Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2023; 29(6): 1109-1122
Published online Feb 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1109
Published online Feb 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1109
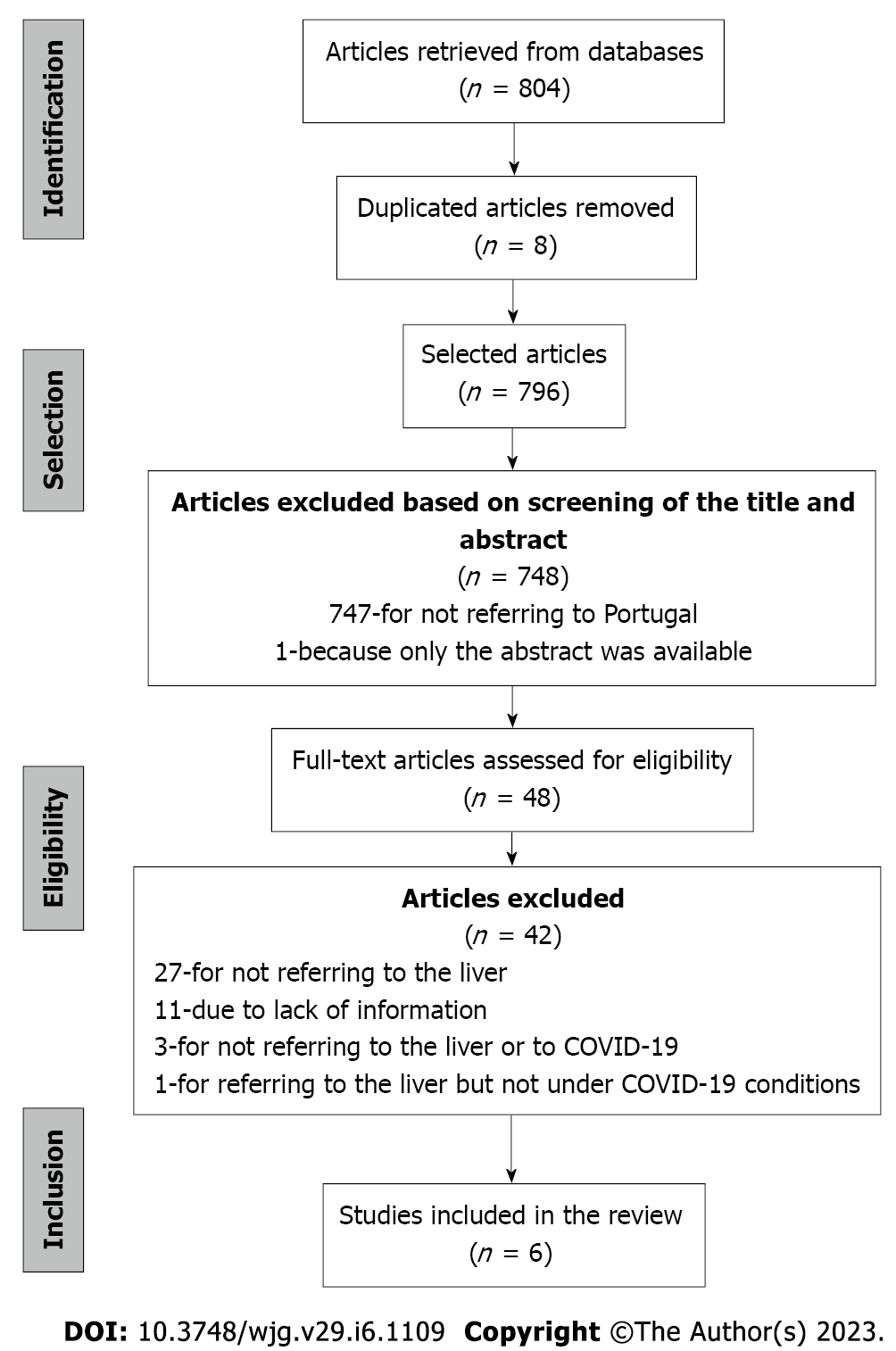
Figure 1 Flowchart of the studies selection process.
