©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2025; 31(16): 105378
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105378
Published online Apr 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105378
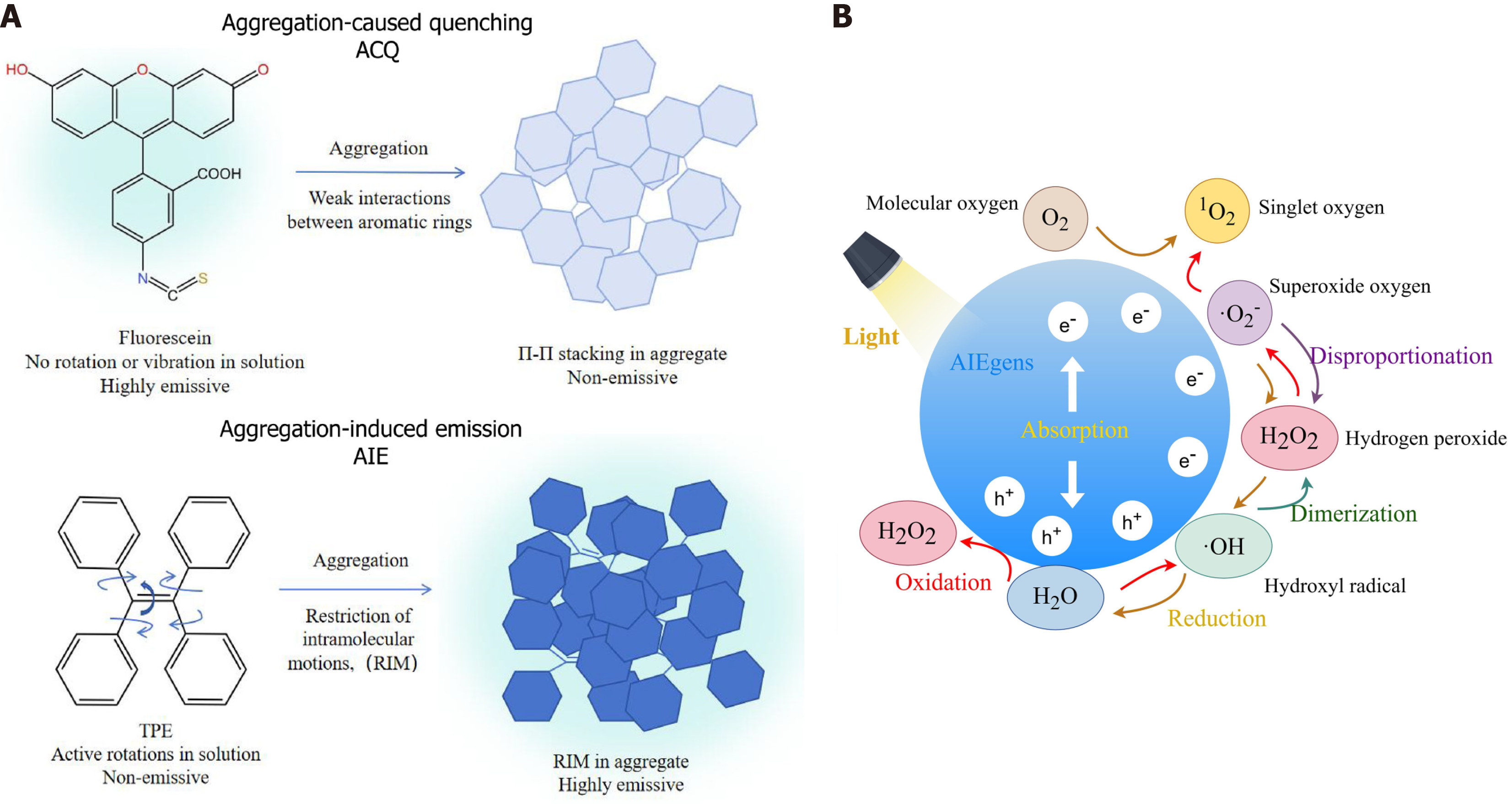
Figure 1 Aggregation-induced emission luminogens (AIEgens) overcomes the aggregation-caused fluorescence quenching effect, enhancing luminescence efficiency at high concentrations.
