©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2024; 30(40): 4339-4353
Published online Oct 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i40.4339
Published online Oct 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i40.4339
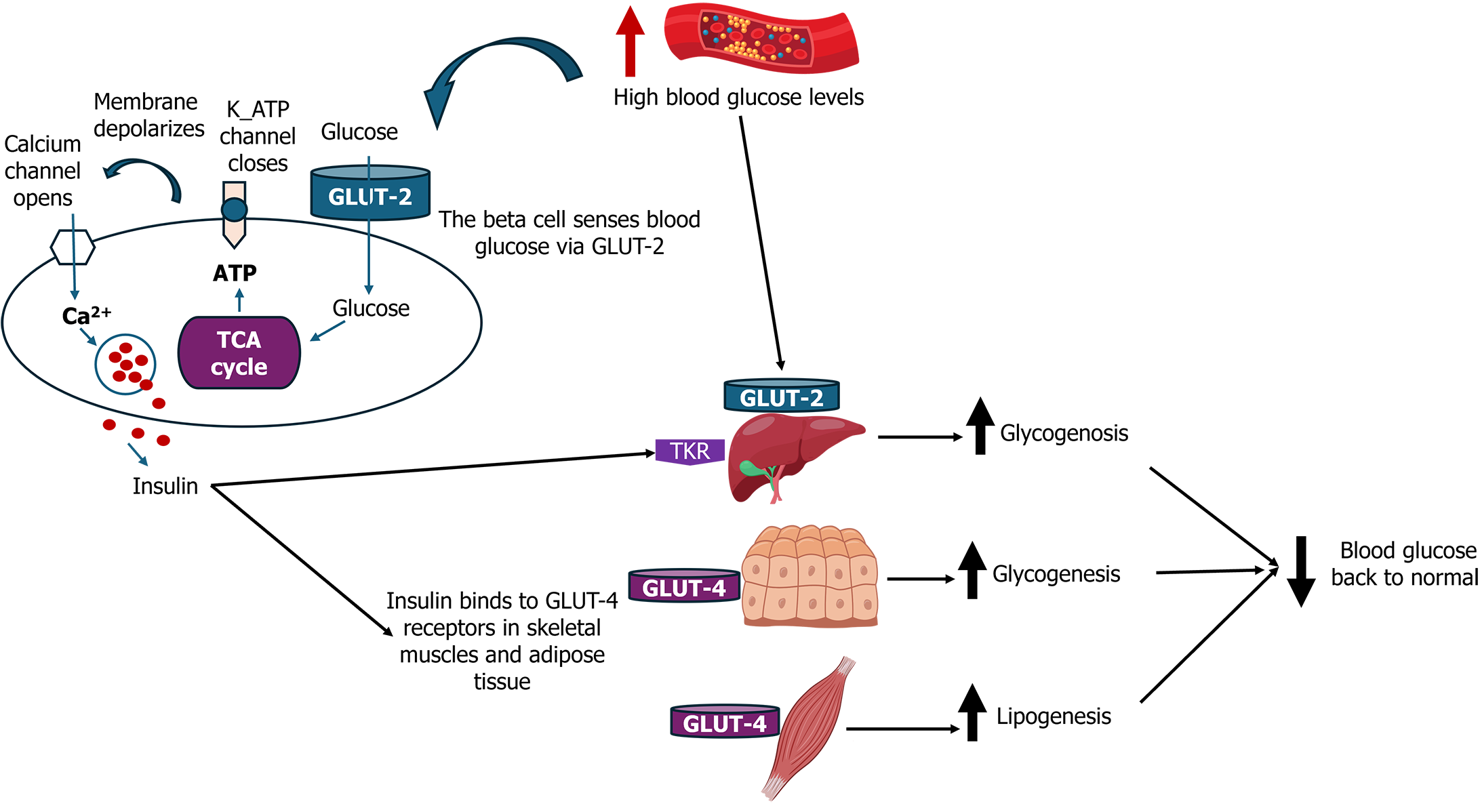
Figure 1 Overview of beta-cell function and insulin secretion.
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; Ca²+: Calcium ion; GLUT-2: Glucose transporter 2; GLUT-4: Glucose transporter 4; K_ATP: Adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel; TCA cycle: Tricarboxylic acid cycle.
