Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2024; 30(9): 1189-1212
Published online Mar 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1189
Published online Mar 7, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1189
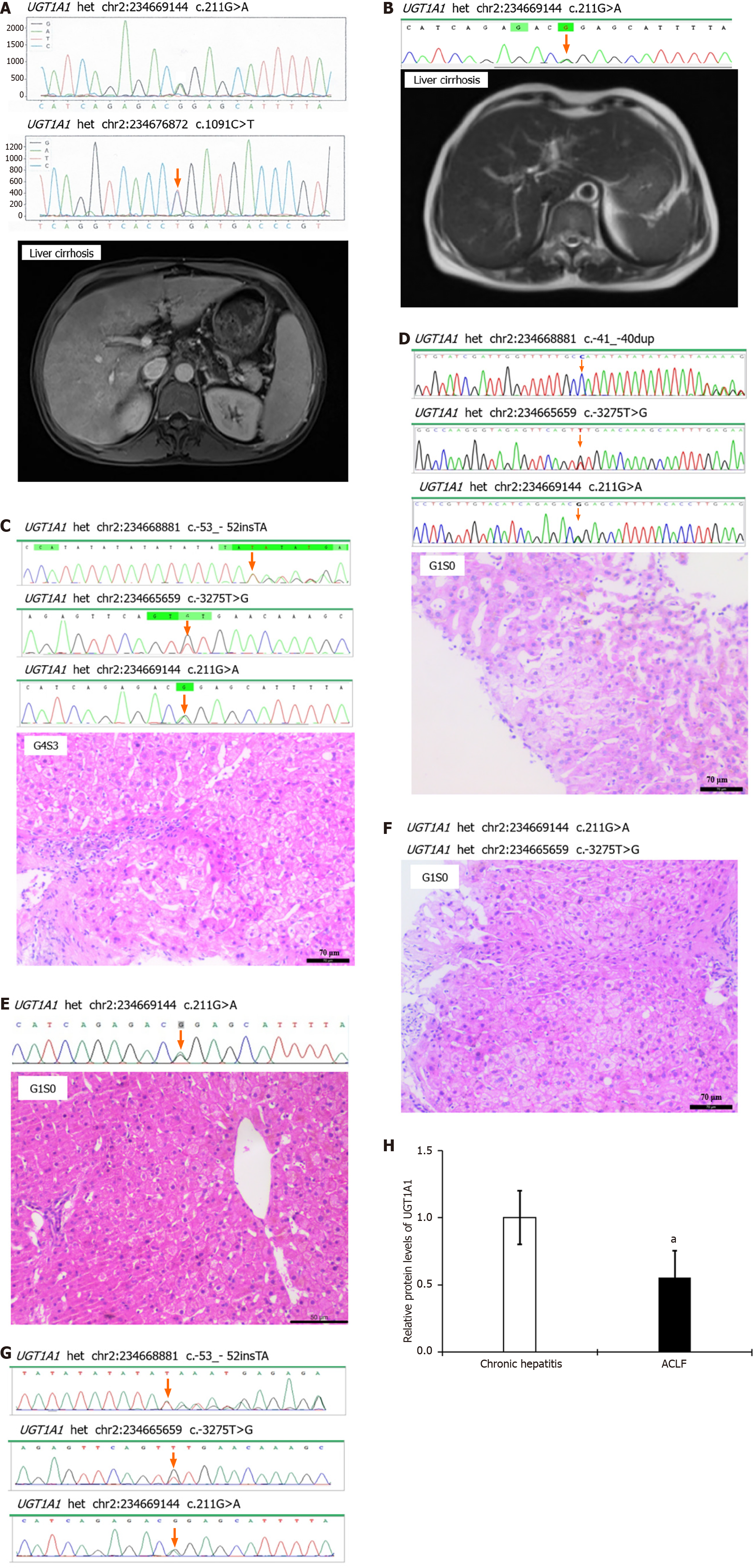
Figure 1 Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 gene mutation is closely associated with liver injury.
A-G: The uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) gene sequencing, imaging, and pathological biopsy results for patients 1 to 7; H: Relative protein levels of UGT1A1 in chronic hepatitis and acute-on-chronic liver failure. aP < 0.05 vs the chronic hepatitis group. UGT1A1: Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1.
