Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2024; 30(8): 984-990
Published online Feb 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.984
Published online Feb 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.984
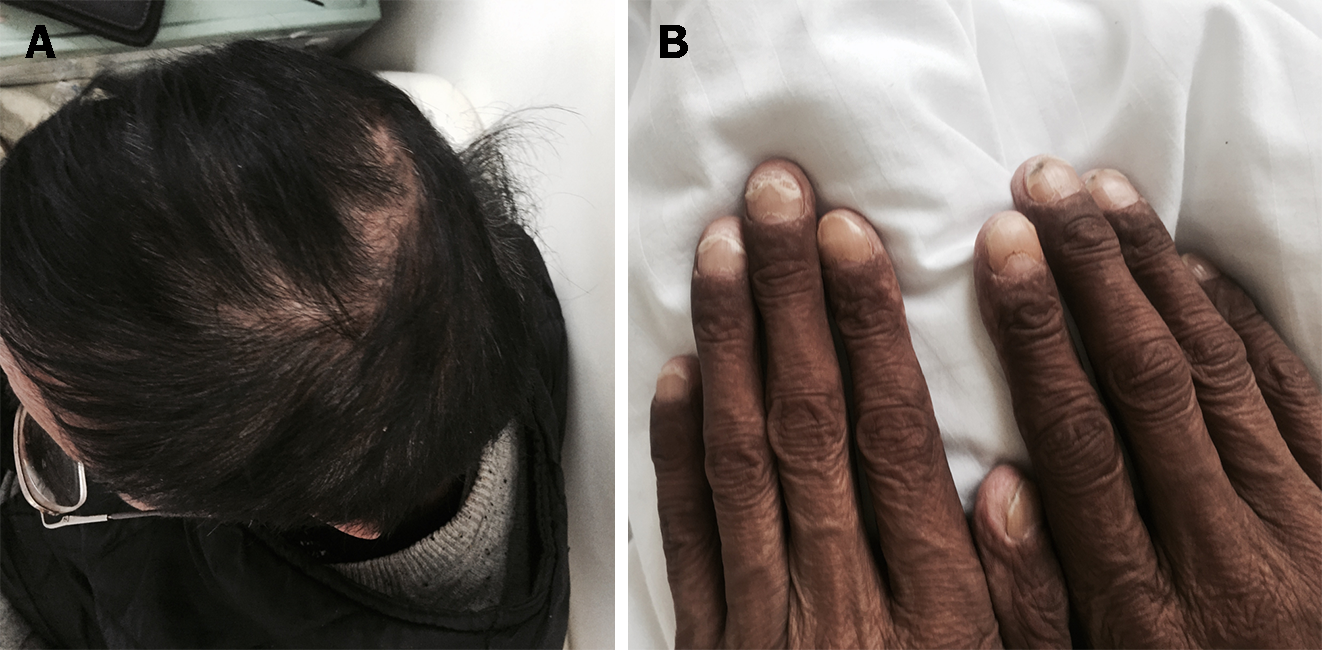
Figure 1 Clinical presence of ectodermal abnormalities.
A: Alopecia; B: Nail dystrophy.
