©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2024; 30(2): 146-157
Published online Jan 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i2.146
Published online Jan 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i2.146
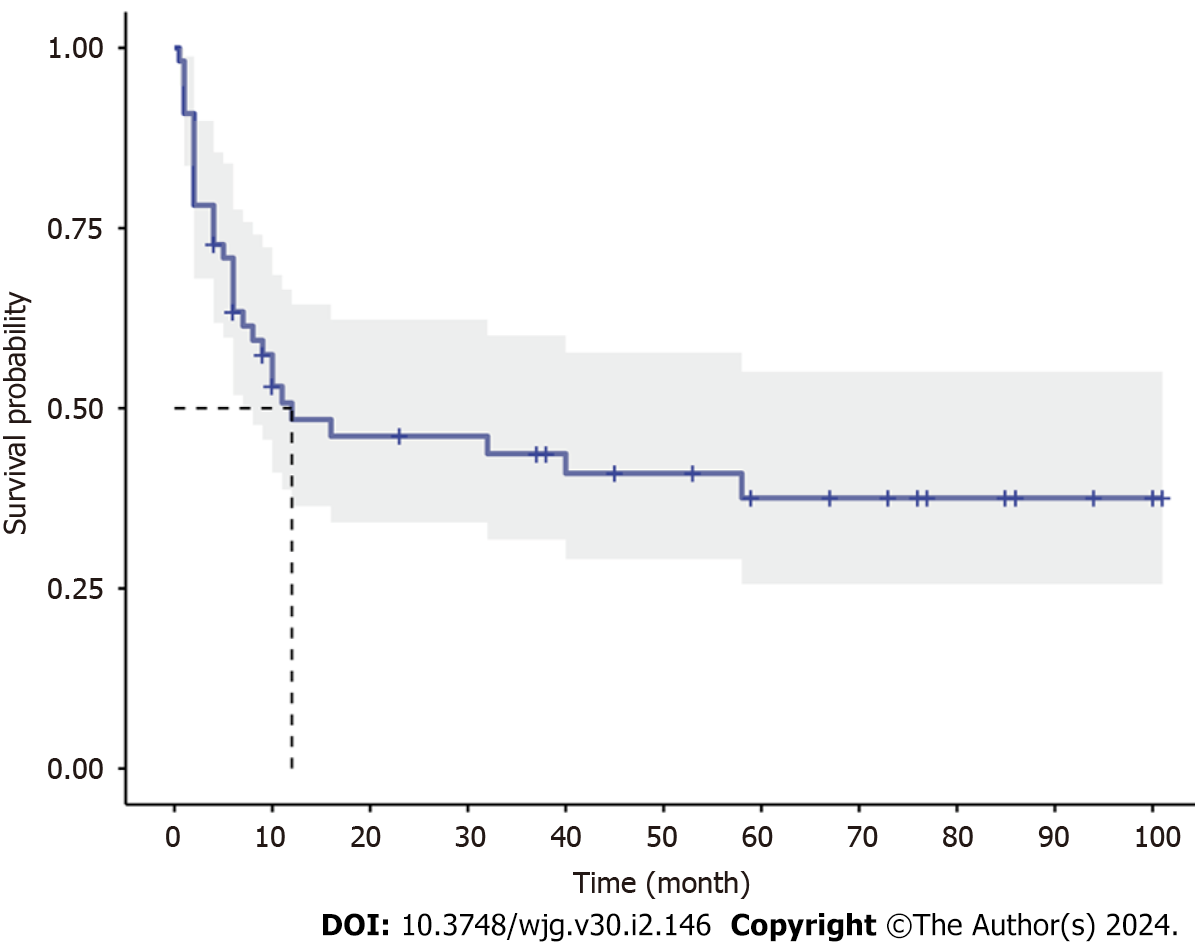
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier survival curve of the recurrence-free survival for all eosinophilic gastroenteritis patients (median relapse-free survival time: 12 mo).
6-mo, 1-year and 2-year relapse-free survival rate were 63.4%, 48.4% and 46.1% respectively.
