©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2022; 28(32): 4649-4667
Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4649
Published online Aug 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4649
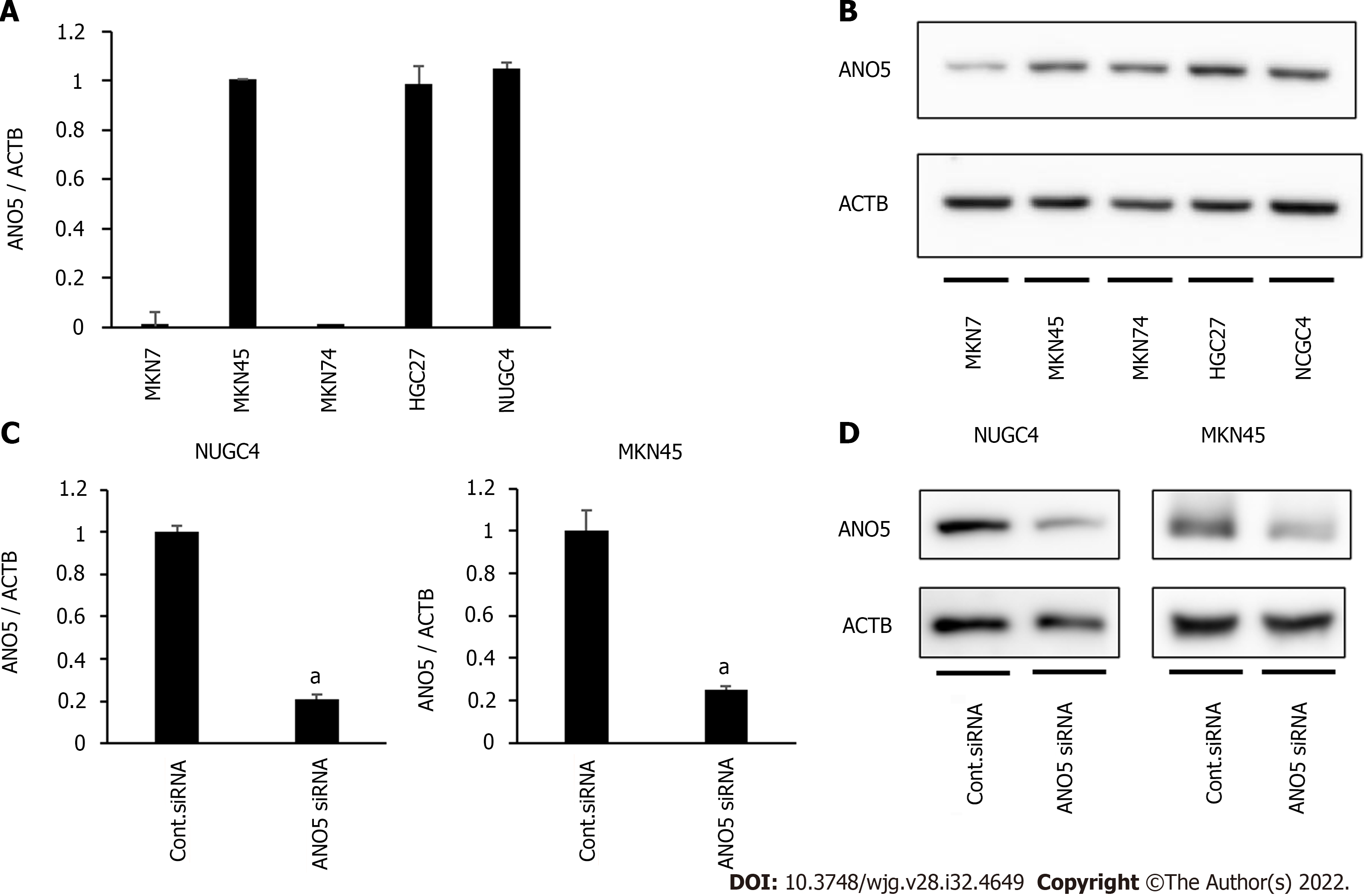
Figure 1 Anoctamin 5 expression in gastric cancer cells.
A: Real-time quantitative reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) showed the expression of anoctamin 5 (ANO5) in various cell lines in gastric cancer; B: Western blotting showed the expression of ANO5 in various cell lines in GC; C: Real-time quantitative PCR revealed that ANO5 small interfering RNA (siRNA) effectively reduced ANO5 mRNA levels in NUGC4 and MKN45 cells; D: Western blotting revealed that ANO5 siRNA effectively reduced ANO5 protein levels in NUGC4 and MKN45 cells. n = 3, mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05 (significantly different from control siRNA). ANO5: Anoctamin 5; ACTB: β-actin; siRNA: Small interfering RNA.