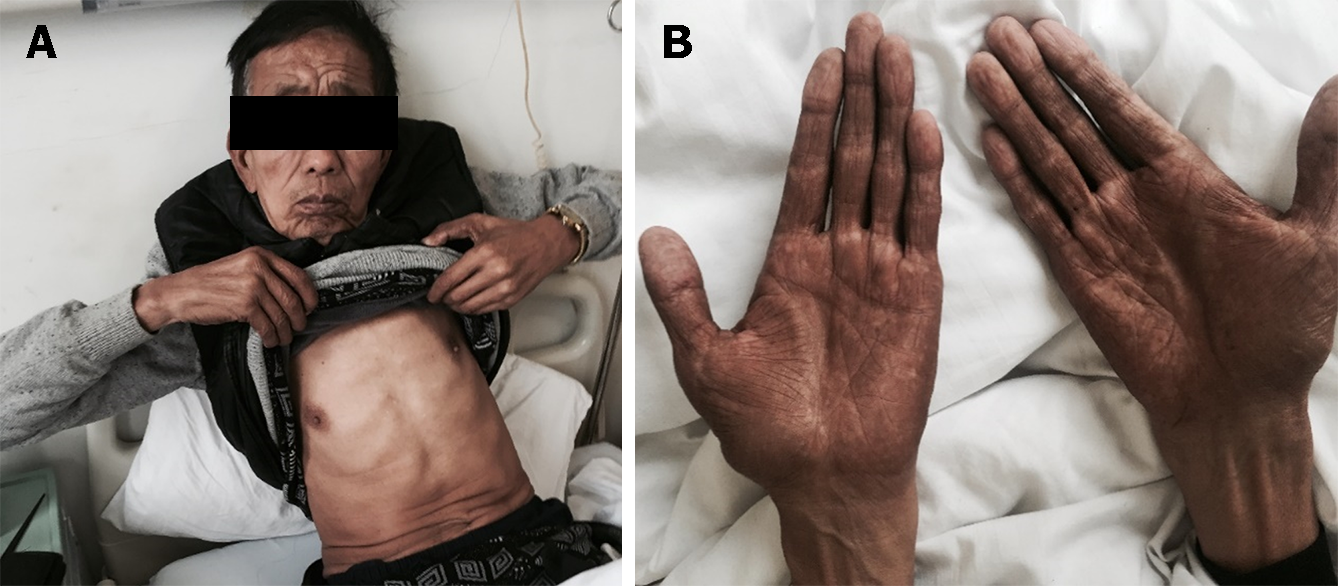
Figure 2 Hyperpigmentation of the skin.
A and B: It was most evident on his face (A) and bilateral upper extremities (B).
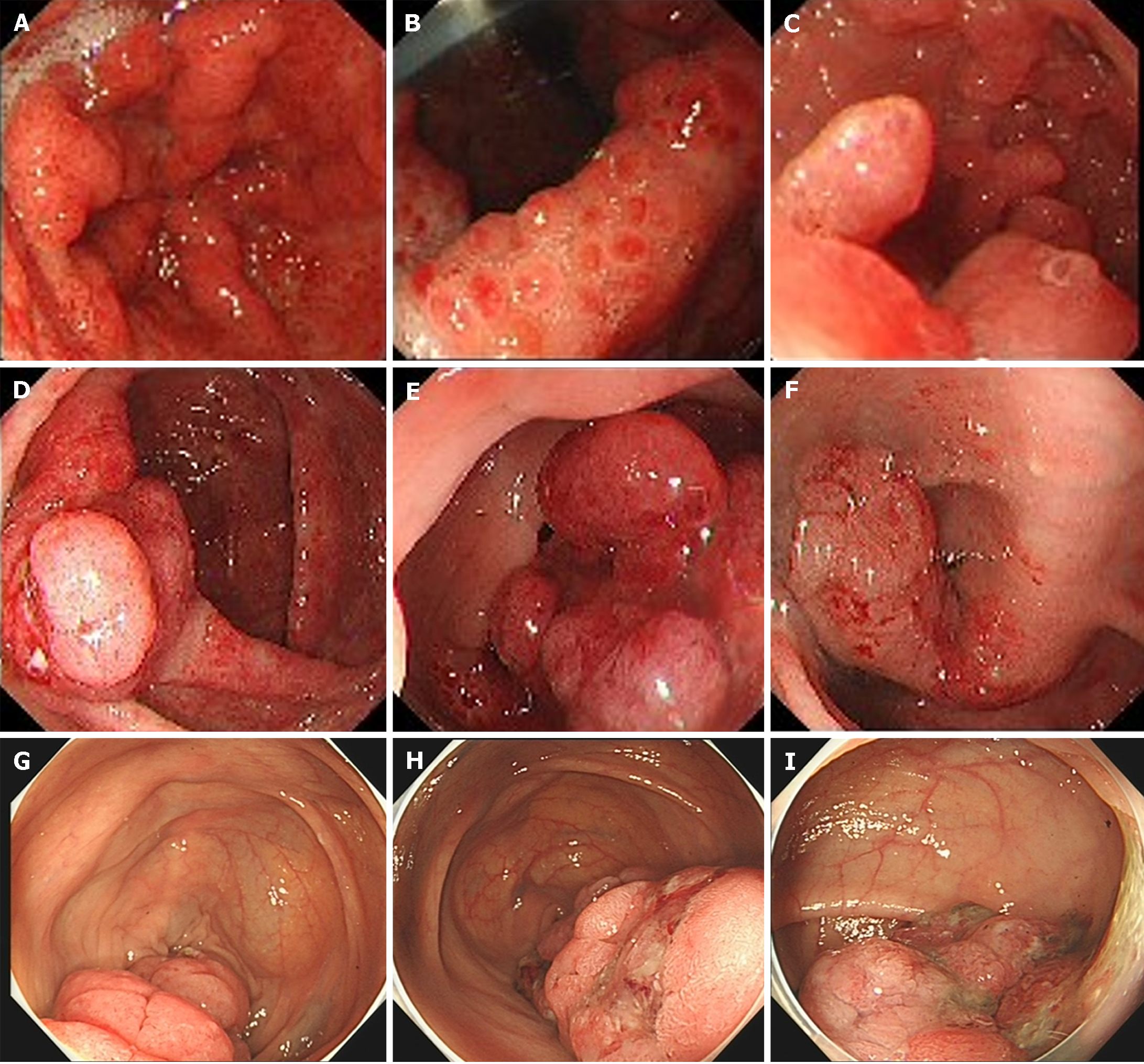
Figure 3 Endoscopy results.
A: Granular apophyses below the dentate line were observed by the endoscopist, although they were not so obvious; B and C: Gastroscopy showed multiple polyps hyperplasia of the stomach and the duodenum; D-F: Colonoscopy