Upon light exposure, they generate reactive oxygen species through a series of reaction processes. A: The common fluorescent dye fluorescein exhibits fluorescence quenching in the aggregated state, while the classic aggregation-induced emission (AIE) molecule tetraphenylethylene overcomes the aggregation-caused fluorescence quenching effect and shows enhanced fluorescence at high concentrations; B: AIEgens generate various reactive oxygen species upon light irradiation. AIEgens: Aggregation-induced emission luminogens; AuNPs: Gold nanoparticles; TPE: Tetraphenylethylene; ACQ: Aggregation-induced fluorescence quenching. Created in Figdraw, and the compound structures were drawn using KingDraw.
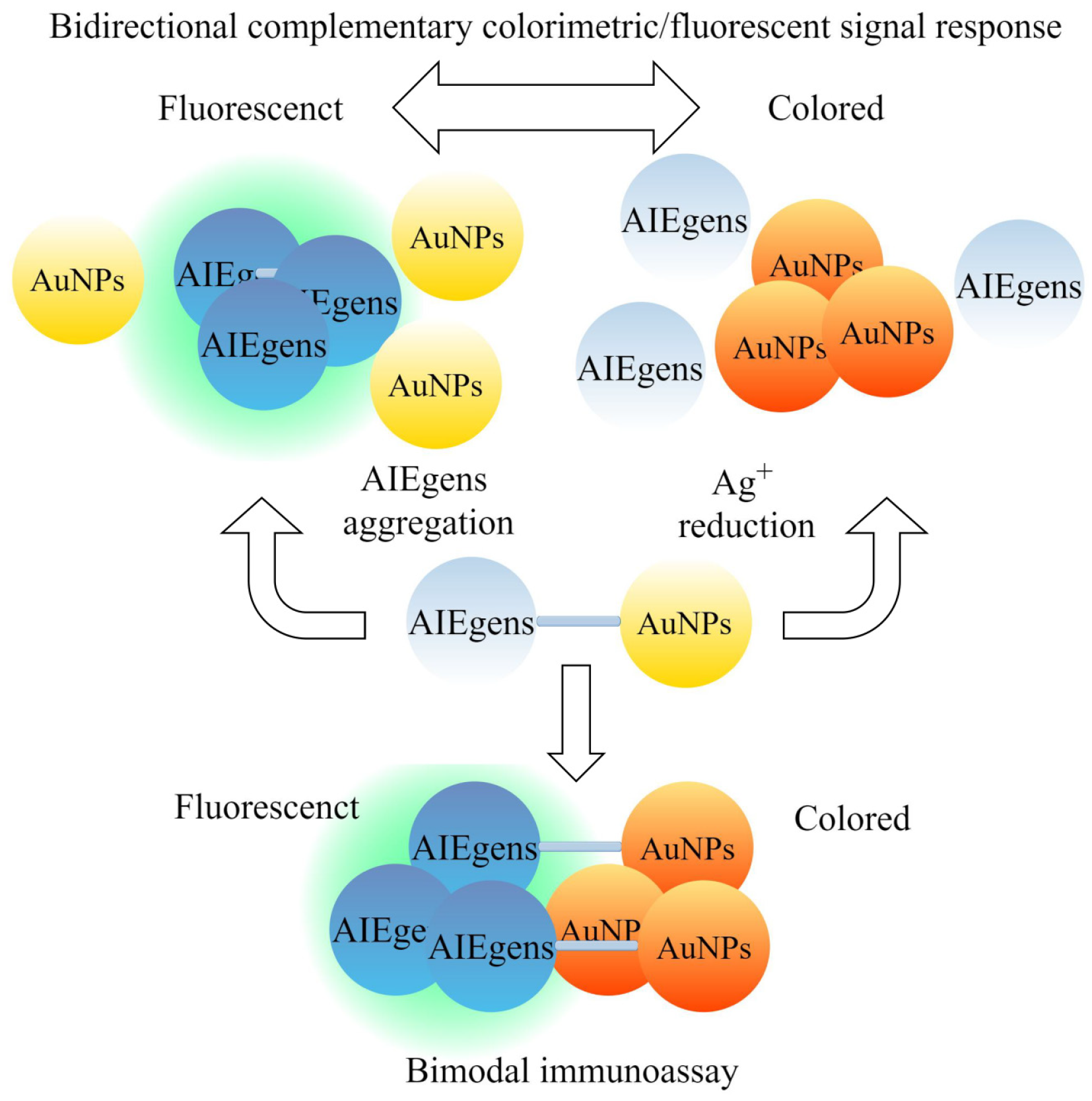
Figure 2 Dual-correspondence system based on gold nanoparticles and aggregation-induced emission luminogens enhances detection of gastrointestinal pathogens.