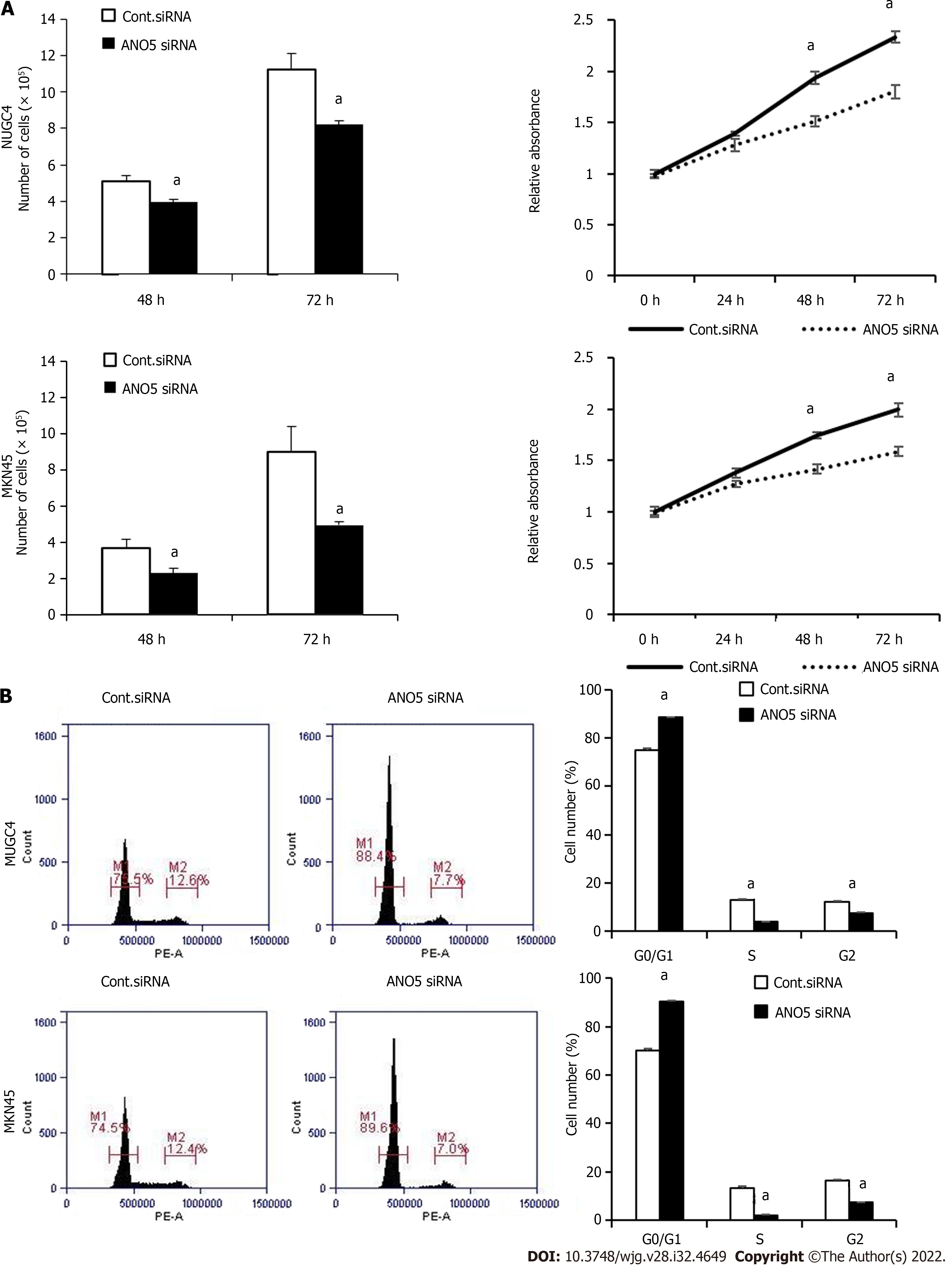
Figure 2 Anoctamin 5 controlled the proliferation and the cell cycle in gastric cancer cells.
A: The downregulation of anoctamin 5 (ANO5) inhibited the proliferation of NUGC4 and MKN45 cells. Cell numbers were counted 48 h and 72 h after small interfering RNA transfection (left panel). The proliferative ability of NUGC4 and MKN45 cells was significantly suppressed following ANO5 downregulation (right panel); B: The downregulation of ANO5 increased the number of cells in the G0/G1 phase in NUGC4 and MKN45 cells. Cells transfected with control or ANO5 small interfering RNA were stained with propidium iodide and analyzed by flow cytometry. n = 3, mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05 (significantly different from control small interfering RNA). ANO5: Anoctamin 5; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; Cont.: Control.