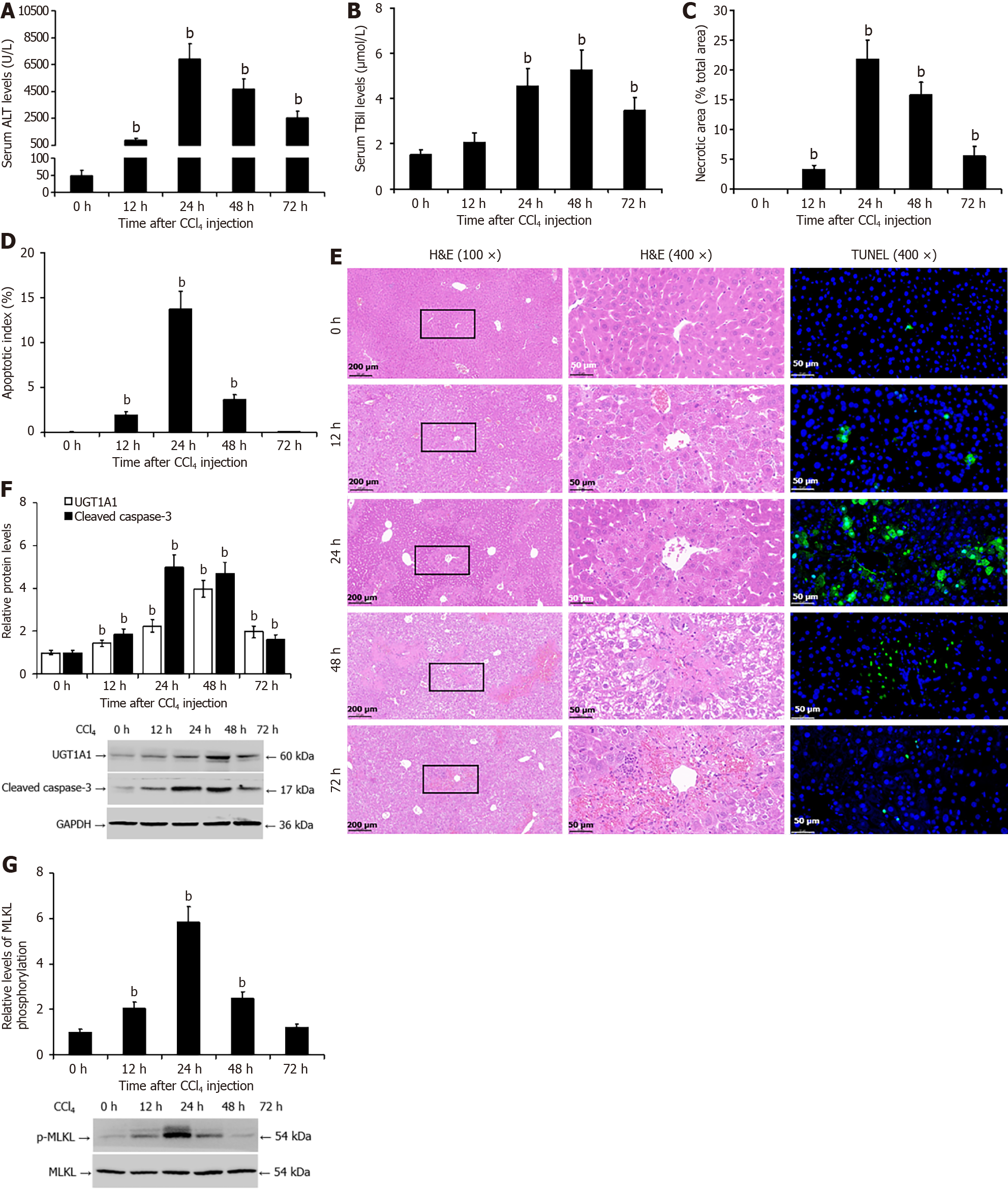
Figure 2 Increased uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 protein levels in the livers of mice with carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury.
A: The enzyme rate method was used to detect the serum level of alanine transaminase in mice; B: The diazo method was used to detect the serum total bilirubin level; C and E: Pathological analysis of liver tissue by hematoxylin and eosin staining; D and E: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling assay was used to measure hepatocyte apoptosis; F: Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 and cleaved caspase-3; G: Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase. bP < 0.01 vs the 0 h (control) group. UGT1A1: Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1; ALT: Alanine transaminase; TBil: Total bilirubin; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; TUNEL: Transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling; p-MLKL: Phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase; CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase.