Due to the aggregation of gold nanoparticles, the colorimetric signal increases, while the fluorescence signal of aggregation-induced emission luminogens decreases due to the inner filter effect, resulting in a bidirectional complementary colorimetric/fluorescent signal response. When combined, they exhibit a more sensitive bimodal immunoassay. AIEgens: Aggregation-induced emission luminogens; AuNPs: Gold nanoparticles. Created in Figdraw.
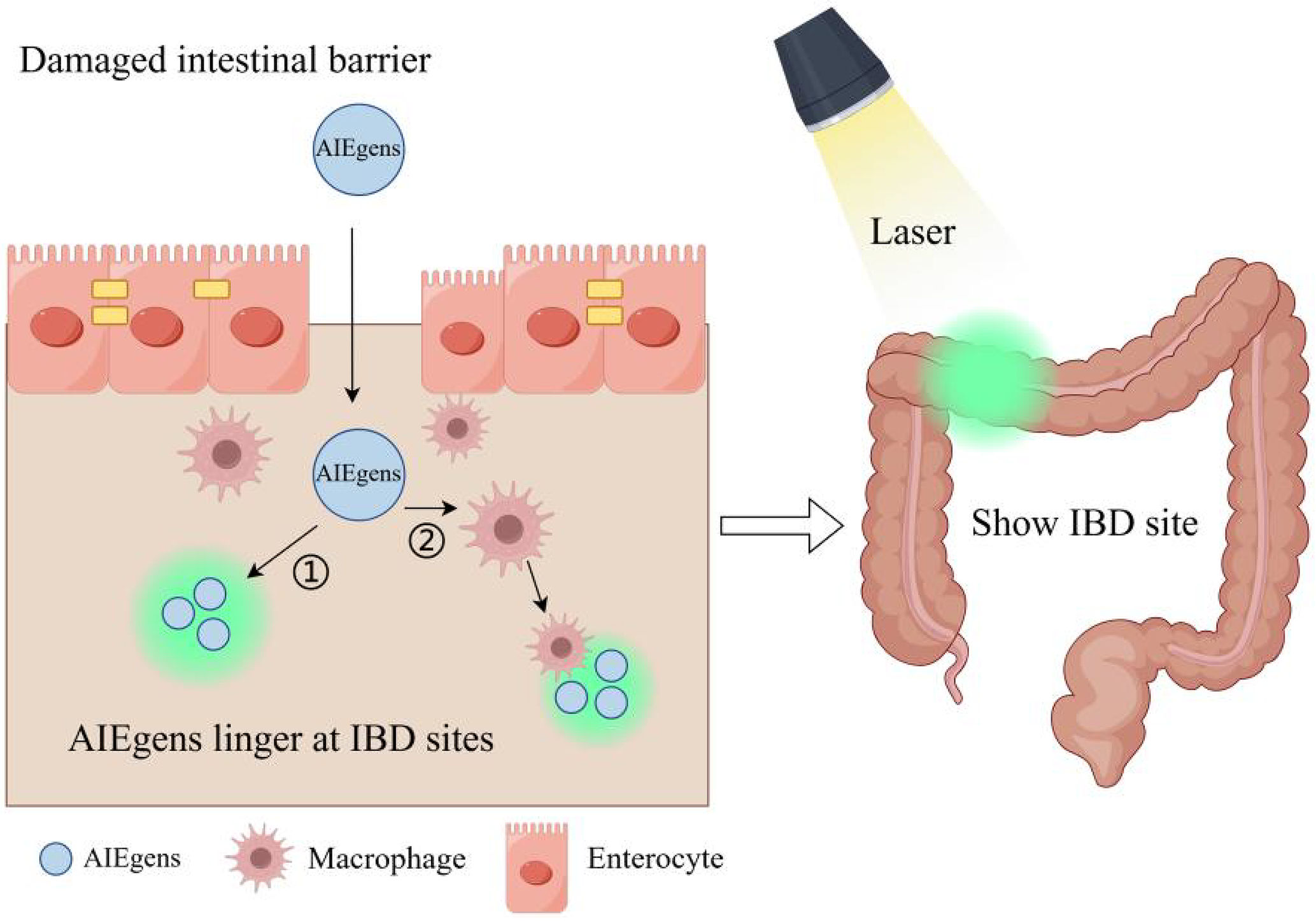
Figure 3 Aggregation-induced emission luminogens detect inflammatory bowel disease by intestinal barrier damage or targeting inflammatory markers.
