©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2023; 29(5): 890-903
Published online Feb 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i5.890
Published online Feb 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i5.890
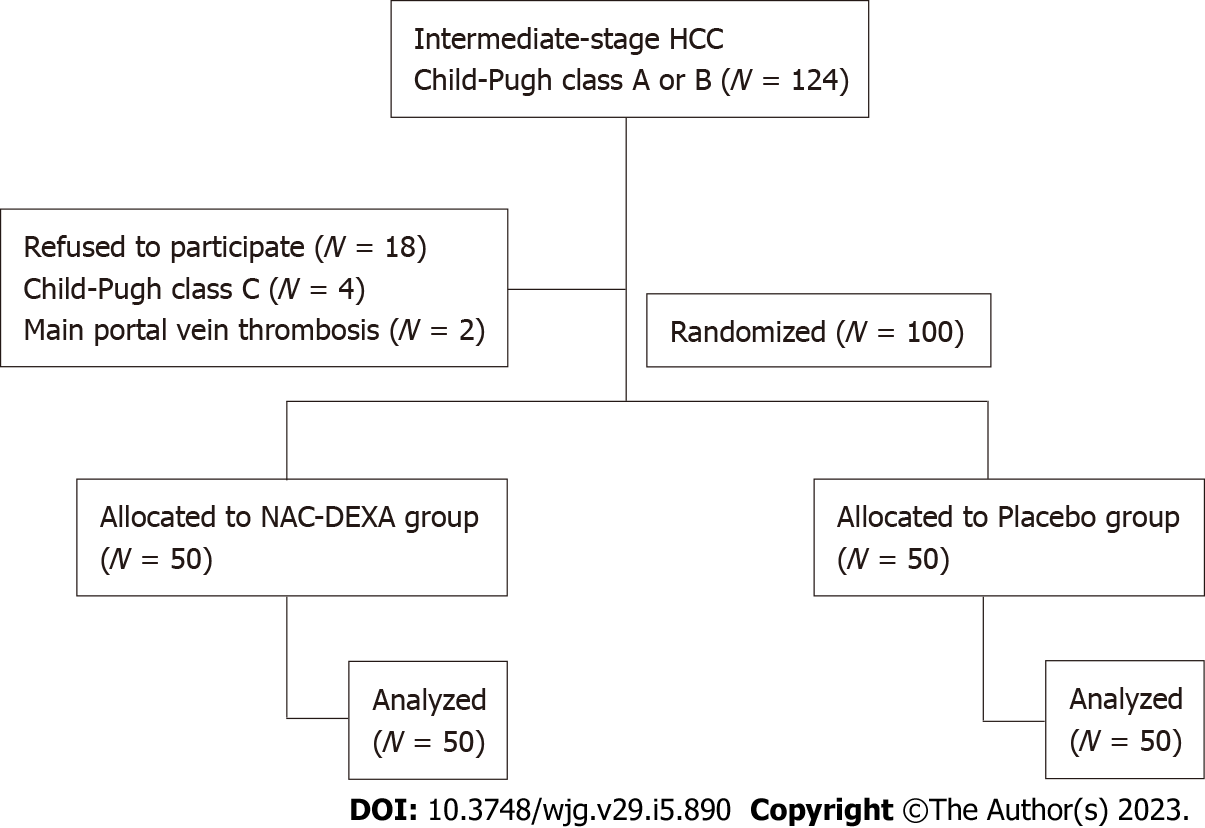
Figure 1 Flow chart of patient screened, recruited, and analyzed in the study (consort diagram).
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; NAC: N-acetylcysteine; DEXA: Dexamethasone.