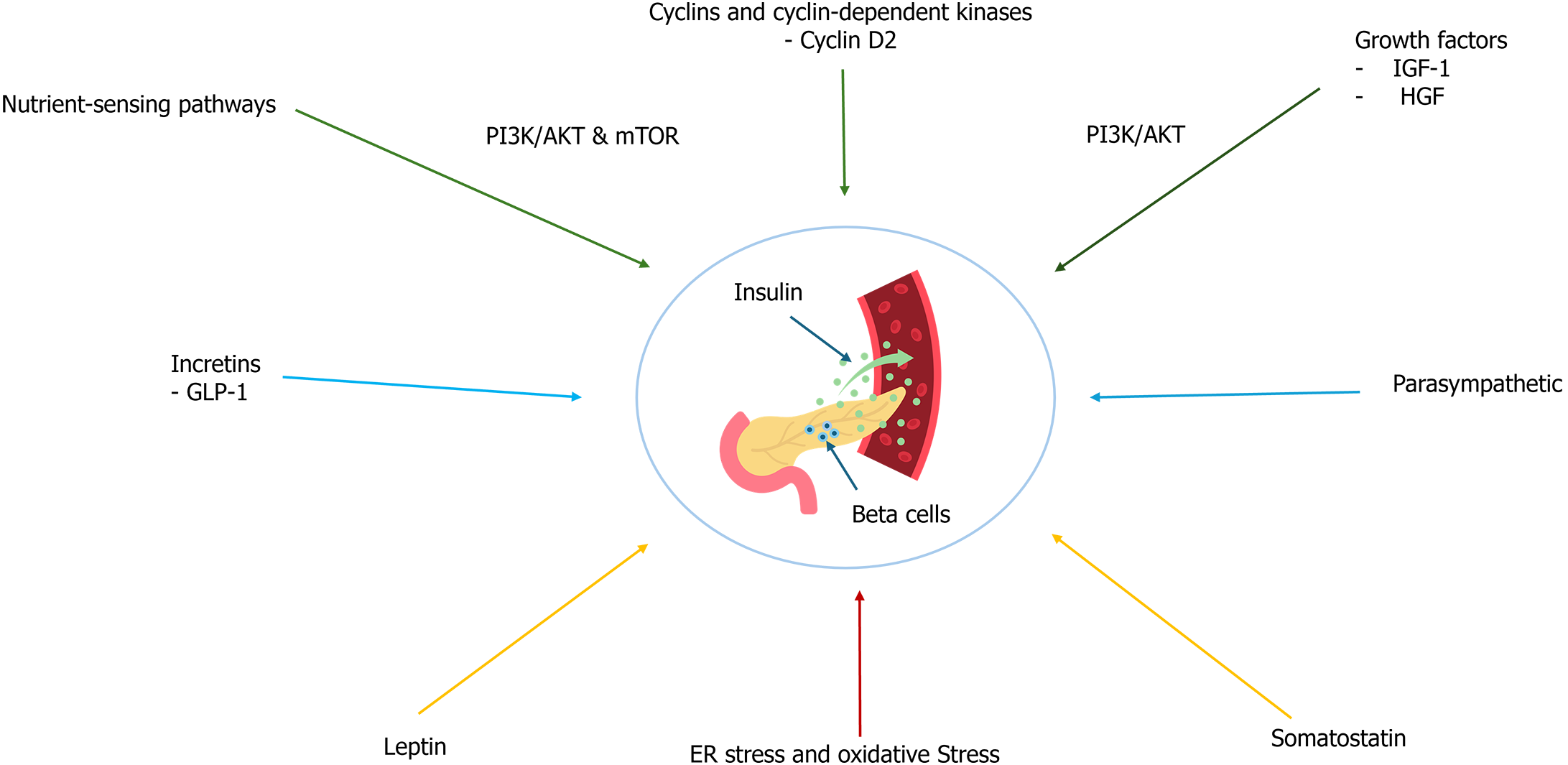
Figure 2 Factors influencing beta-cell function and insulin secretion.
