©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2024; 30(36): 4036-4043
Published online Sep 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i36.4036
Published online Sep 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i36.4036
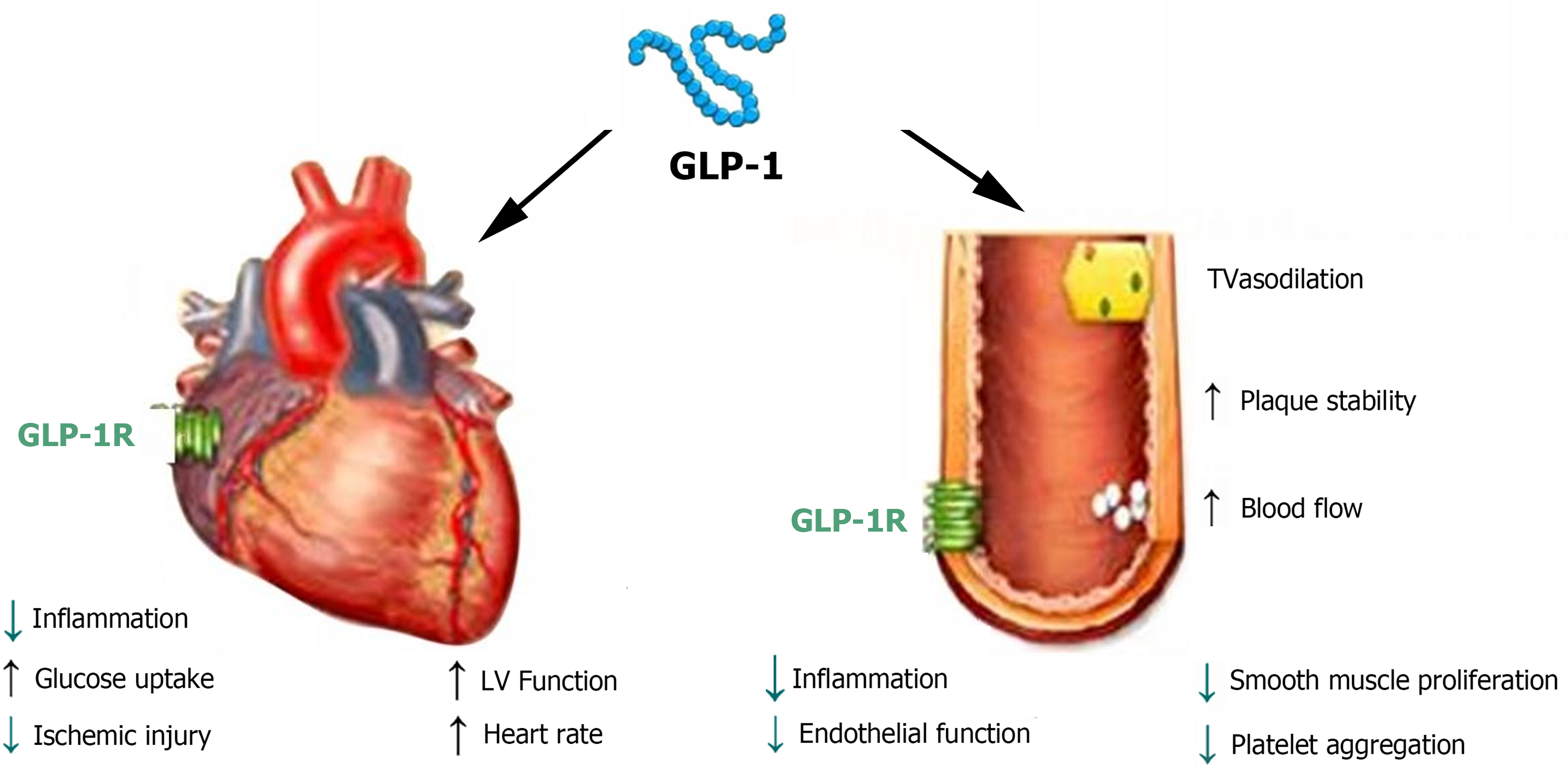
Figure 1 Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors are expressed in both cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells, exerting direct and indirect effects on the heart and blood vessels.
GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP-1R: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; LV: Left ventricle; TV: Tricuspid valve.
