©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2023; 29(30): 4671-4684
Published online Aug 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i30.4671
Published online Aug 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i30.4671
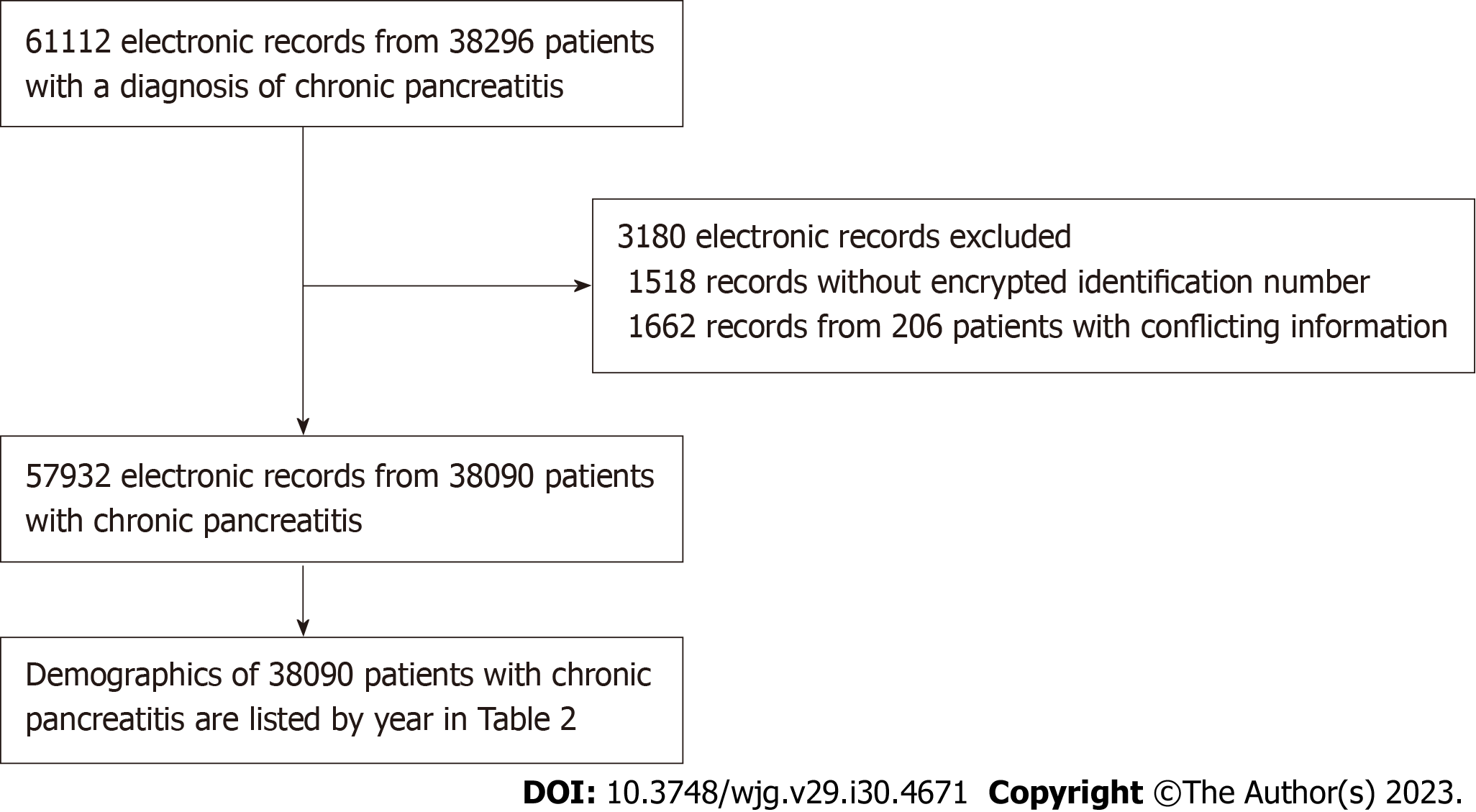
Figure 1 Flowchart of the inclusion and exclusion processes.
A total of 61112 electronic records from 38296 patients with a diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis were retrieved from the Health Information Center of Sichuan Province. A total of 3180 records were excluded due to missing encrypted patient identification numbers (1518 records) and conflicting information (1662 records from 206 individuals). A total of 57932 electronic records from 38090 unique patients with chronic pancreatitis were ultimately included in this study.