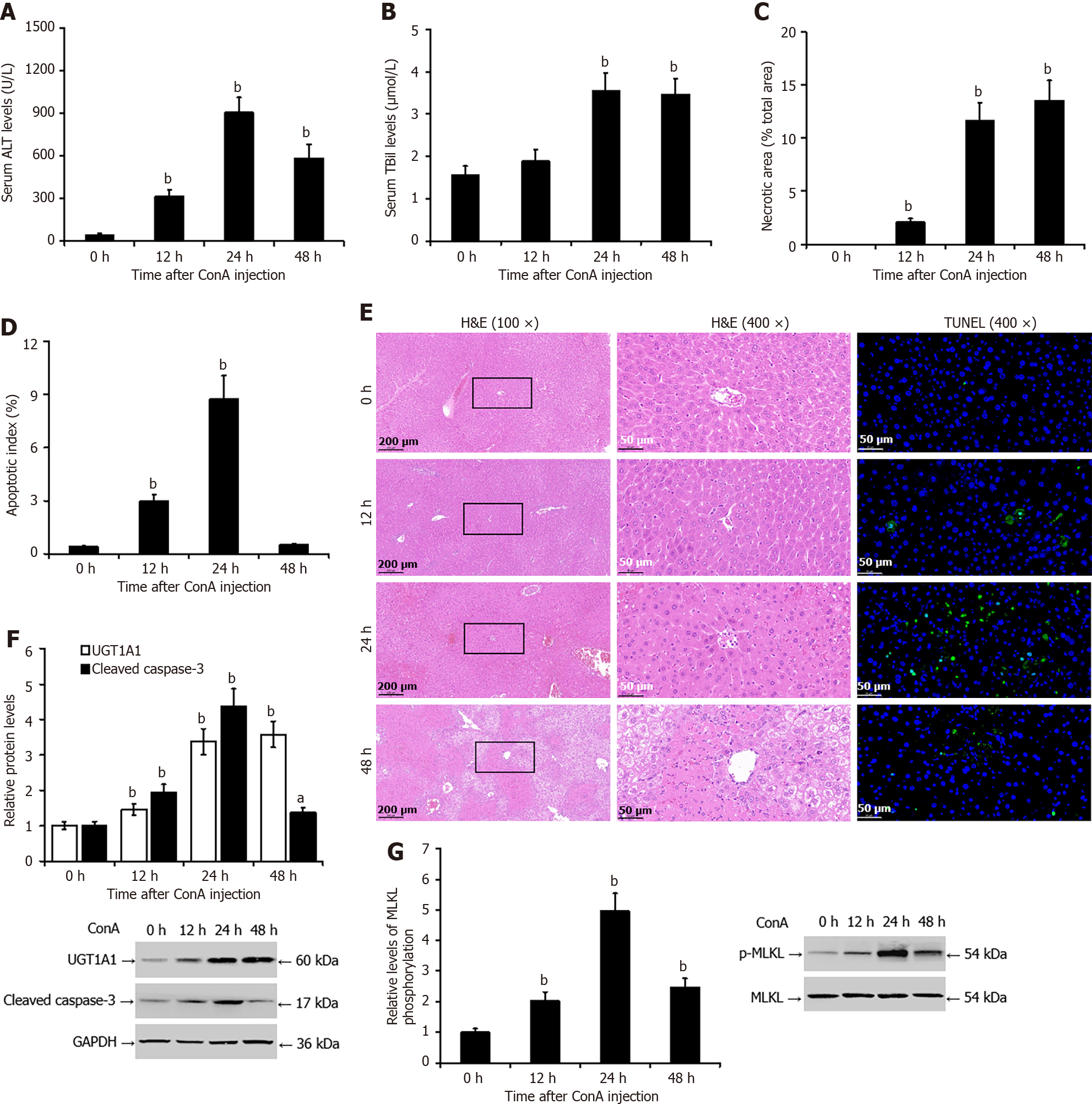
Figure 3 Increased levels of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 protein in the livers of mice with concanavalin A-induced liver injury.
A: The enzyme rate method was used to detect the serum level of alanine transaminase in mice; B: The diazo method was used to detect the serum level of total bilirubin; C and E: Pathological analysis of liver tissue by hematoxylin and eosin staining; D and E: terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling assay was used to measure hepatocyte apoptosis; F: Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 and cleaved caspase-3; G: Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase. bP < 0.01 vs the 0 h (control) group. UGT1A1: Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1; ALT: Alanine transaminase; TBil: Total bilirubin; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; TUNEL: Transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling; p-MLKL: Phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase; ConA: Concanavalin A; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase.
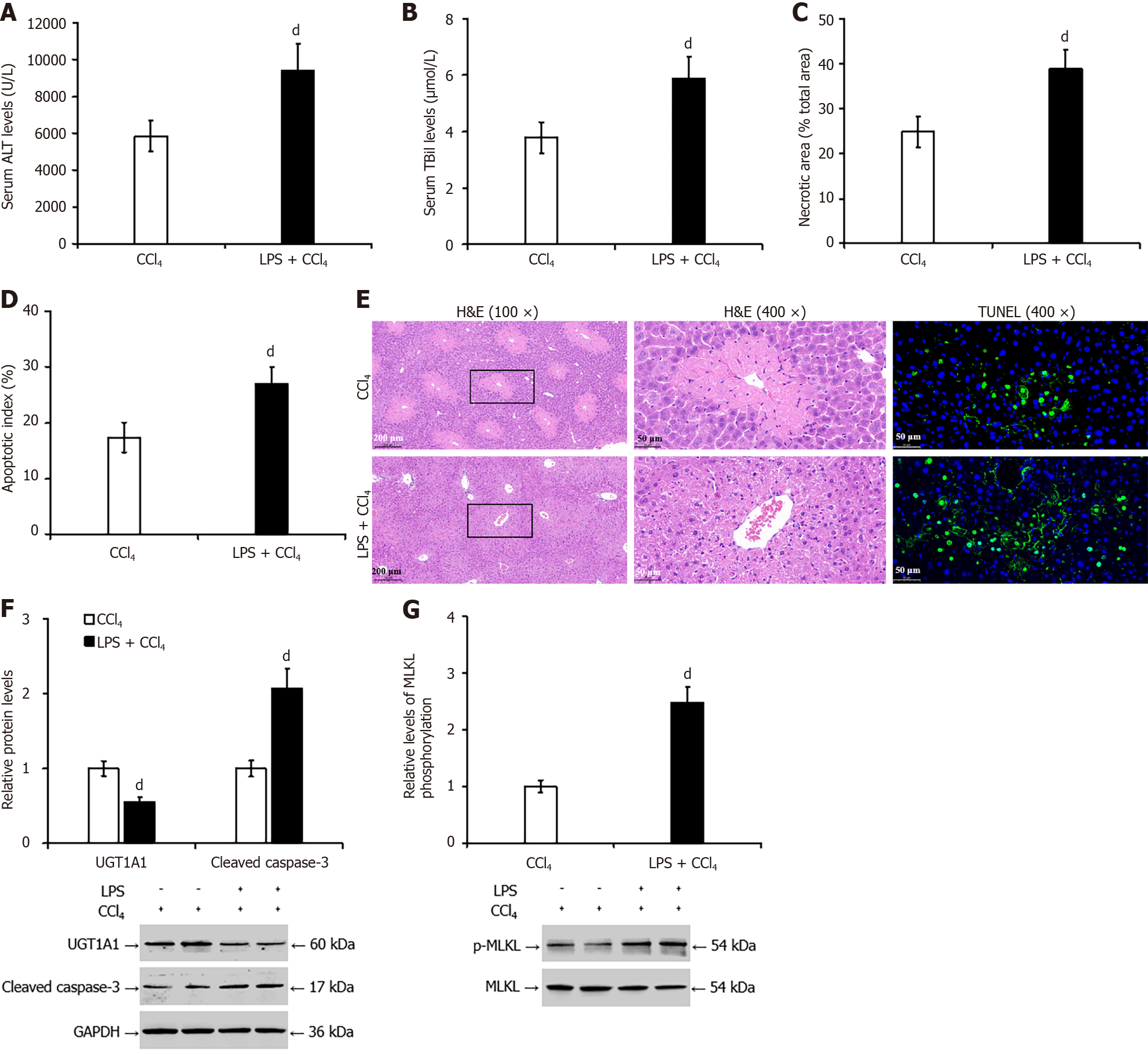
Figure 4 Lipopolysaccharide exacerbated carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice and decreased hepatic uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 expression.
A: The enzyme rate method was used to detect the serum levels of alanine transaminase in mice; B: Pathological analysis of liver tissue by hematoxylin and eosin staining; C and E: The terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling assay was used to measure hepatocyte apoptosis; D and E: The diazo method was used to detect the serum level of total bilirubin; F: Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 