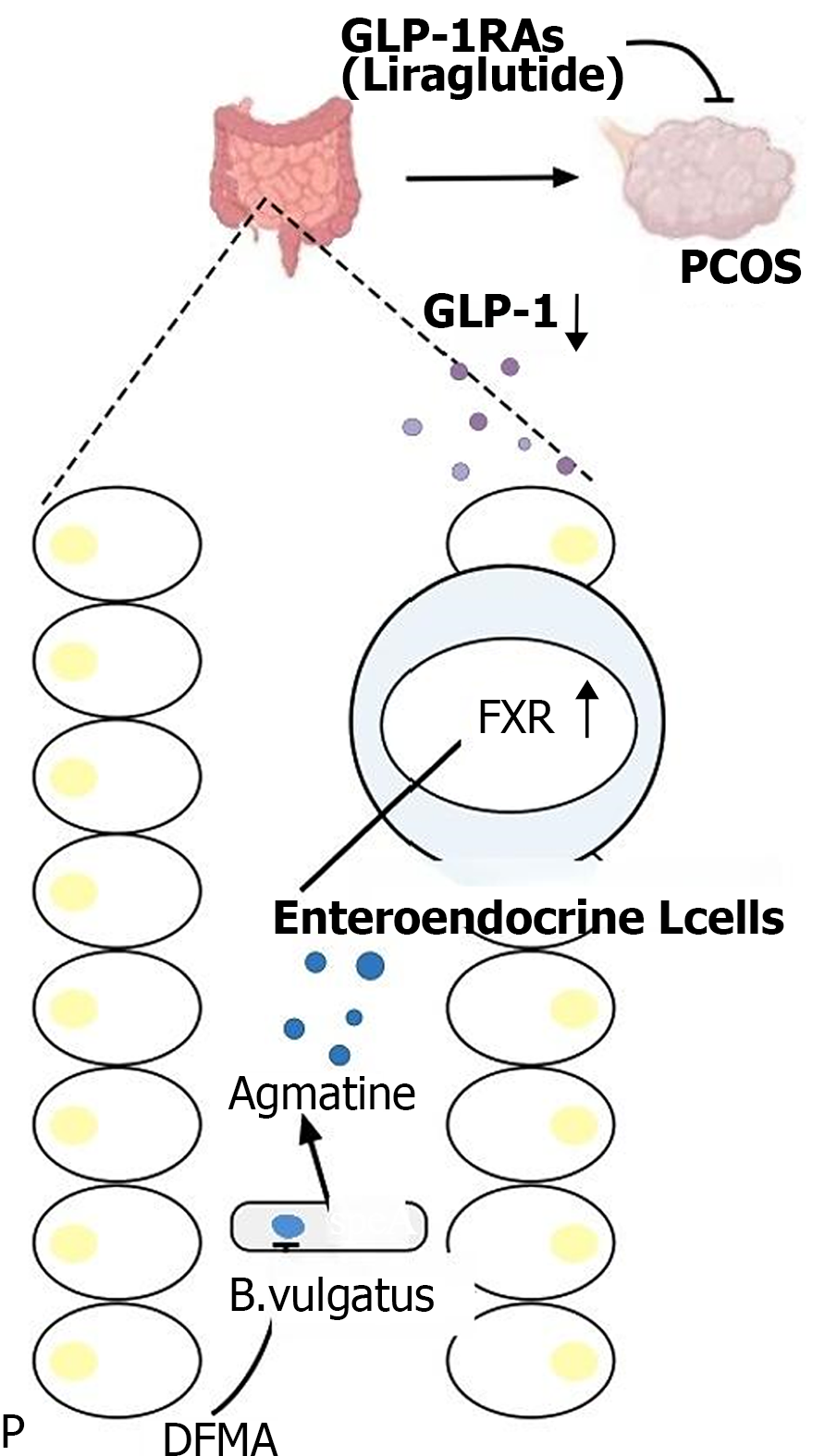
Figure 2 Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists improve ovarian dysfunction in a mouse model of polycystic ovary syndrome.
GLP-1RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; PCOS: Polycystic ovary syndrome; DFMA: Difluoro methylarginine.