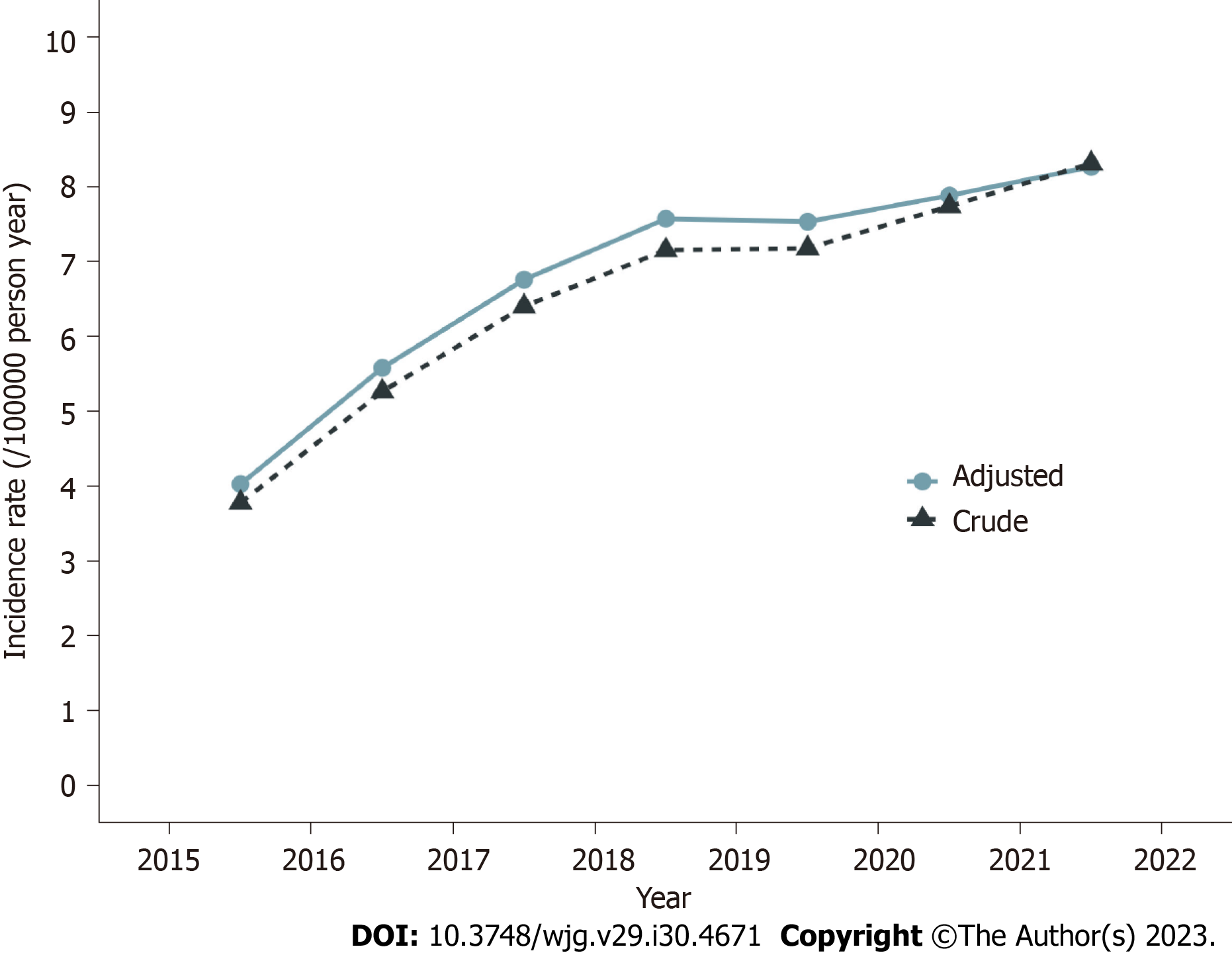
Figure 2 Incidence trends of chronic pancreatitis.
Crude and age-adjusted annual incidence trends of chronic pancreatitis from 2015 to 2021 in Sichuan Province, China (per 100000 person-years).
Figure 3 Sex- and age-grouped incidence of chronic pancreatitis.
A and B: The crude incidence of chronic pancreatitis in the population grouped by sex (A) and age (B) (per 100000 person-years) from 2015 to 2021.
Figure 4 The prevalence of chronic pancreatitis.
A and B: The age distribution of chronic pancreatitis patients (A) and the prevalence of chronic pancreatitis by sex and age groups (B) in 2021.