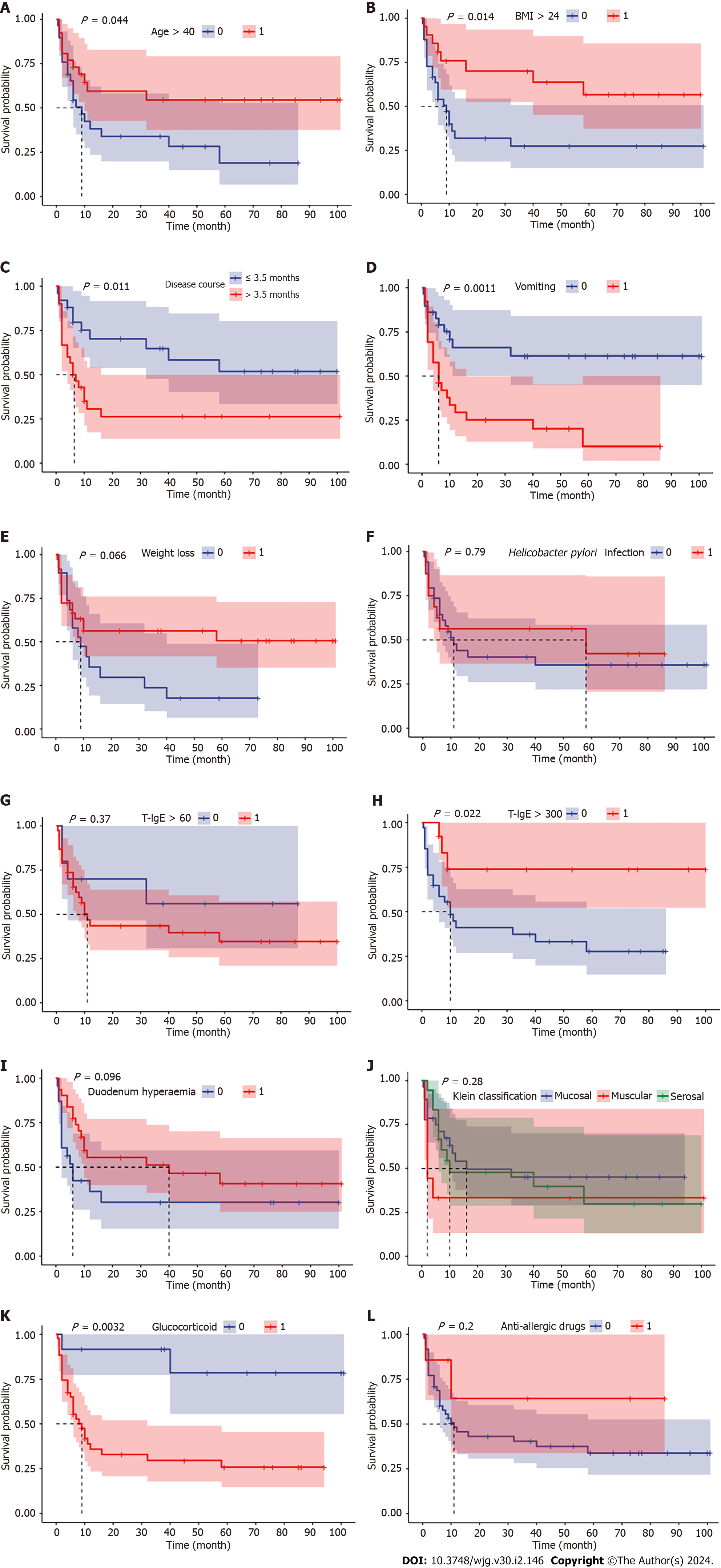
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier survival curves according to different prognostic factors for disease relapse.
Age < 40, body mass index (BMI) < 24, disease duration > 3.5 mo, vomiting, immunoglobin E (IgE) level < 300 KU/L, and glucocorticoid treatment showed a statistical difference between the relapse group and relapse-free group. Other variables included weight loss, Hp infection, IgE level > 60 KU/L, duodenal hyperaemia, Klein classification and anti-allergic drugs. A: Age, P = 0.044; B: BMI, P = 0.014; C: Disease duration, P = 0.011; D: Vomiting, P = 0.0011; E: Weight loss, P = 0.066; F: Helicobacter pylori infection, P = 0.790; G: T-IgE > 60, P = 0.370; H: T-IgE > 300, P = 0.022; I: Duodenal hyperaemia, P = 0.096; J: Klein classification, P = 0.280; K: Glucocorticoid, P = 0.0032; L: Anti-allergic drugs, P = 0.200.