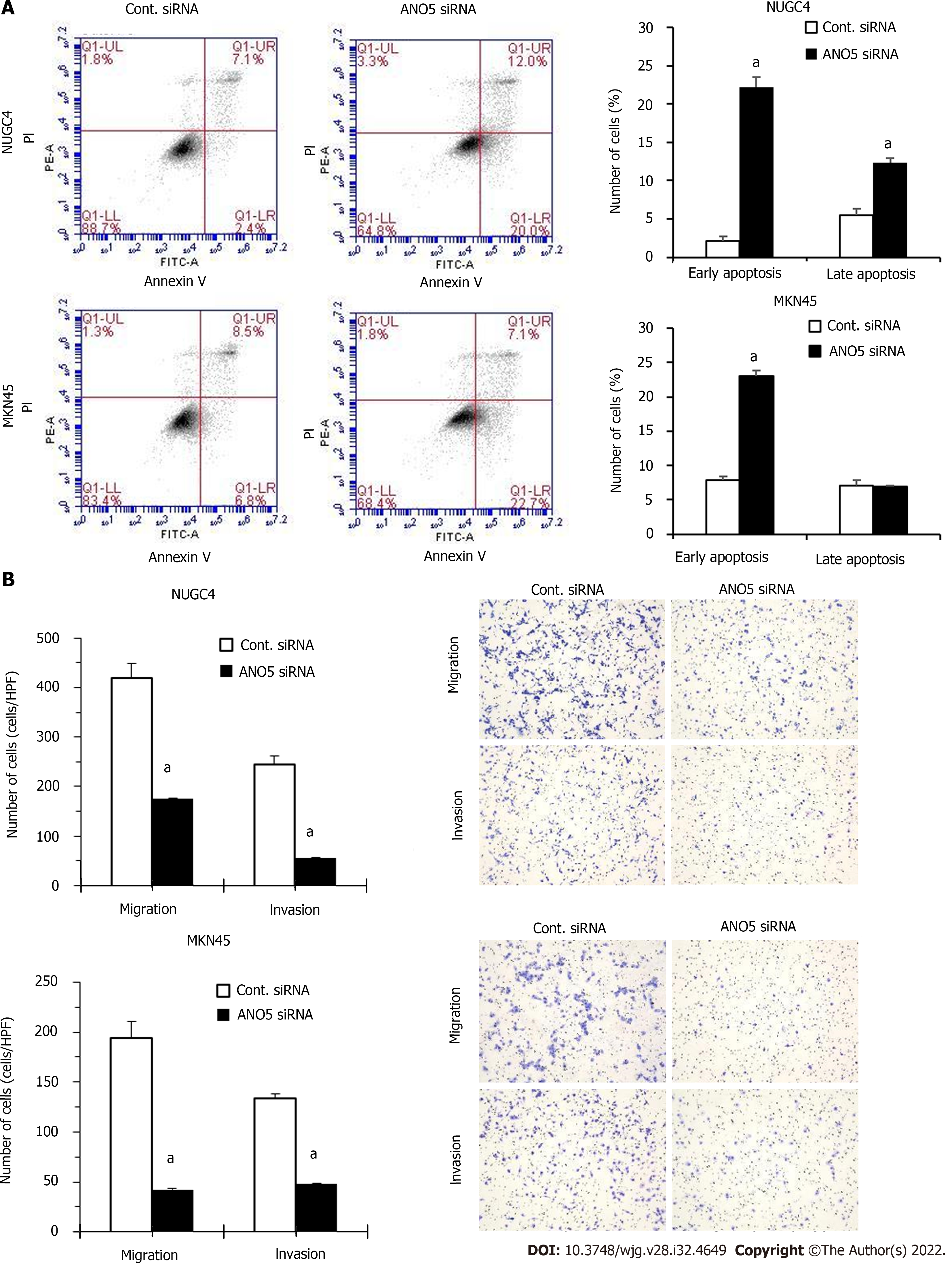
Figure 3 Anoctamin 5 controlled apoptosis, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer cells.
A: The downregulation of anoctamin 5 (ANO5) increased the early and late apoptotic cell proportions of NUGC4 and MKN45 cells. Control or ANO5 small interfering RNA-transfected cells were stained with propidium iodide and annexin V and subjected to flow cytometry; B: The downregulation of ANO5 significantly decreased NUGC4 and MKN45 cell migration and invasion, which were evaluated using a Boyden chamber assay. Magnification: × 40. n = 3, mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05 (significantly different from control small interfering RNA). ANO5: Anoctamin 5; PI: Propidium iodide; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; Cont.: Control.
