©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2023; 29(37): 5327-5338
Published online Oct 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i37.5327
Published online Oct 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i37.5327
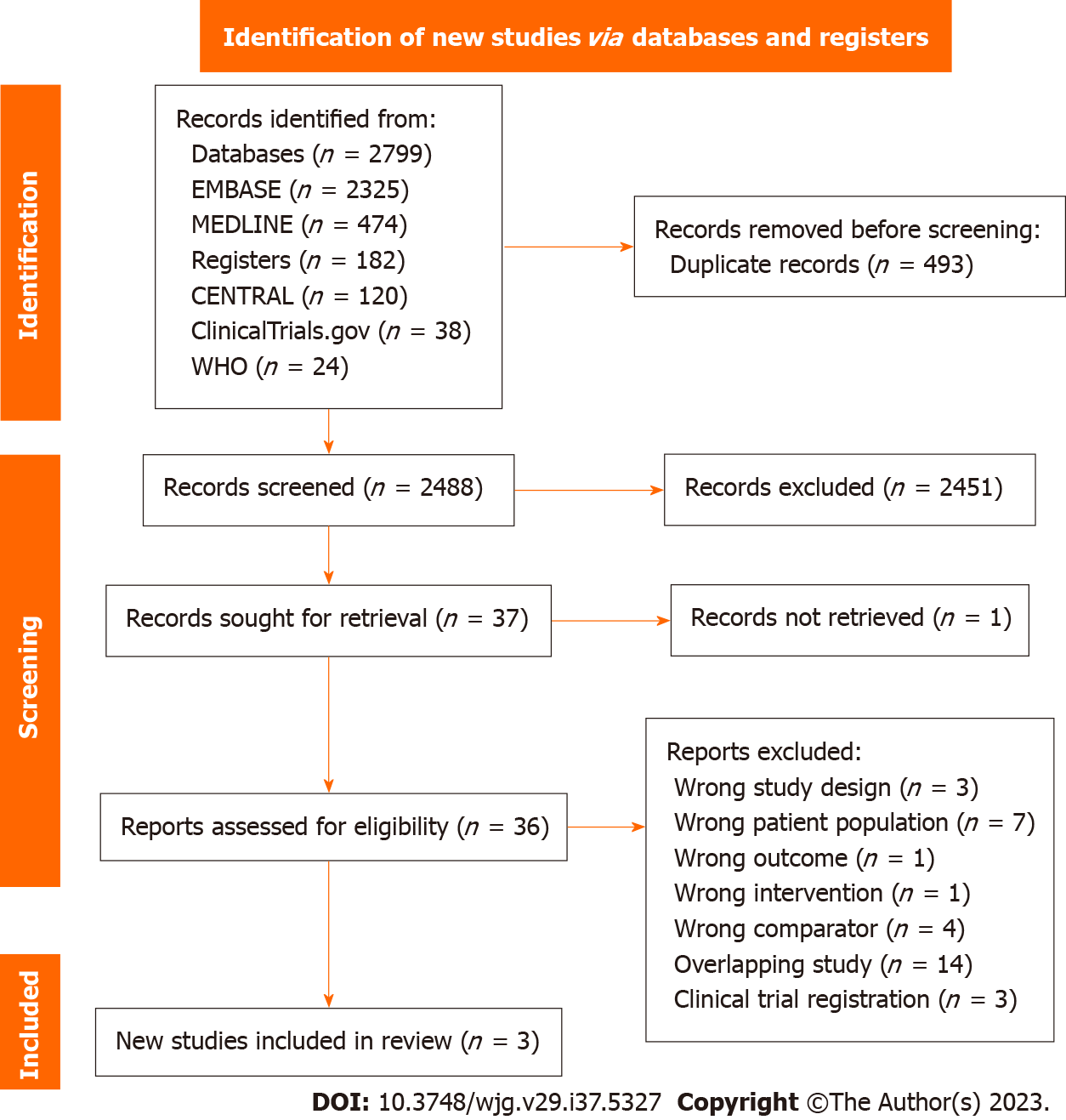
Figure 1 PRISMA flow diagram of study selection.
WHO: World health organization.