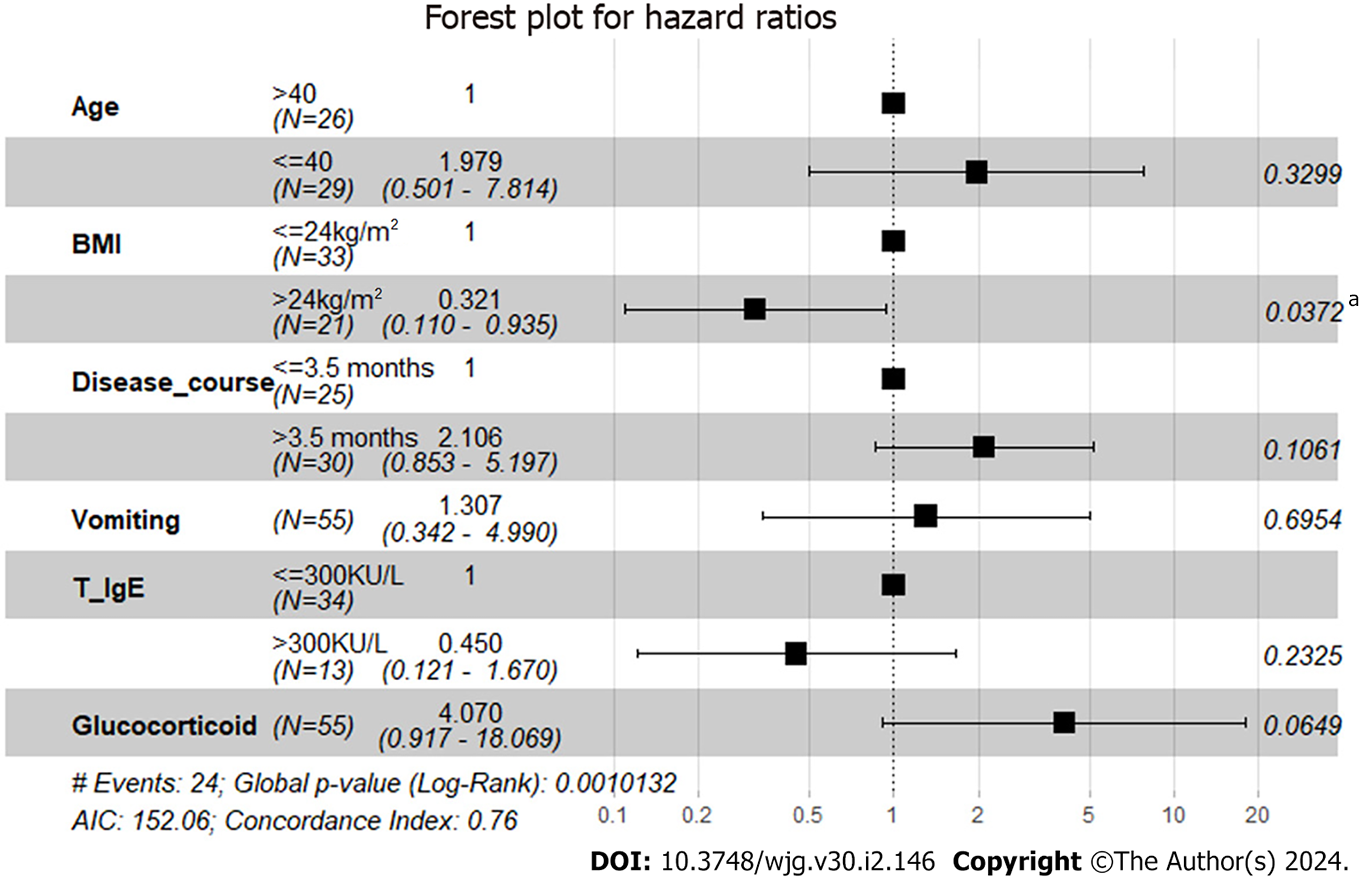
Figure 3 Forest plot for hazard ratios for predictors included in the Cox regression model.
BMI: Body mass index; T_IgE: Total serum immunoglobin E. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Li KW, Ruan GC, Liu S, Xu TM, Ma Y, Zhou WX, Liu W, Zhao PY, Du ZR, Li J, Li JN. Long-term prognosis and its associated predictive factors in patients with eosinophilic gastroenteritis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(2): 146-157
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i2/146.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i2.146