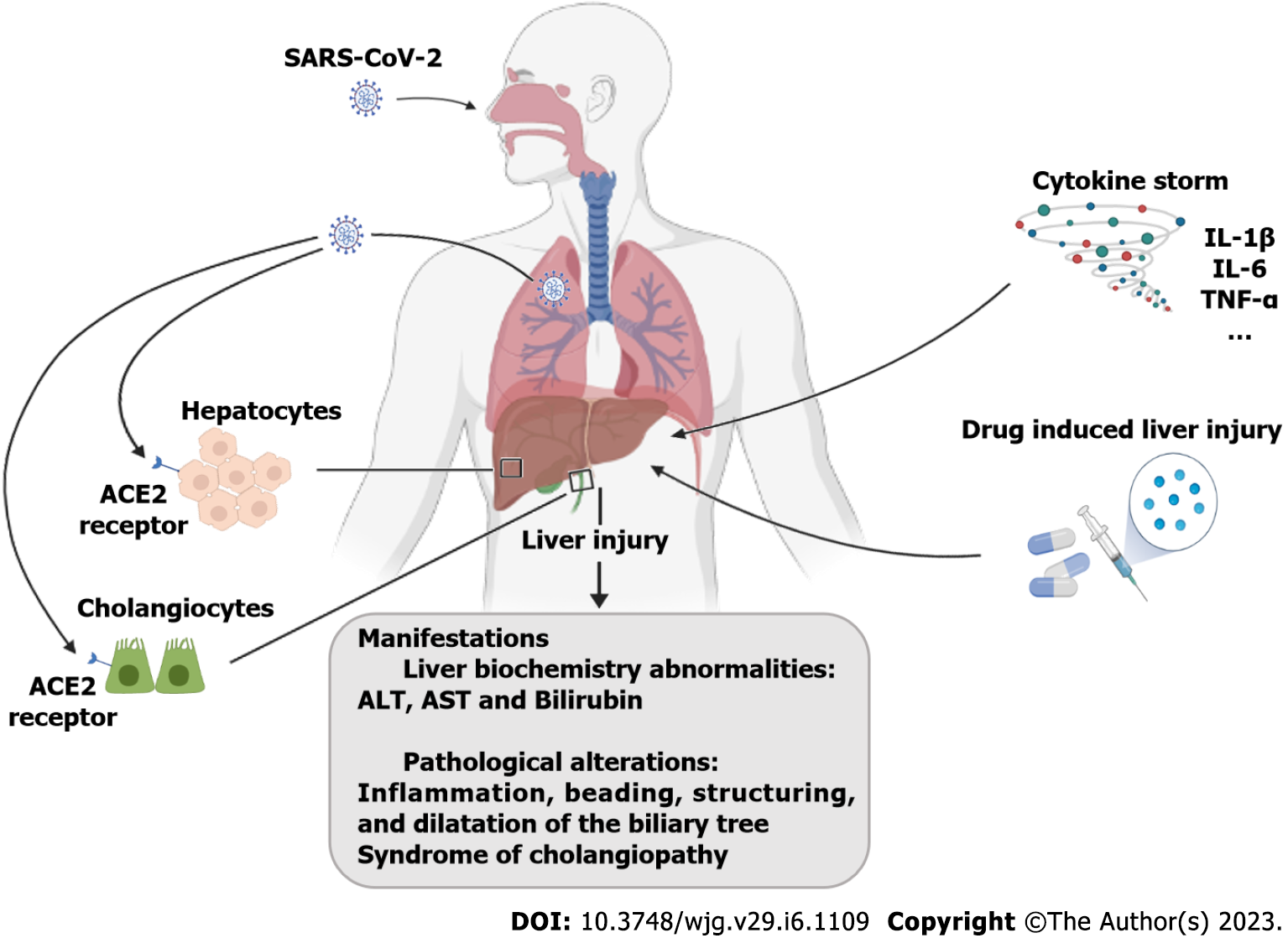
Figure 2 Mechanisms that may lead to liver injury in individuals with coronavirus disease 2019.