showed that mucosa erosion and multiple apophyses with the appearance of polypuses were observed in the ileocecal valve, and numerous polyps were found in the whole colon; G-I: The endoscopic findings showed no improvement at 6-year follow-up.
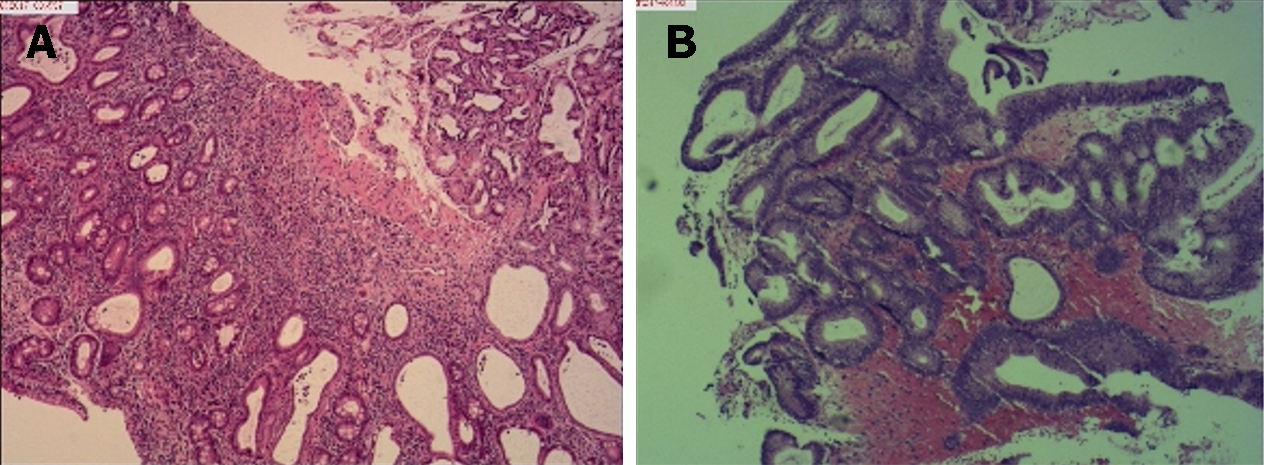
Figure 4 Histological examination of biopsy specimens obtained from duodenal bulb and the colon.
A: Duodenal bulb; B: The colon. Haematoxylin and eosin staining (× 10).