and cleaved caspase-3; G: Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase. dP < 0.01 vs the carbon tetrachloride group. UGT1A1: Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1; ALT: Alanine transaminase; TBil: Total bilirubin; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; TUNEL: Transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling; p-MLKL: Phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase; CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase.
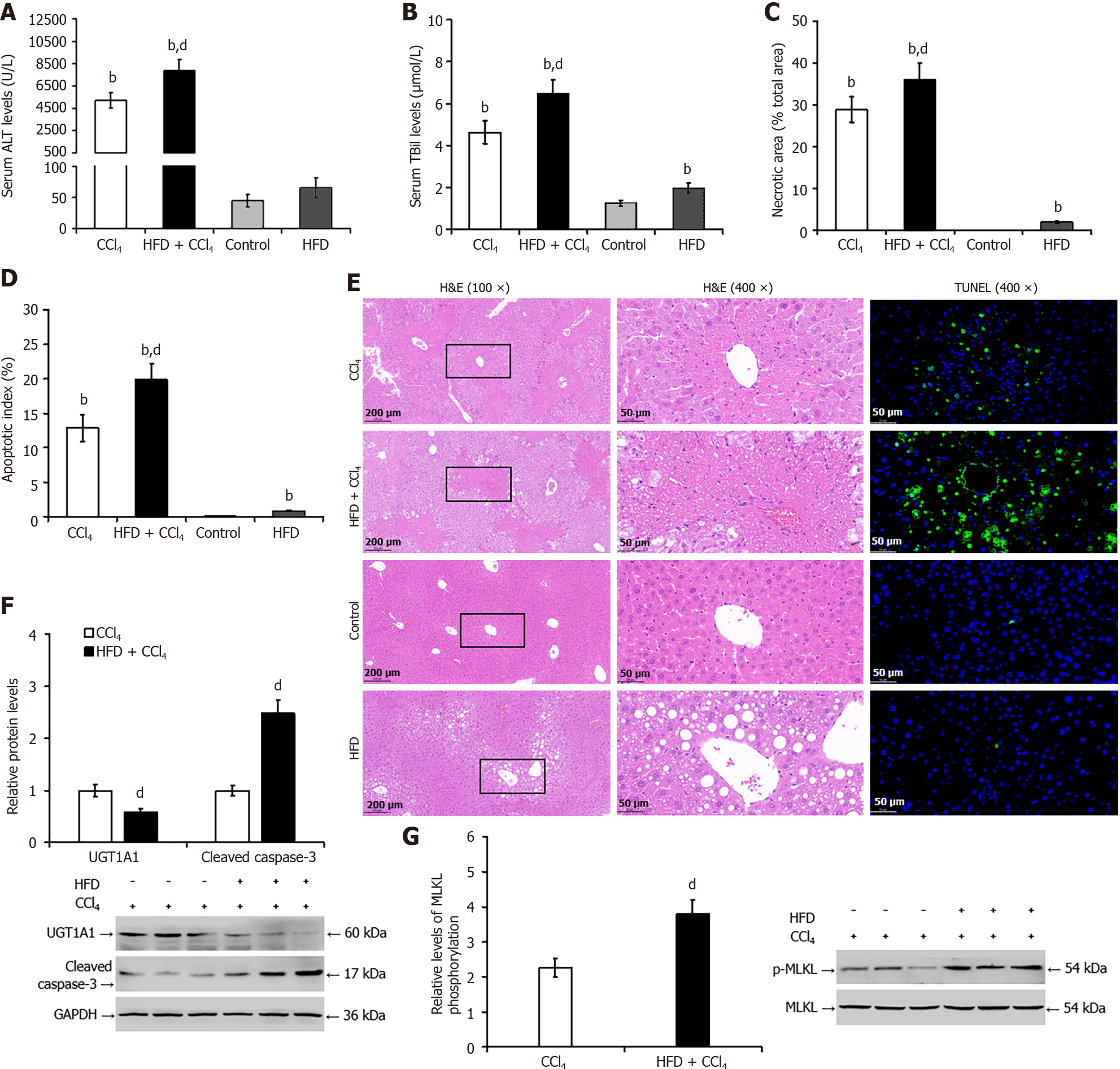
Figure 5 Liver steatosis worsens carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury and reduces hepatic uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltrans
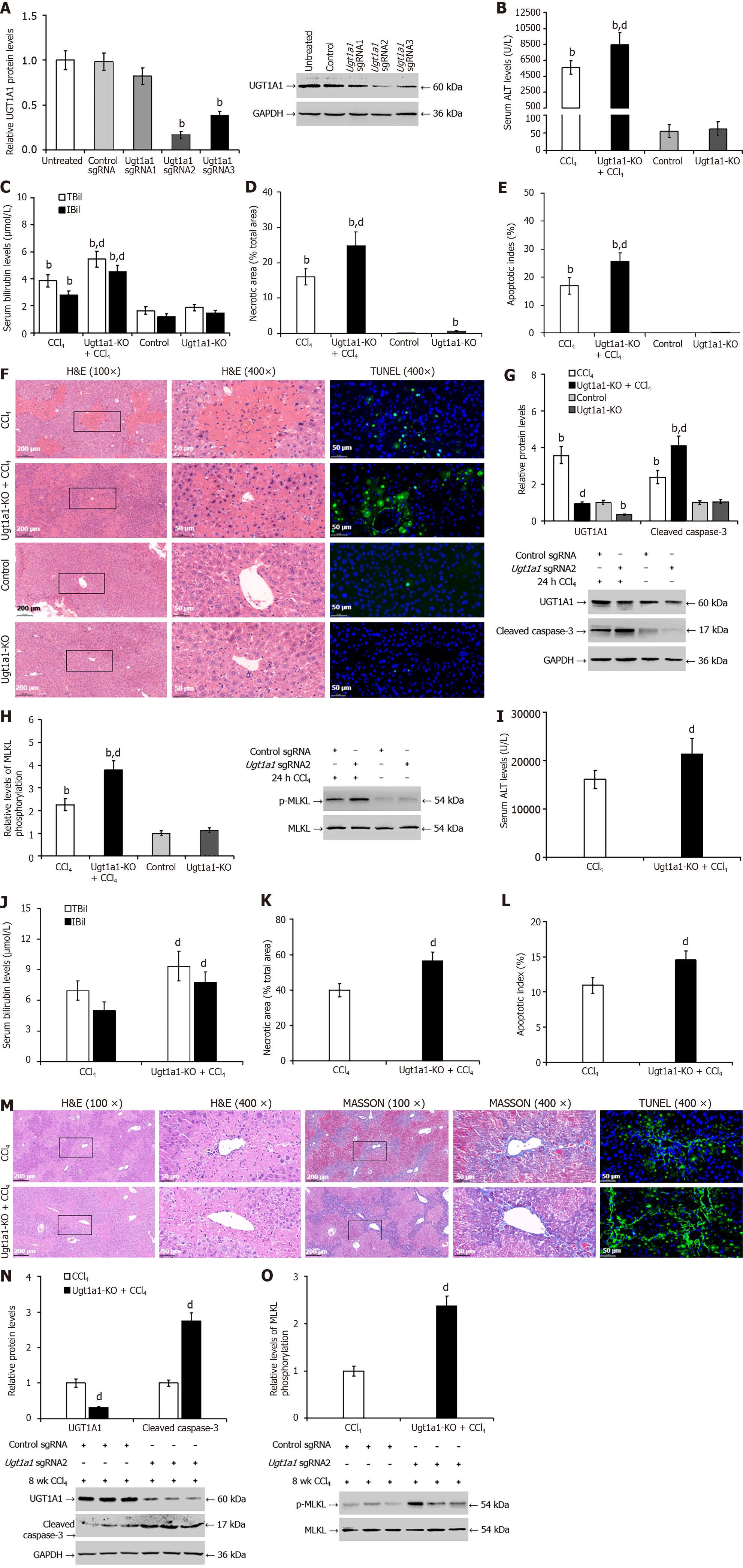
Figure 6 Knocking out uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 worsened carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice.