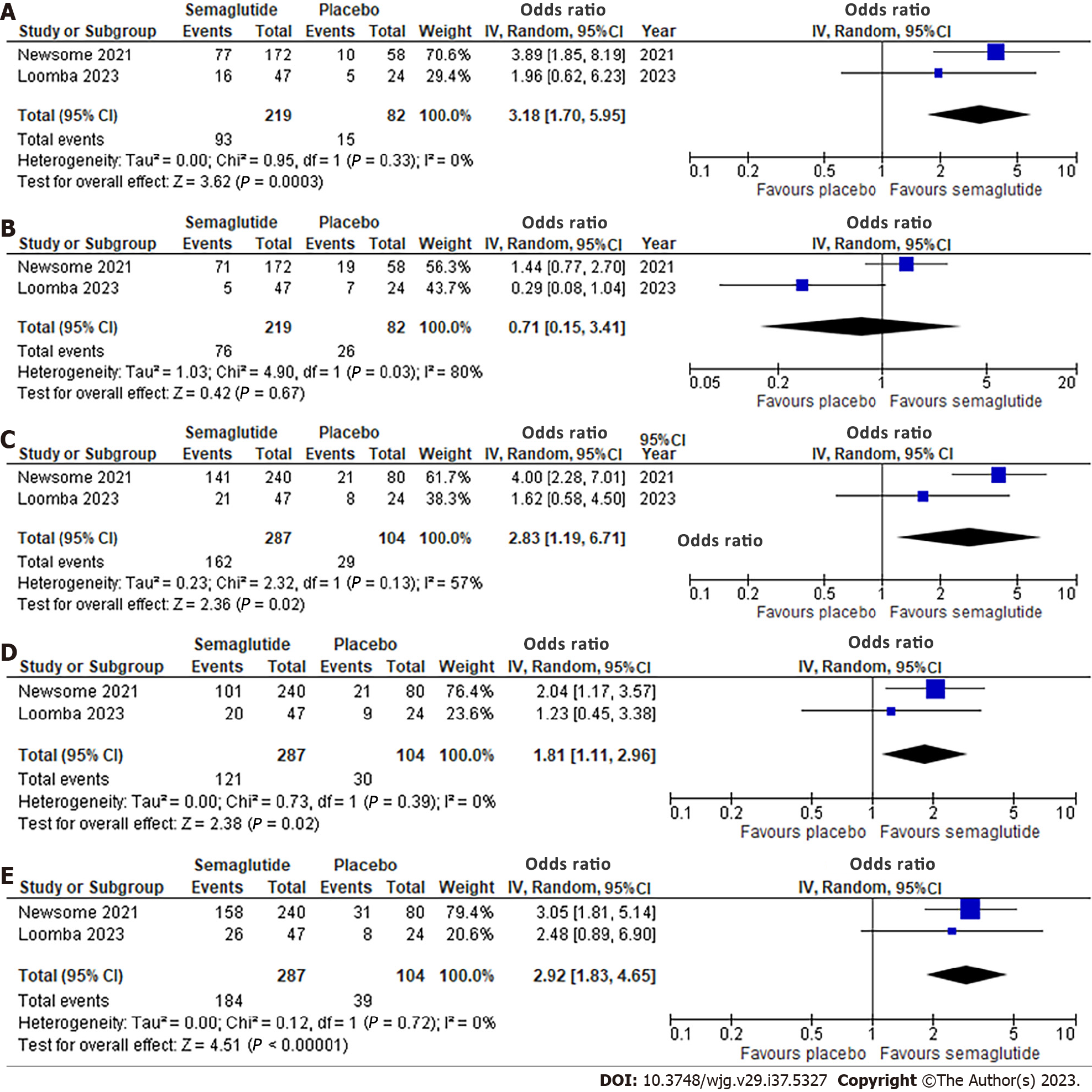
Figure 2 Effect of semaglutide on histologic parameters.
A: Resolution of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) with no worsening of liver fibrosis; B: Improvement in liver fibrosis stage without worsening of NASH; C: Improvement in steatosis; D: Improvement in lobular inflammation; E: Improvement in hepatocellular ballooning. 95%CI: 95% confidence intervals.
