©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2023; 29(15): 2272-2282
Published online Apr 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2272
Published online Apr 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2272
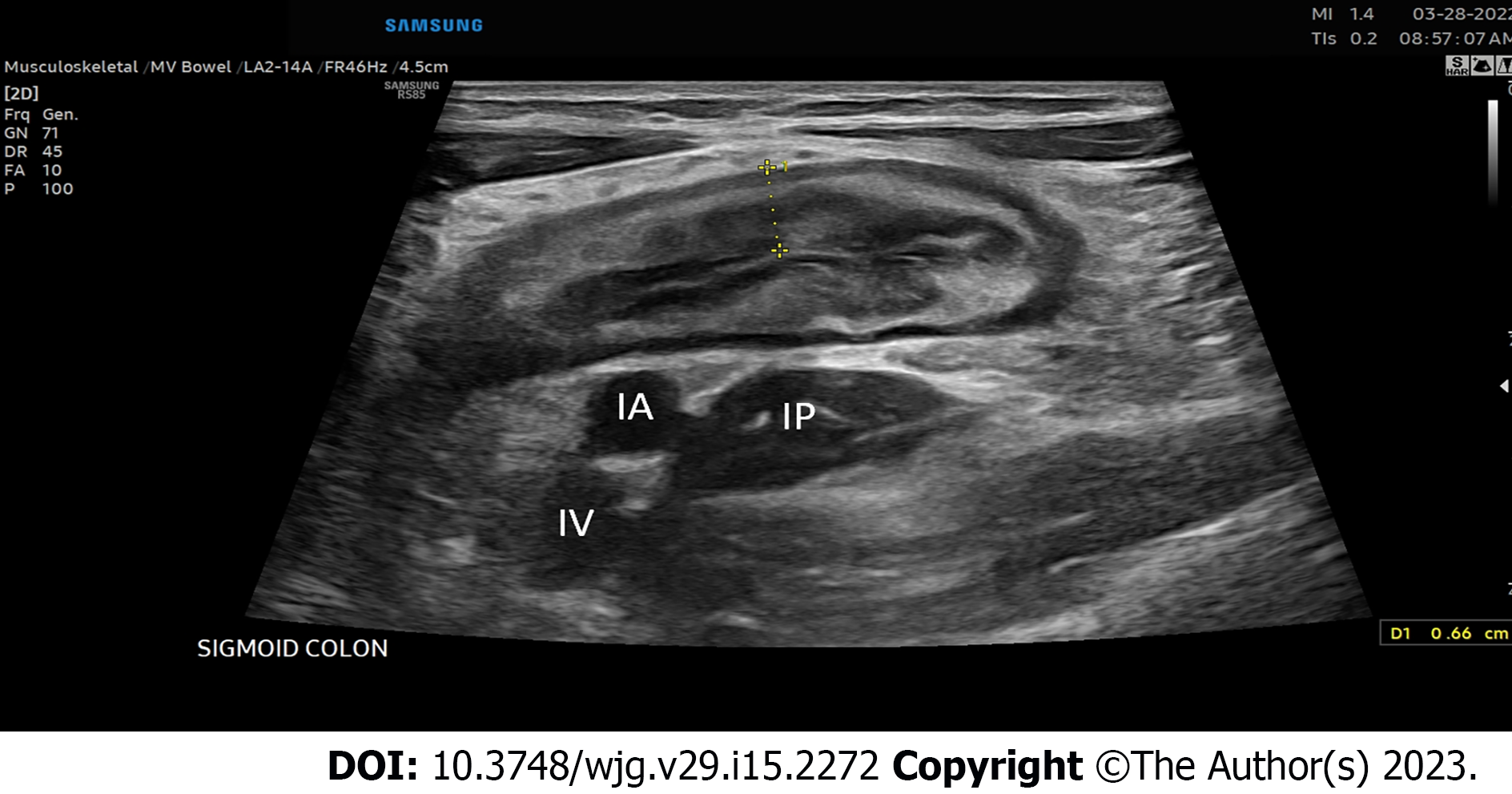
Figure 1 Inflamed sigmoid colon located super to the iliac vessels and iliopsoas muscle in the left lower quadrant of the abdomen.
IA: Iliac artery; IV: Iliac vein; IP: Iliopsoas muscle.