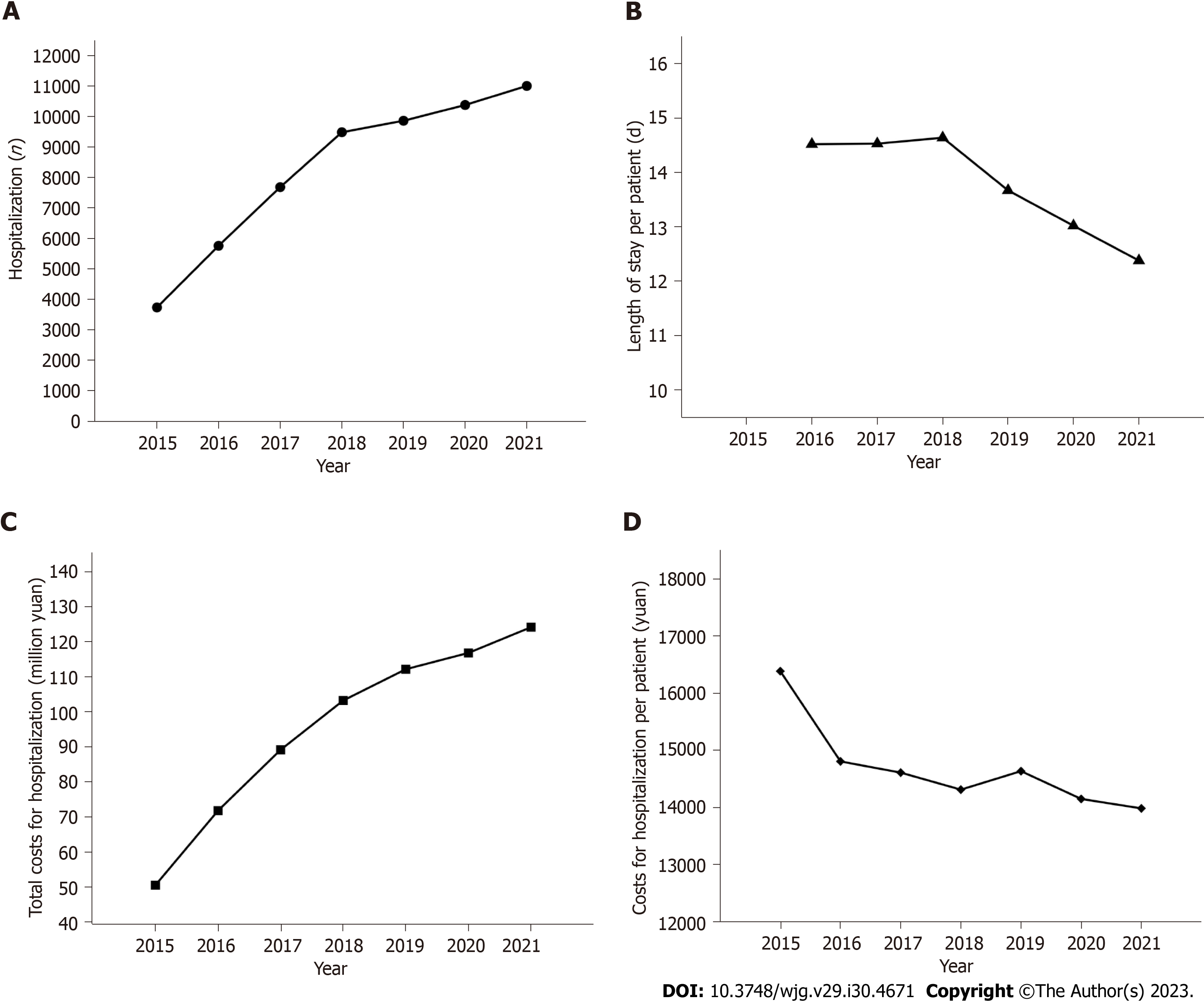
Figure 5 Disease burden of chronic pancreatitis.
A: Annual number of chronic pancreatitis-associated hospitalizations; B: Mean length of stay per patient; C: Total costs for hospitalization; D: Costs for hospitalization per patient. Costs were adjusted by the consumer price index every year to 2021 costs (yuan).
- Citation: Cai QY, Tan K, Zhang XL, Han X, Pan JP, Huang ZY, Tang CW, Li J. Incidence, prevalence, and comorbidities of chronic pancreatitis: A 7-year population-based study. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(30): 4671-4684
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i30/4671.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i30.4671