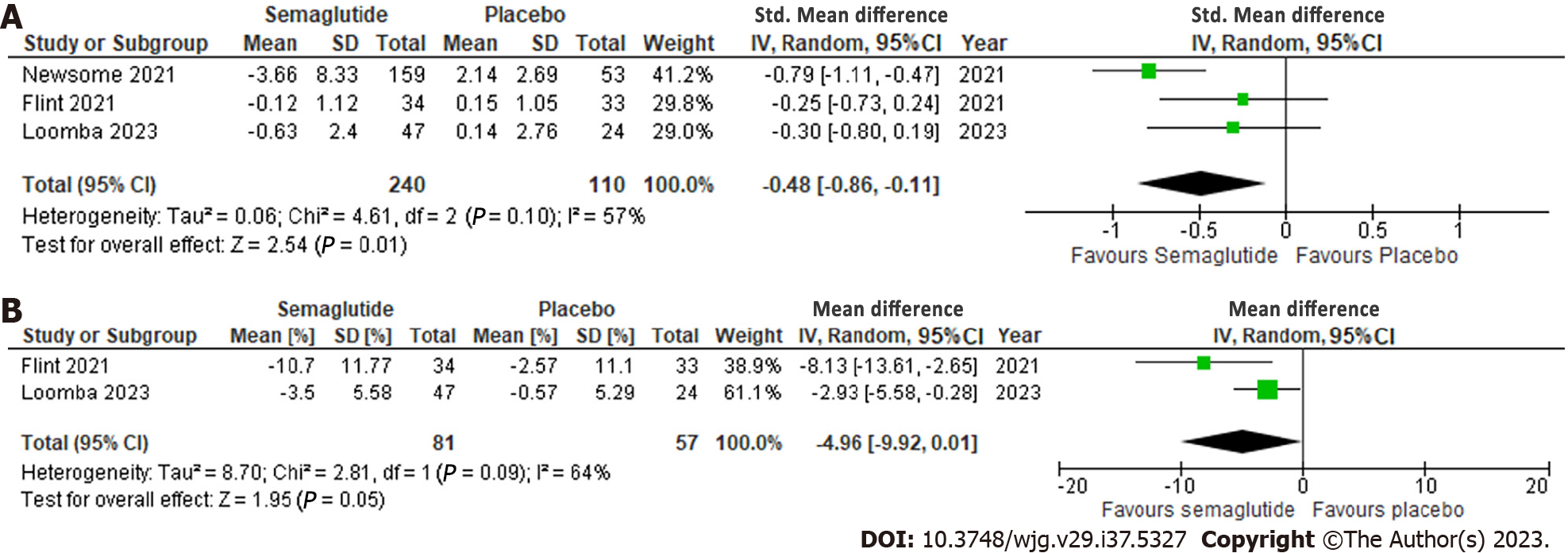
Figure 3 Effect of semaglutide on radiologic parameters.
A: Liver stiffness assessed by magnetic resonance enterography or Fibroscan; B: Liver steatosis assessed by MRI proton density fat fraction. 95%CI: 95% confidence intervals.
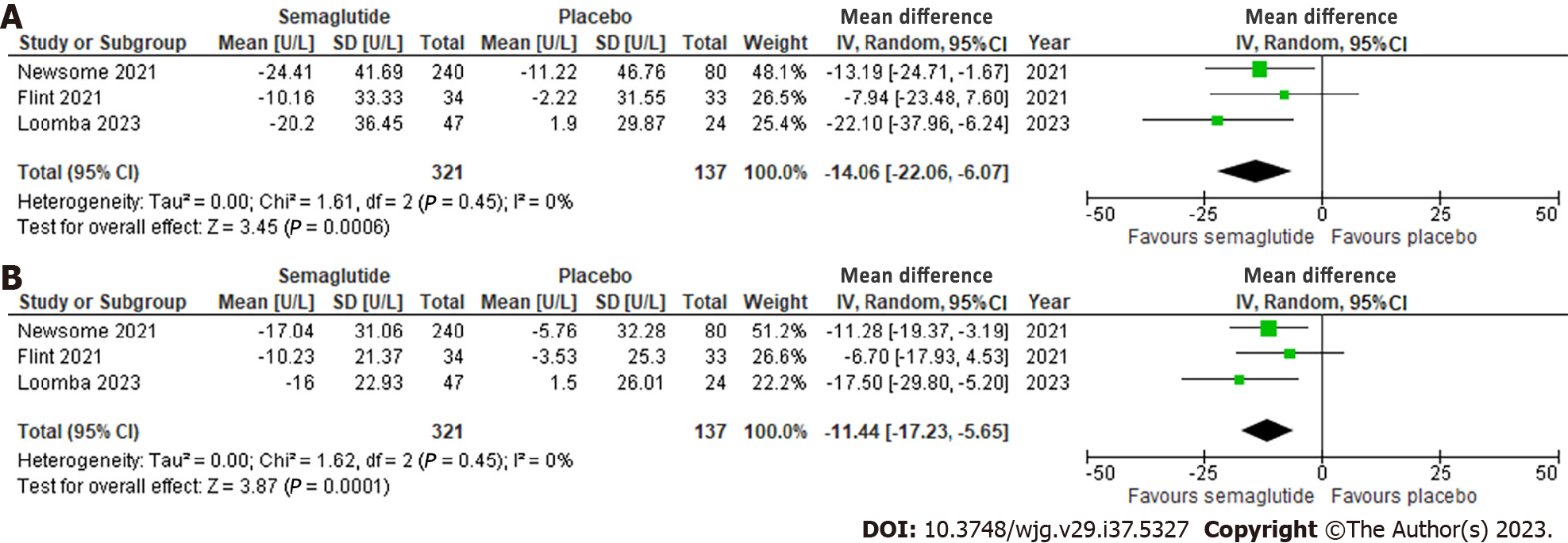
Figure 4 Effect of semaglutide on liver enzymes.