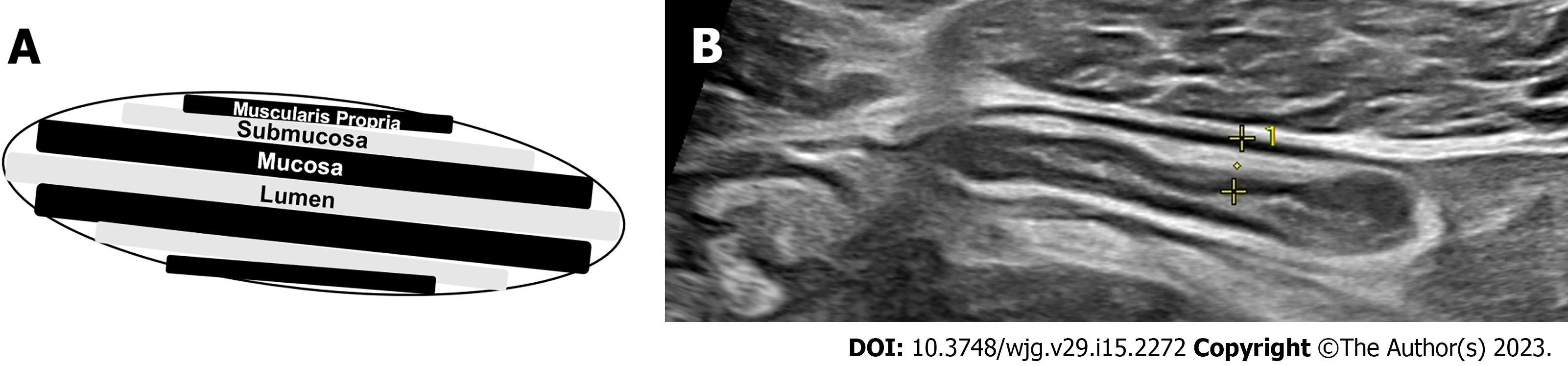
Figure 2 Measurements for bowel wall thickness.
A: Schematic of bowel wall layers; B: Bowel wall thickness measurement in the inflamed terminal ileum, yellow lines indicate the measurement of bowel wall thickness from the lumen-mucosa interface to the muscularis propria-serosal interact.
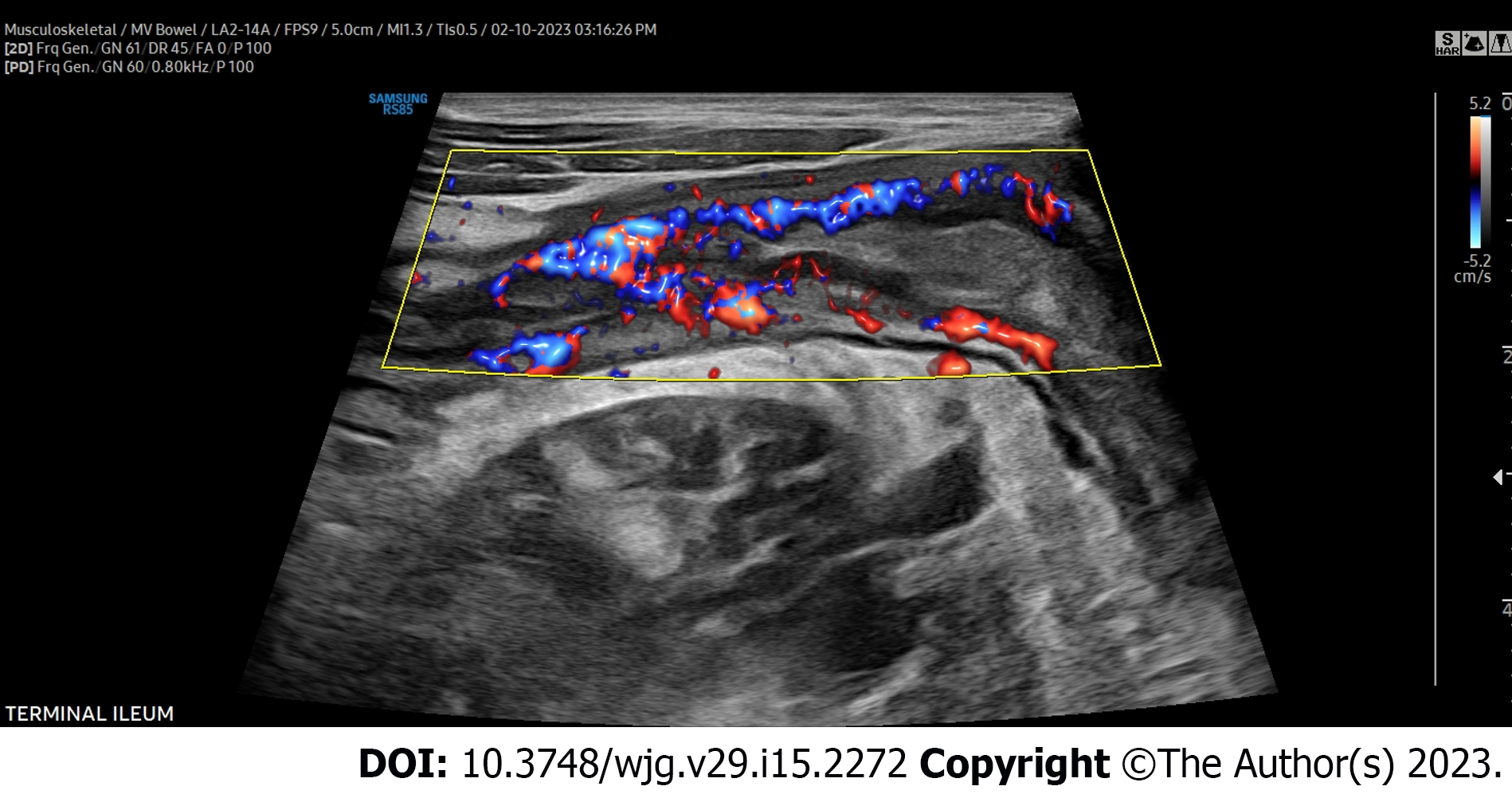
Figure 3 Severe hyperemia assessed by color Doppler signal.