A: Western blotting was utilized to screen for the specific Ugt1a1 sgRNA that induced Ugt1a1 gene knockout; B and I: The enzyme rate method was used to detect the serum level of alanine transaminase in mice; C and J: The diazo method was used to detect the serum levels of total bilirubin and indirect bilirubin; D, F, K, and M: Pathological analysis of liver tissue by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Masson staining; E, F, L, and M: The terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling assay was used to measure hepatocyte apoptosis; G and N: Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 and cleaved caspase-3; H and O: Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase. bP < 0.01 vs the control sgRNA or control group; dP < 0.01 vs the carbon tetrachloride group. UGT1A1: Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1; ALT: Alanine transaminase; TBil: Total bilirubin; IBil: Indirect bilirubin; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; TUNEL: Transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling; p-MLKL: Phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase; CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; KO: Knockout; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase.
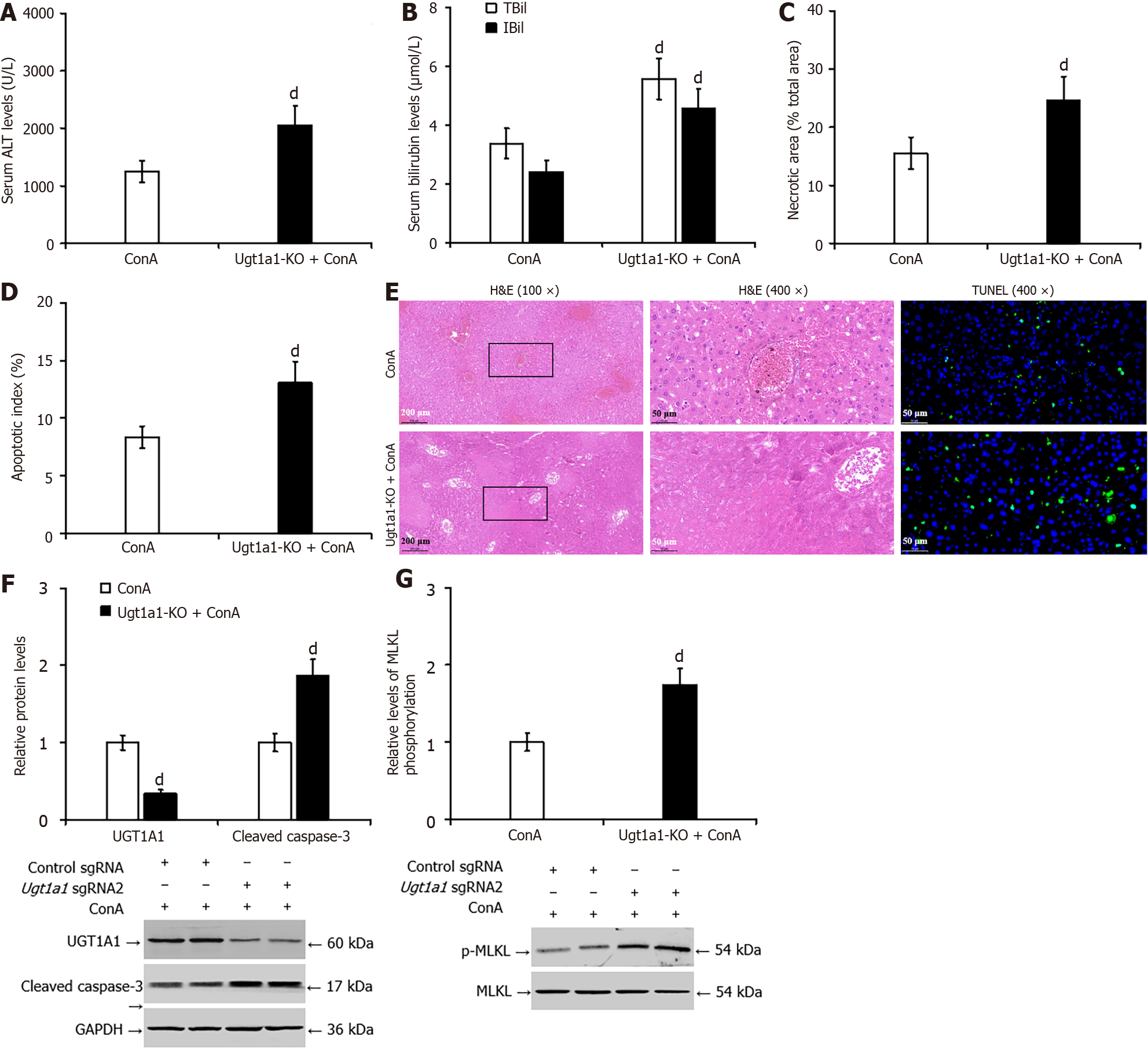
Figure 7 Knocking out uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 worsened concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice.
