©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2022; 28(43): 6099-6108
Published online Nov 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i43.6099
Published online Nov 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i43.6099
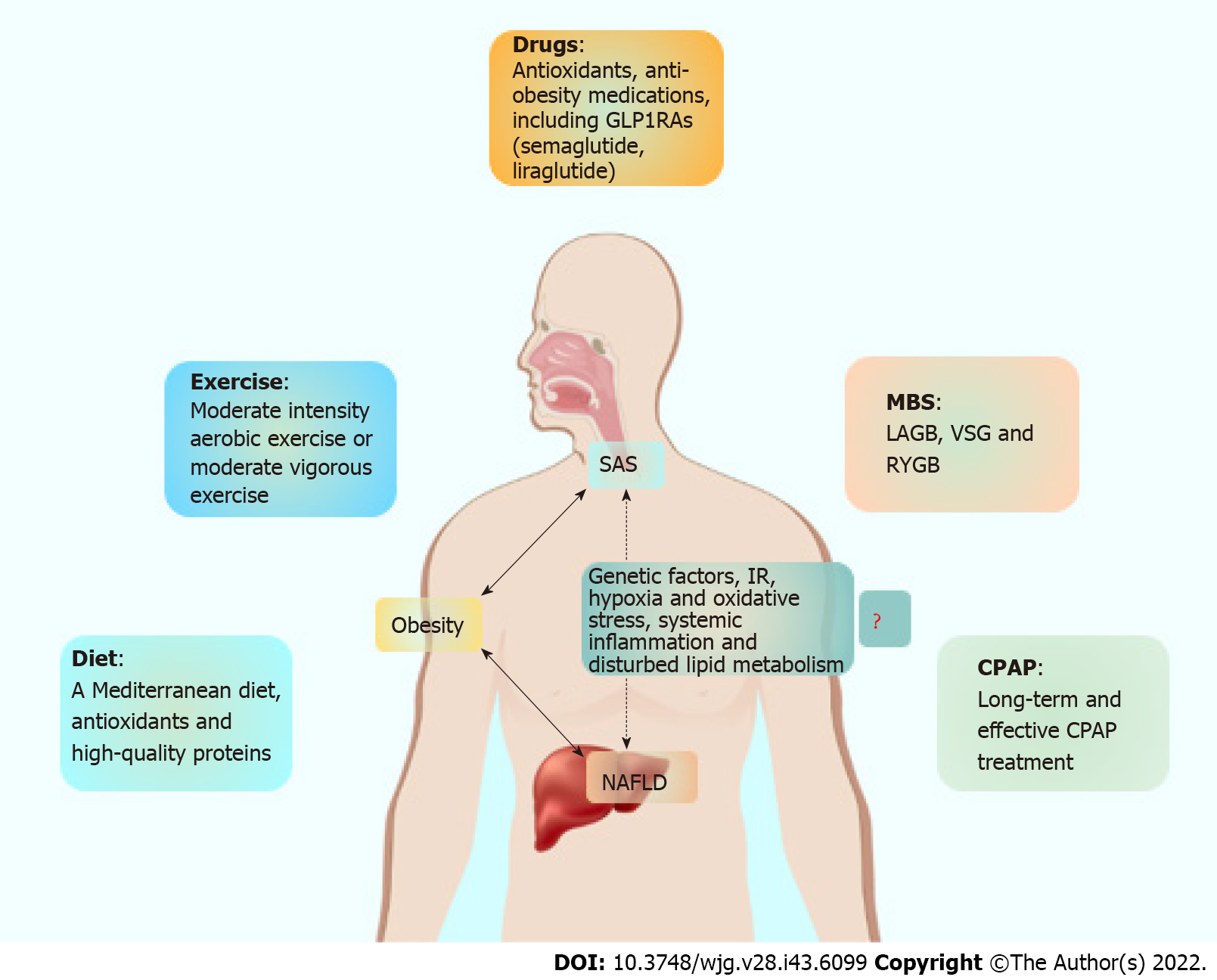
Figure 1 Management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with sleep apnea syndrome.
Healthy lifestyle management remains the current first-line recommendation for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with sleep apnea syndrome (SAS), including diet, exercise, and weight loss. For patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes, drug intervention should also include anti-obesity medications and insulin-sensitizing drugs. Metabolic bariatric surgery can be considered when lifestyle changes and medical interventions are not effective. In addition, continuous positive airway pressure therapy may improve both intermittent hypoxia and liver injury in patients with NAFLD and SAS. MBS: Metabolic bariatric surgery; CPAP: Continuous positive airway pressure; IR: Insulin resistance; LAGB: Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding; VSG: Vertical sleeve gastrectomy; RYGB: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; SAS: Sleep apnea syndrome; NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Citation: Sheng W, Ji G, Zhang L. Management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients with sleep apnea syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(43): 6099-6108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i43/6099.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i43.6099