Color Doppler signal graded by the modified Limberg score. Shown here is a modified Limberg score of 3 in the terminal ileum. A score of 0 = absent signal. A score of 1: Short signals inside the bowel. A score of 2: Long signals inside the bowel, and a score of 3: Long signals inside and outside of the bowel.
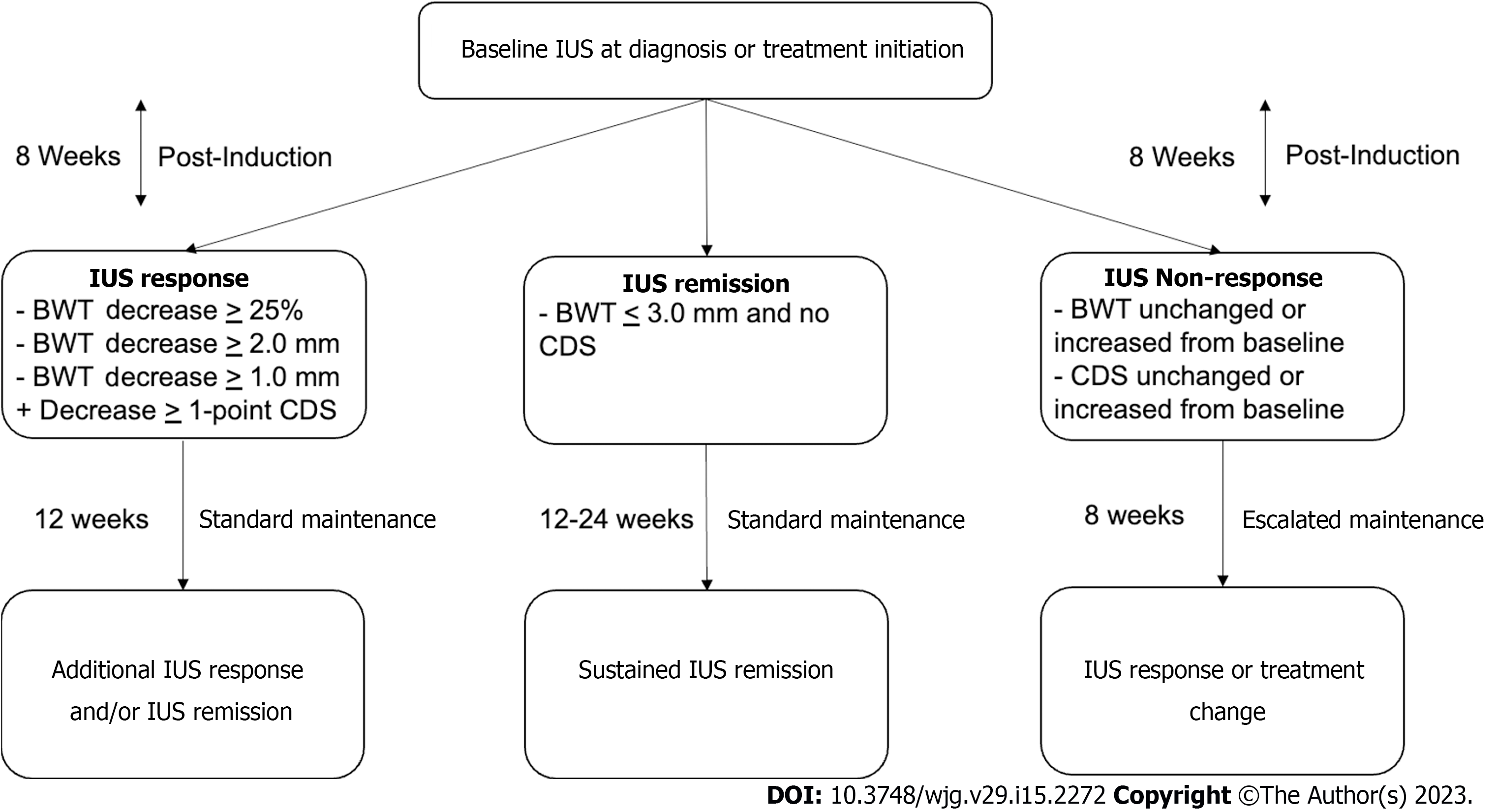
Figure 4 Intestinal ultrasound-based tight control monitoring algorithm.
IUS: Intestinal ultrasound; BWT: Bowel wall thickness; CDS: Color Doppler signal.
- Citation: Dolinger MT, Kayal M. Intestinal ultrasound as a non-invasive tool to monitor inflammatory bowel disease activity and guide clinical decision making. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(15): 2272-2282
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i15/2272.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2272