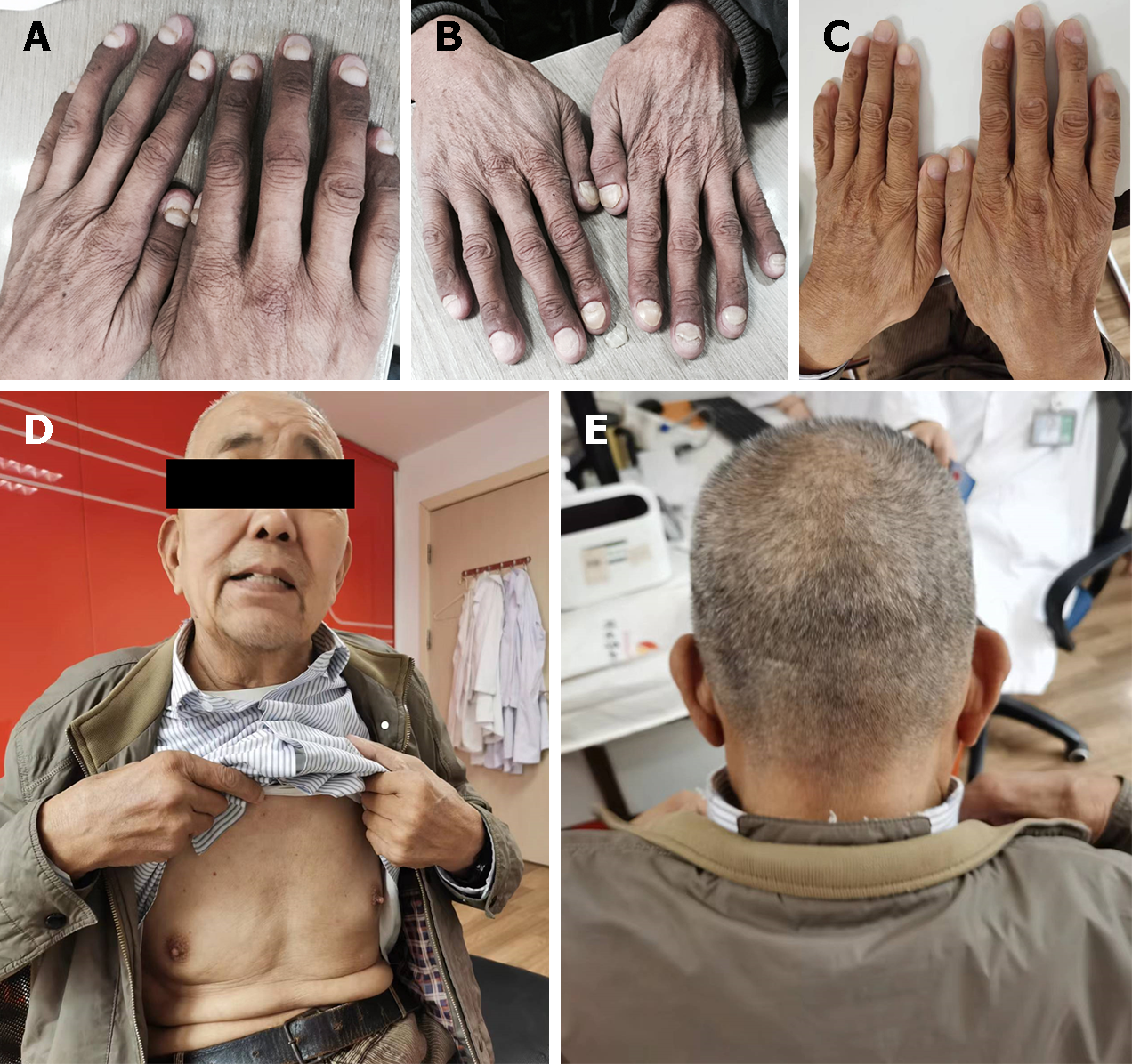
Figure 5 Improvement of the clinical symptoms.
A-E: Hyperpigmentation of the skin, nail dystrophy, and alopecia were relieved at one-month (A), five months (B), and four years (C-E) follow-up.
- Citation: Tang YC. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome with esophagus involvement and six-year follow-up: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(8): 984-990
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i8/984.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i8.984