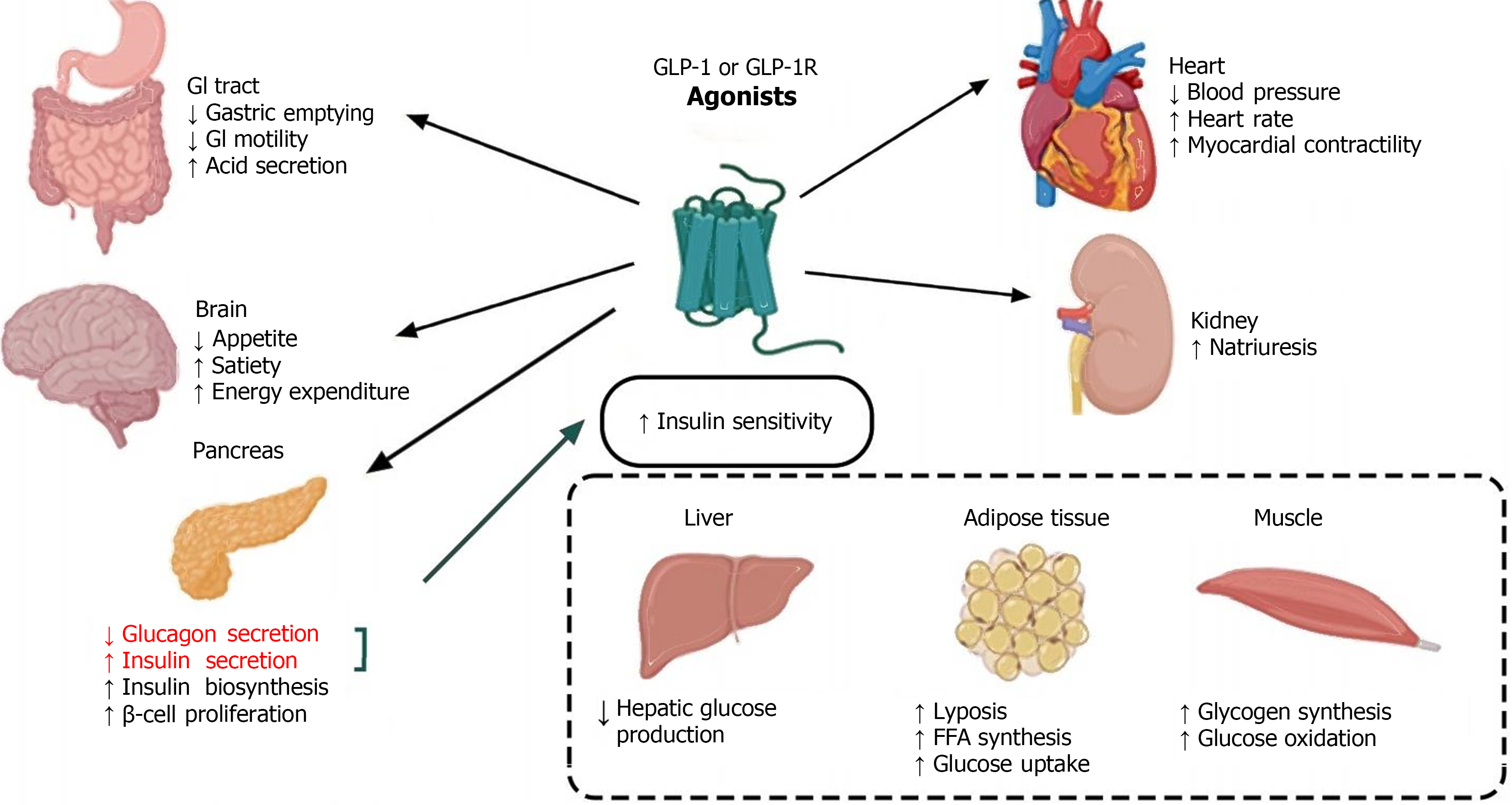
Figure 3 Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists are extensively involved in various systemic diseases and hold therapeutic potential for a range of conditions.
GLP-1R: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; GI: Gastrointestinal.
- Citation: Kong MW, Yu Y, Wan Y, Gao Y, Zhang CX. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: Exploring the mechanisms from glycemic control to treatment of multisystemic diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(36): 4036-4043
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i36/4036.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i36.4036