After oral administration, aggregation-induced emission luminogens (AIEgens) pass through the mucosal layer through the damaged intestinal barrier site. 1AIEgens spontaneously aggregate and are retained. 2AIEgens track macrophages, aggregate, and are retained at the inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) site. Fluorescence indicates the IBD site after illumination. AIEgens: Aggregation-induced emission luminogens; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease. Created in Figdraw.
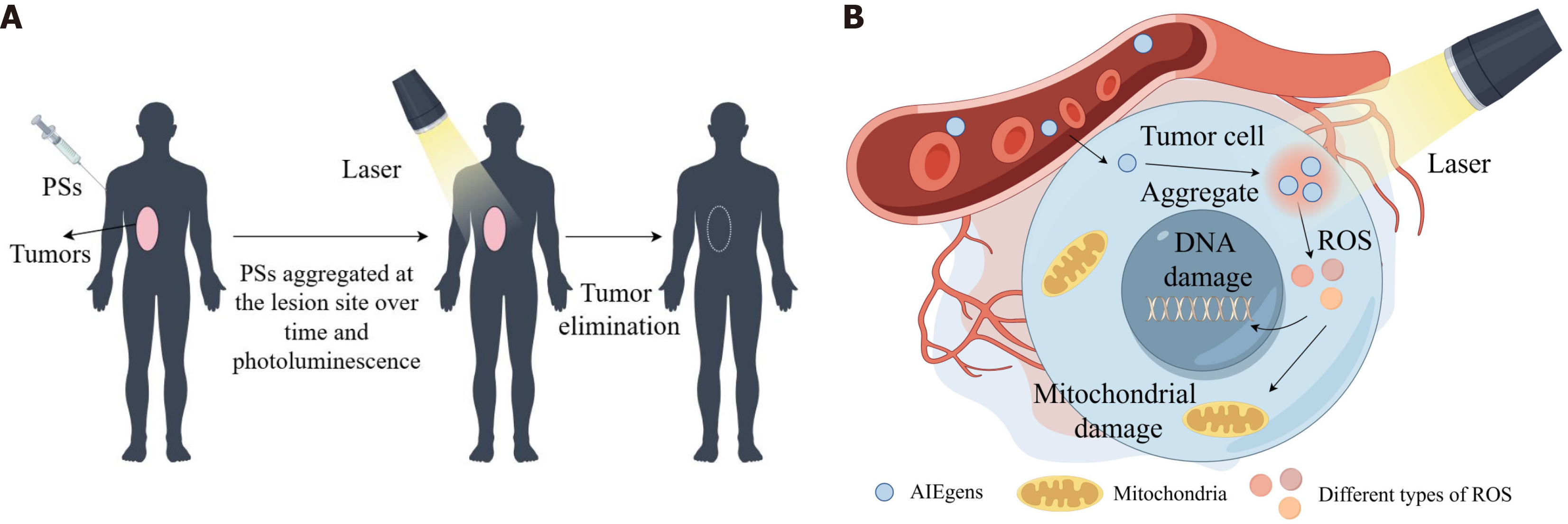
Figure 4 Aggregation-induced emission luminogens treatment of tumor processes by photodynamic therapy and cancer cell damage triggered by generation of reactive oxygen species.
A: The process and principle of photodynamic therapy for tumor treatment; B: Aggregation-induced emission photosensitizers accumulate in tumor cells and generate reactive oxygen species to kill tumor cells after illumination. AIEgens: Aggregation-induced emission luminogens; PSs: Photosensitizers; ROS: Reactive oxygen species. Created in Figdraw.