An infection by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 may result in liver injury due to viral entry through angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors on hepatocytes and cholangiocytes, pharmacological treatment, or an exaggerated immune response. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
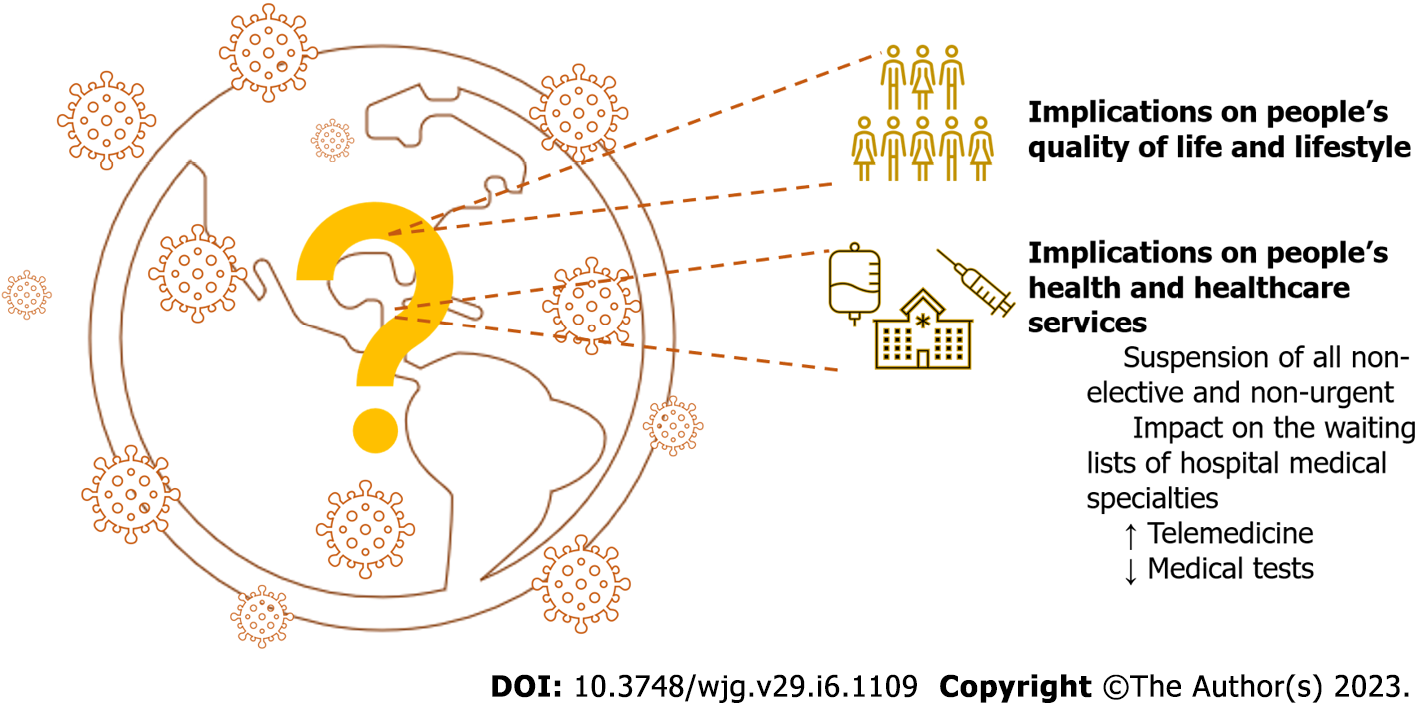
Figure 3 Alterations in people's quality of life and healthcare systems due to coronavirus disease 2019.
- Citation: Fernandes S, Sosa-Napolskij M, Lobo G, Silva I. Relation of COVID-19 with liver diseases and their impact on healthcare systems: The Portuguese case. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(6): 1109-1122
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i6/1109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1109