A: Alanine aminotransferase; B: Aspartate aminotransferase. 95%CI: 95% confidence intervals.
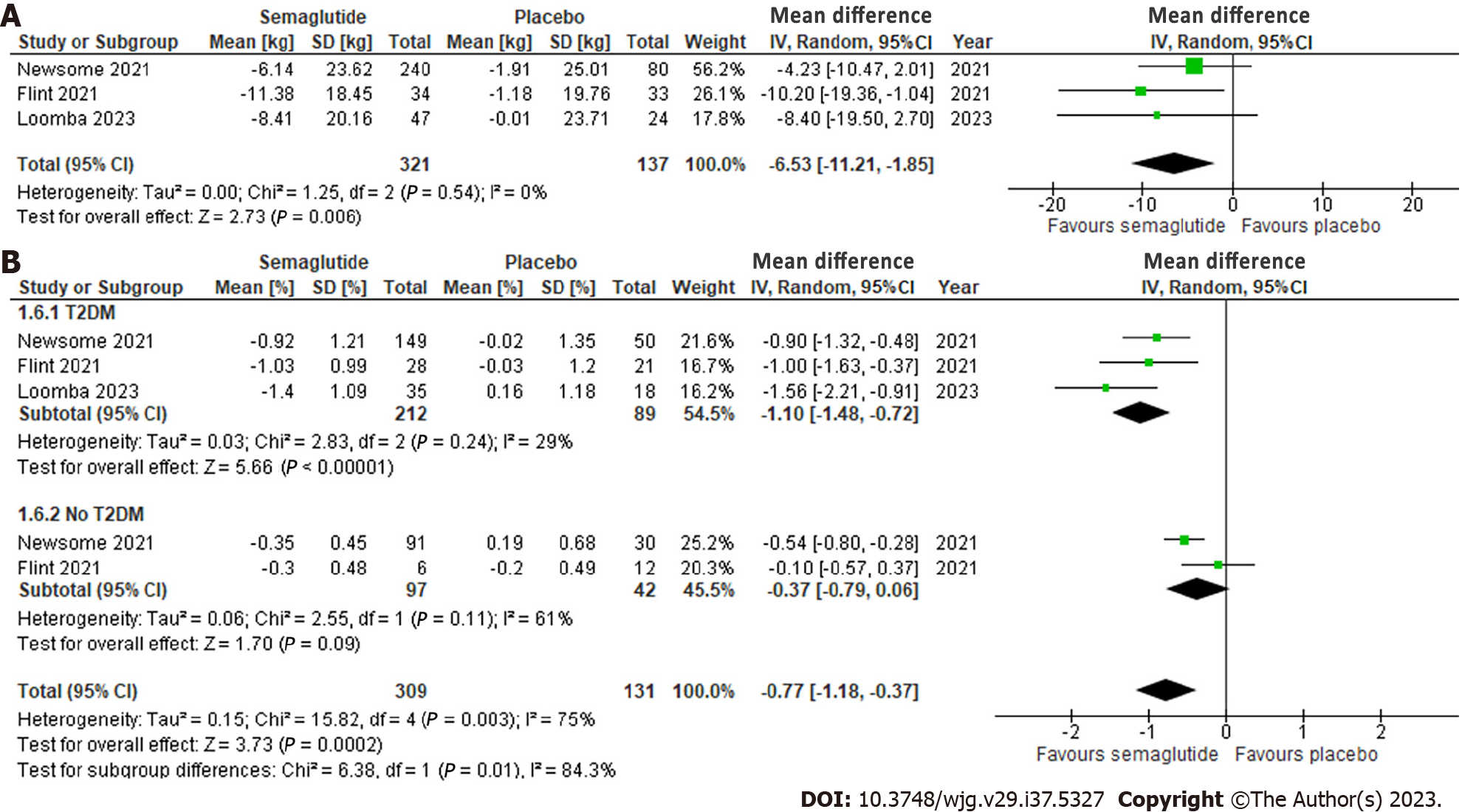
Figure 5 Effect of semaglutide on cardiometabolic parameters.
A: Body weight; B: HgA1c in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) vs without T2DM. 95%CI: 95% confidence intervals.
Figure 6 Adverse events with semaglutide.
A: Gastrointestinal related side effects; B: Serious adverse events. 95%CI: 95% confidence intervals.
- Citation: Zhu K, Kakkar R, Chahal D, Yoshida EM, Hussaini T. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(37): 5327-5338
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i37/5327.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i37.5327