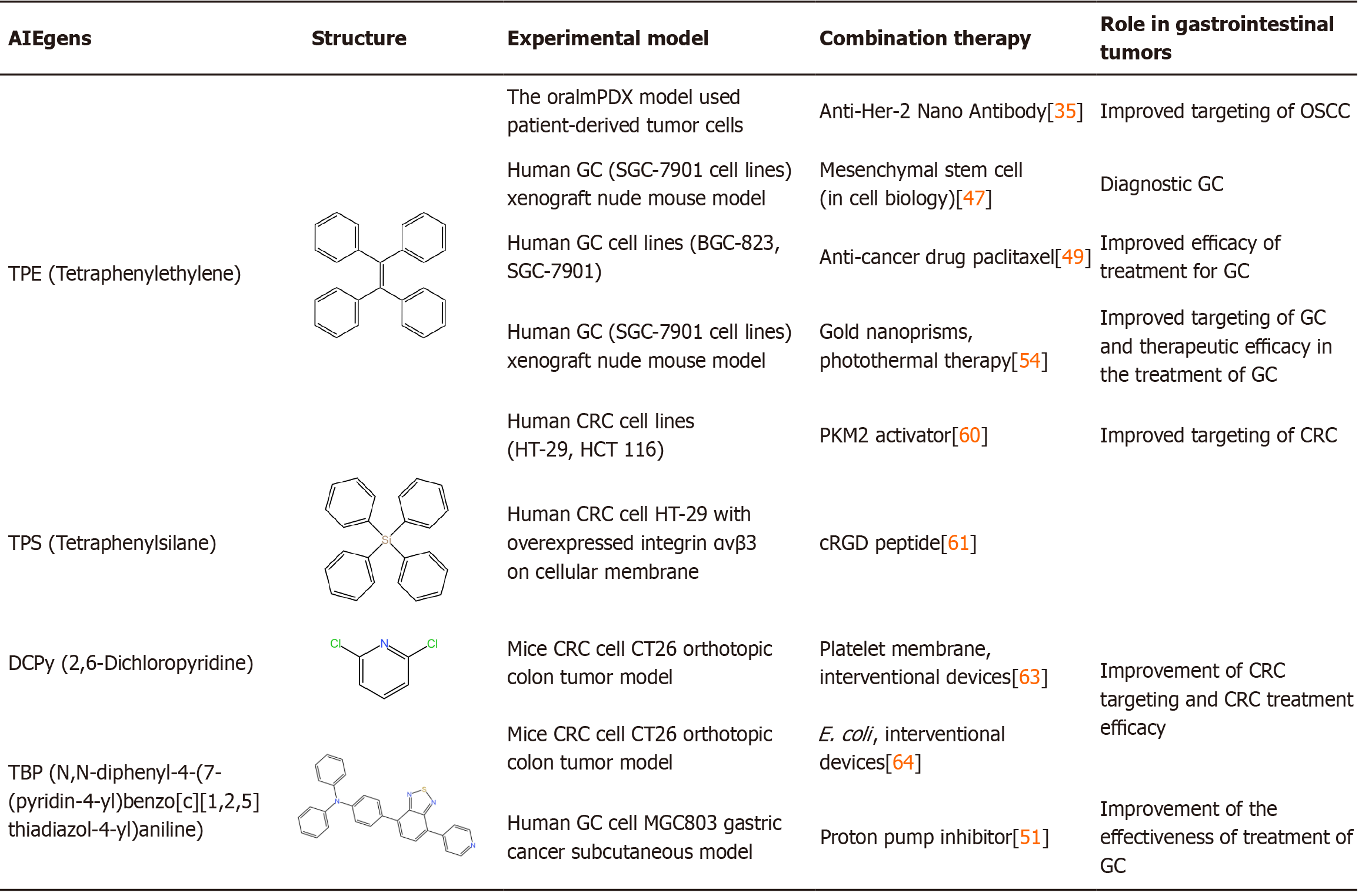
Figure 5 Combination of aggregation-induced emission luminogens with multiple therapies to improve the effectiveness of aggregation-induced emission luminogens in gastrointestinal diseases.
AIEgens: Aggregation-induced emission luminogens; TPE: Tetraphenylethylene; GC: Gastric carcinoma; CRC: Colorectal cancer; E. coli: Escherichia coli; OSCC: Oral squamous cell carcinoma. The compound structures were drawn using KingDraw.
- Citation: Li YR, Wang G, He WT, Liu T. Application of aggregation-induced emission materials in gastrointestinal diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(16): 105378
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i16/105378.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i16.105378