The green arrow refers to the promotion of beta-cell proliferation. The red arrow refers to promoting beta-cell apoptosis. The blue arrow indicates stimulation of insulin release. The orange arrow indicates inhibiting insulin secretion. AKT: Protein kinase B; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide 1; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
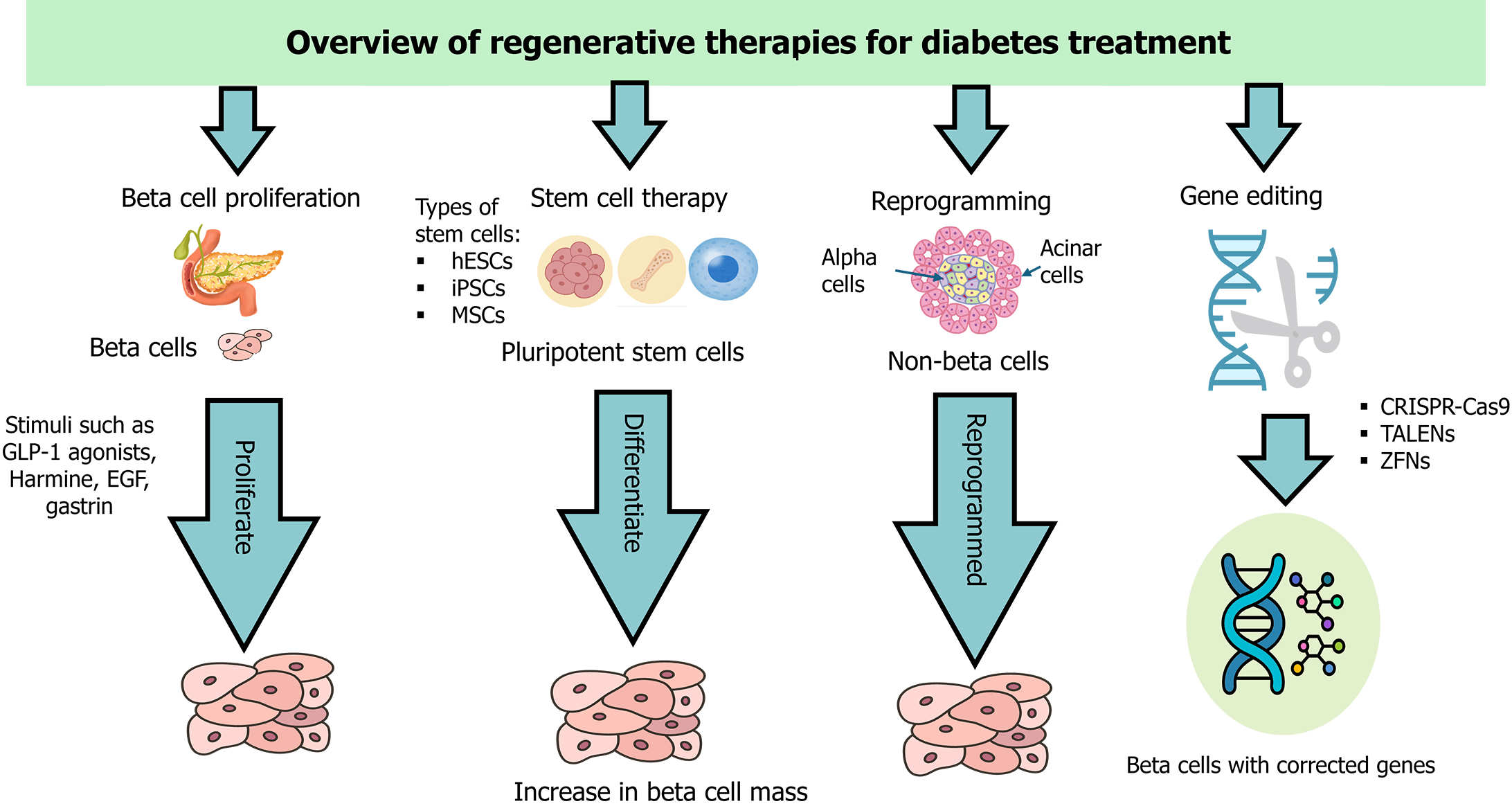
Figure 3 Overview of regenerative therapies for diabetes treatment.
Cas9: CRISPR-associated protein 9; CRISPR: Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; hESCs: Human embryonic stem cells; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; iPSCs: Induced pluripotent stem cells; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; TALENs: Transcription activator-like effector nucleases; ZFNs: Zinc finger nucleases.
- Citation: Abdalla MMI. Advancing diabetes management: Exploring pancreatic beta-cell restoration’s potential and challenges. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(40): 4339-4353
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i40/4339.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i40.4339