A: The enzyme rate method was used to detect the serum level of alanine transaminase in mice; B: The diazo method was used to detect the serum level of total bilirubin and indirect bilirubin; C and E: Pathological analysis of liver tissue by hematoxylin and eosin staining; D and E: The terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling assay was used to measure hepatocyte apoptosis; F: Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 and cleaved caspase-3; G: Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase. dP < 0.01 vs the concanavalin A group. UGT1A1: Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1; ALT: Alanine transaminase; TBil: Total bilirubin; IBil: Indirect bilirubin; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; TUNEL: Transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-nick end labelling; p-MLKL: Phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase; CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; KO: Knockout; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase.
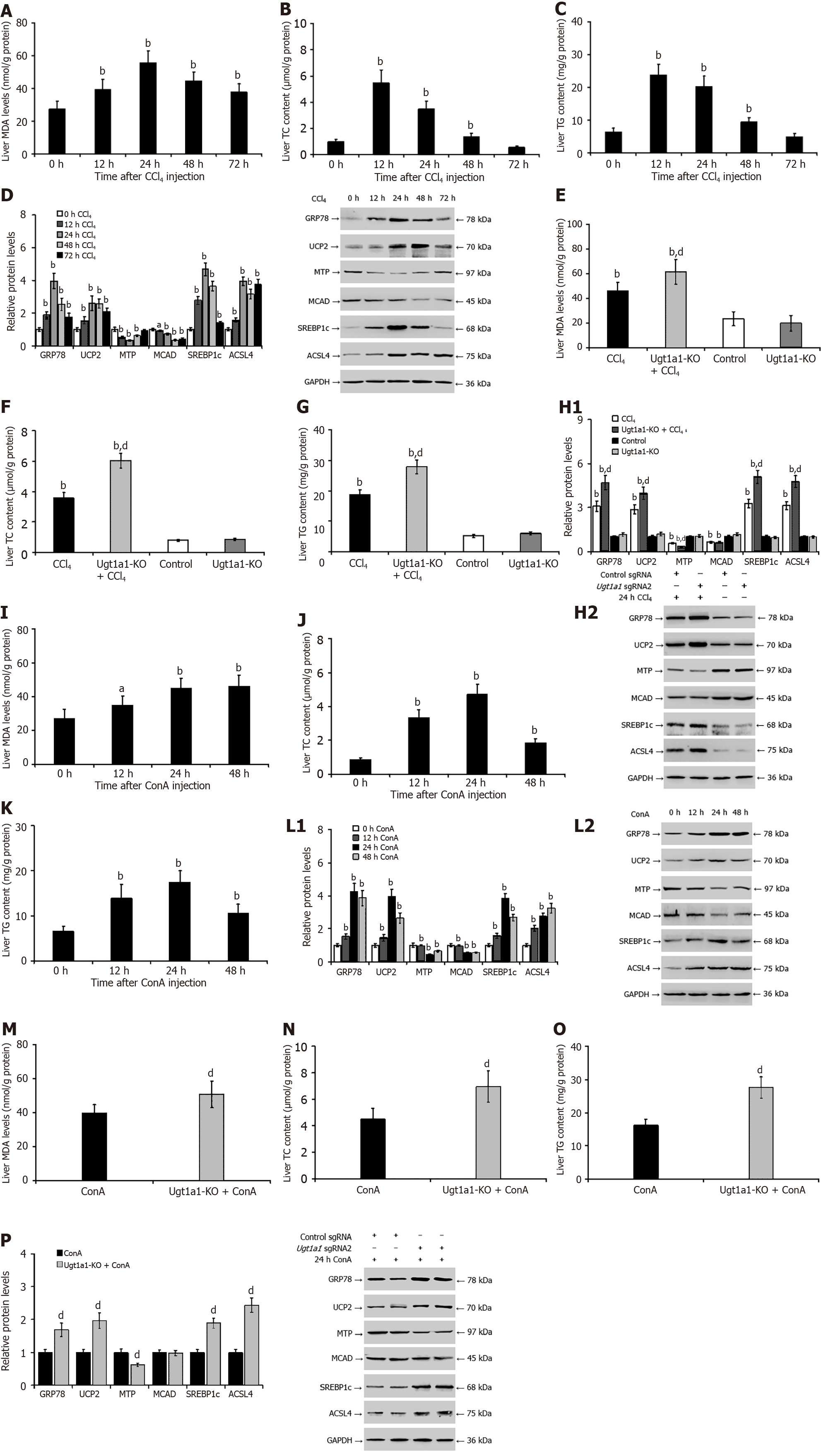
Figure 8 Interference with upregulation of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 exacerbates hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative stress, and lipid metabolism disorder during liver injury.
