Guo YF. Recent advances in machine learning for precision diagnosis and treatment of esophageal disorders. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(23): 105076
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i23/105076.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.105076