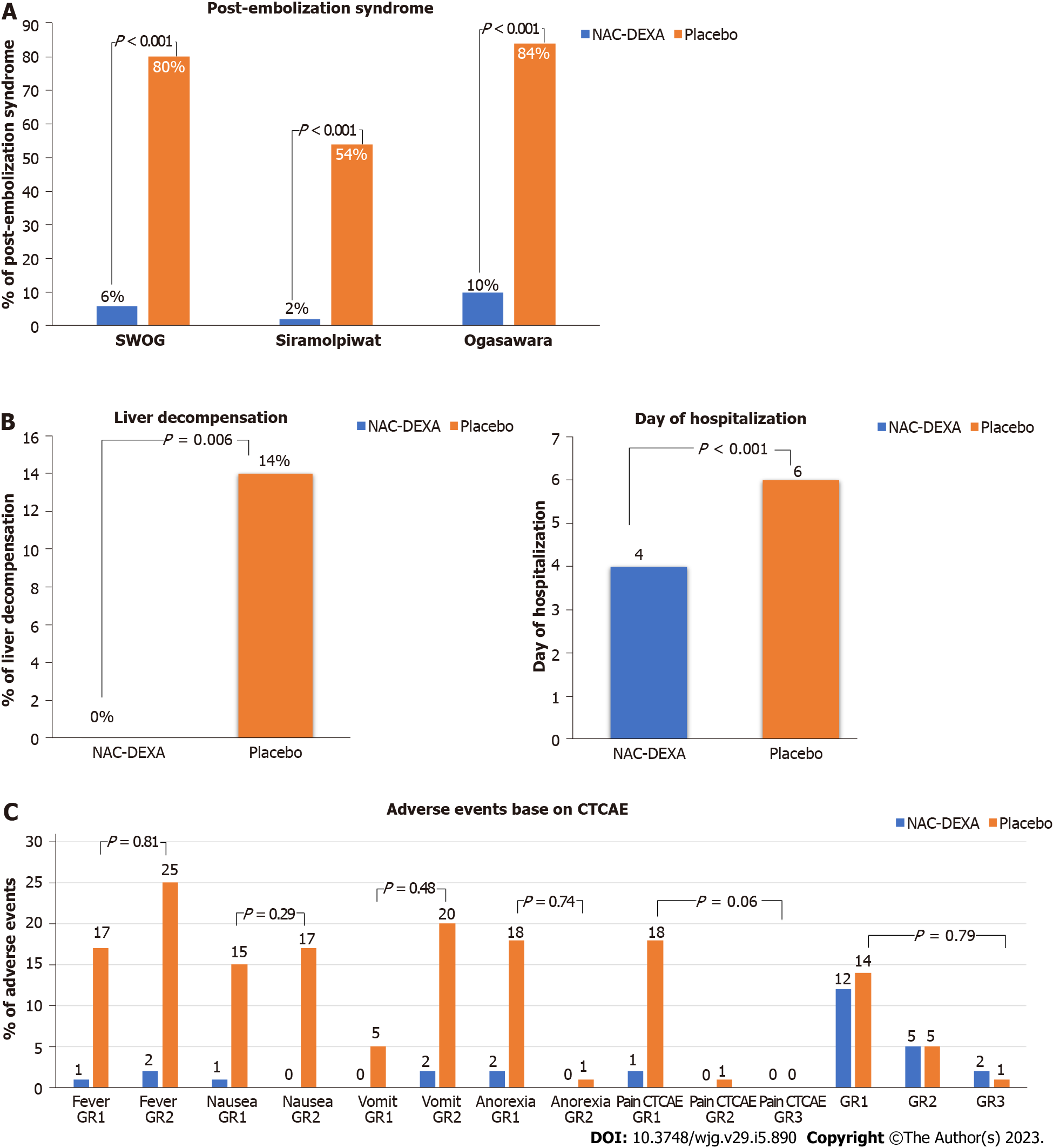
Figure 2 Post-embolization syndrome, liver decompensation and length of hospital stay and adverse events after conventional transarterial chemoembolization.
A: Post-embolization syndrome after conventional transarterial chemoembolization; B: Post-conventional transarterial chemoembolization liver decompensation and length of hospital stay; C: Post-conventional transarterial chemoembolization adverse events. NAC: N-acetylcysteine; DEXA: Dexamethasone.
- Citation: Simasingha N, Tanasoontrarat W, Claimon T, Sethasine S. Efficacy of dexamethasone and N-acetylcysteine combination in preventing post-embolization syndrome after transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(5): 890-903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i5/890.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i5.890