A-C: Malondialdehyde (MDA), triglyceride (TG), and total cholesterol (TC) contents in the livers of mice with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-mediated liver injury; D: Related protein expressions in mice with CCl4-mediated liver injury; E-G: MDA, TG, and TC contents in the livers of mice were measured in the Ugt1a1 knockout model after treatment with CCl4; H: Related protein expressions in CCl4- mediated model mice with Ugt1a1 knockout; I-K: MDA, TG, and TC contents in the livers of mice with concanavalin A (ConA)-mediated liver injury; L: Related protein expressions in mice with ConA-mediated liver injury; M-O: MDA, TG, and TC contents in the livers of mice were measured in the Ugt1a1 knockout model after treatment with CCl4; P: Related protein expressions in ConA-mediated model mice with Ugt1a1 knockout. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the 0 h or control group; dP < 0.01 vs the CCl4 groups or ConA groups. MDA: Malondialdehyde; TG: Triglyceride; TC: Total cholesterol; UGT1A1: Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1; MTP: Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; MCAD: Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; SREBP1c: Cleaved sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; ACSL4: Acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4; GRP78: 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein; UCP2: Uncoupling protein-2; CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; ConA: Concanavalin A; KO: Knockout; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase.
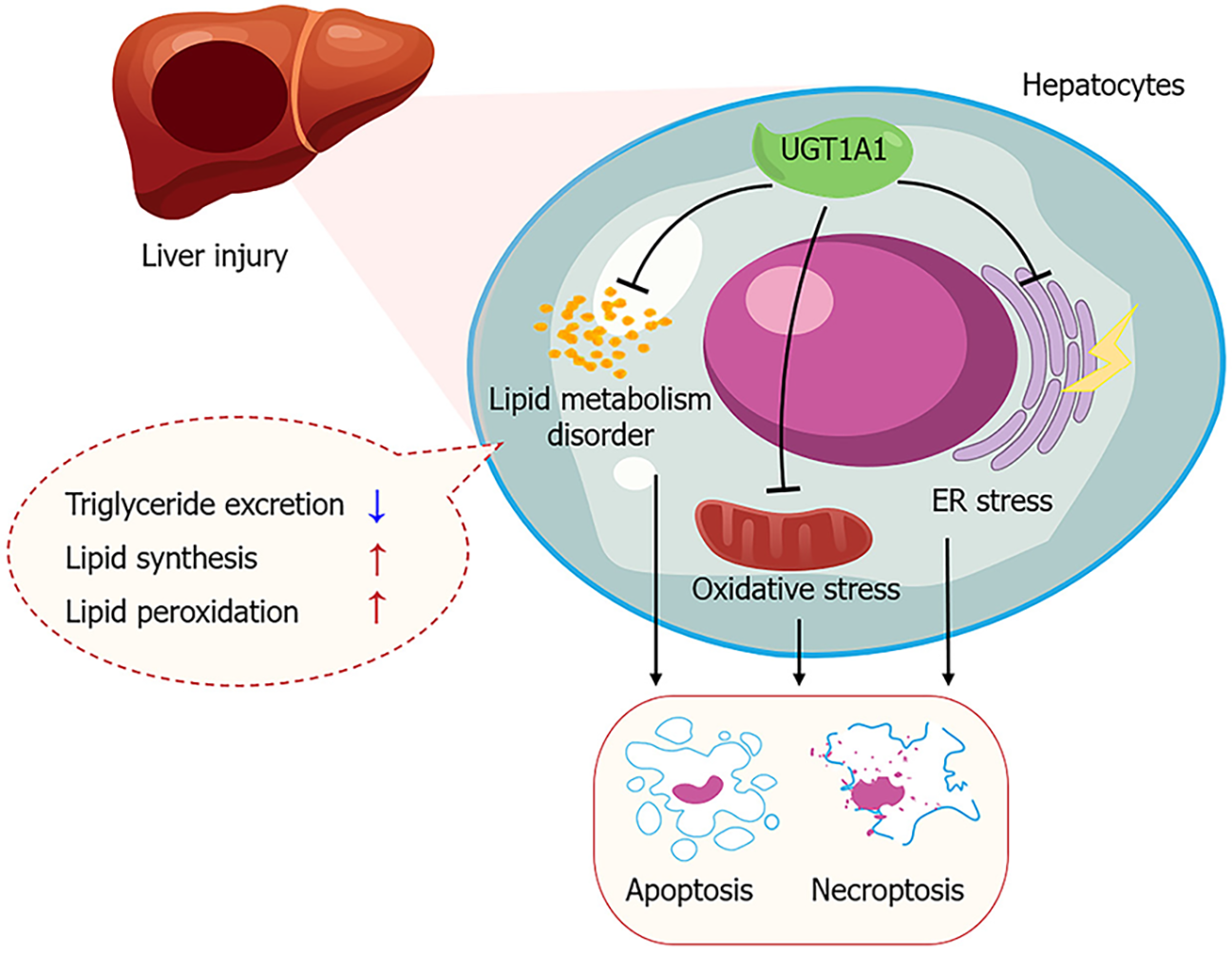
Figure 9 Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 influences the mechanism of liver injury progression.
The reduced activity and low levels of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 exacerbate endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative stress, and disruptions in lipid metabolism, thereby increasing hepatocyte apoptosis and necroptosis, and promoting the progression of liver injury. UGT1A1: Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum.
- Citation: Jiang JL, Zhou YY, Zhong WW, Luo LY, Liu SY, Xie XY, Mu MY, Jiang ZG, Xue Y, Zhang J, He YH. Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 prevents the progression of liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(9): 1189-1212
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i9/1189.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1189