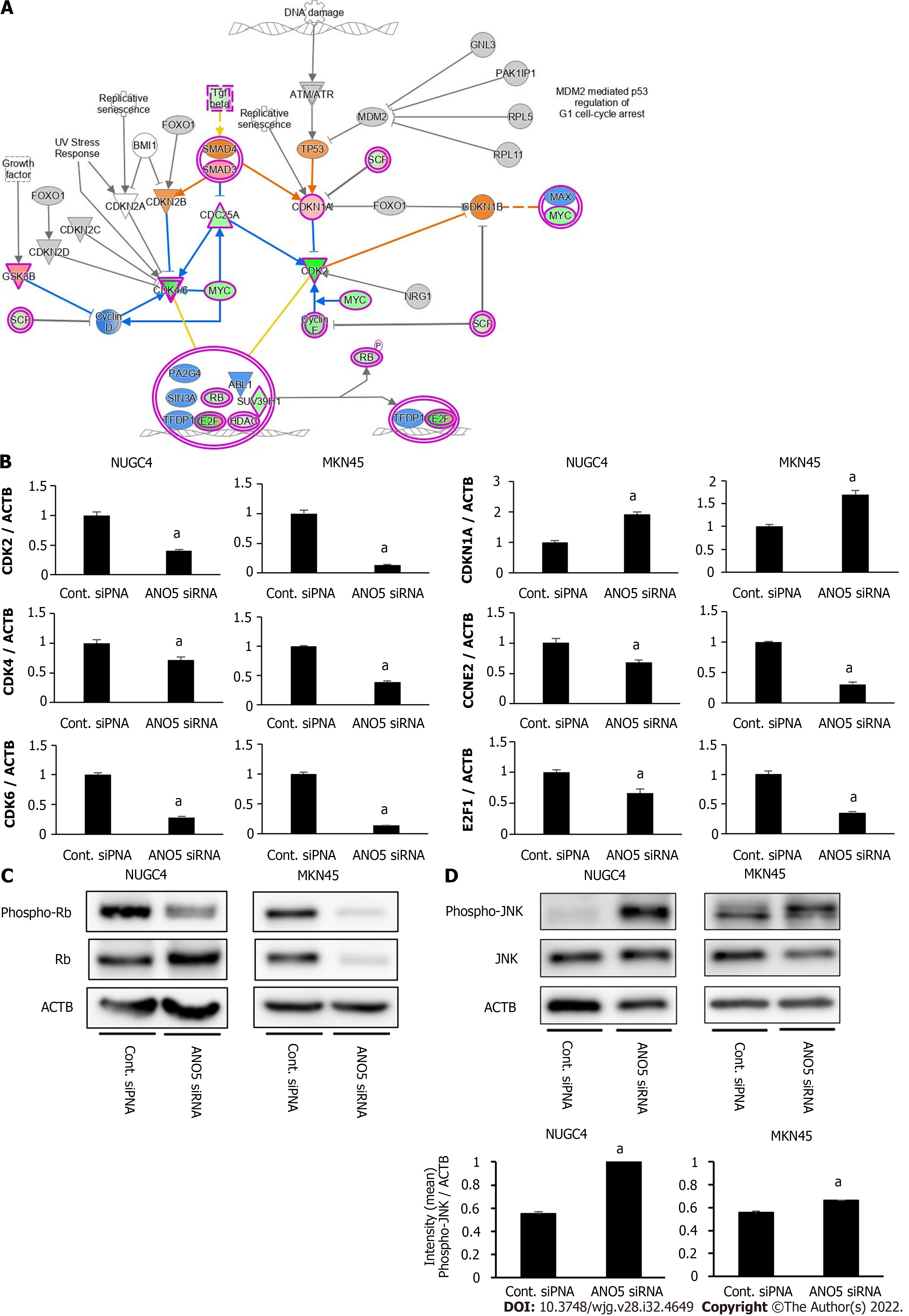
Figure 4 Network analyses by microarray analysis and ingenuity pathway analysis.
A: The signaling map of “Cell Cycle: G1/S Checkpoint Regulation,” one of the top-ranked canonical pathways related to the depletion of anoctamin 5 (ANO5) according to ingenuity pathway analysis. Red and green colors indicate genes with expression levels that were higher or lower, respectively, than reference RNA levels; B: To verify gene expression profiling data, CDK2, CDK4, CDK6, CDKN1A, CCNE2, and E2F1 were examined by real-time reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. The downregulation of ANO5 effectively reduced CDK2, CDK4, CDK6, CCNE2, and E2F1 mRNA levels and increased CDKN1A/p21 mRNA levels in NUGC4 and MKN45 cells; C: The downregulation of ANO5 effectively reduced the phosphorylation levels of Rb protein in NUGC4 and MKN45 cells; D: The downregulation of ANO5 increased the phosphorylation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase protein in NUGC4 and MKN45 cells. n = 3, mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05 (significantly different from control small interfering RNA). ANO5: Anoctamin 5; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; Cont.: Control; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; ACTB: β-actin.
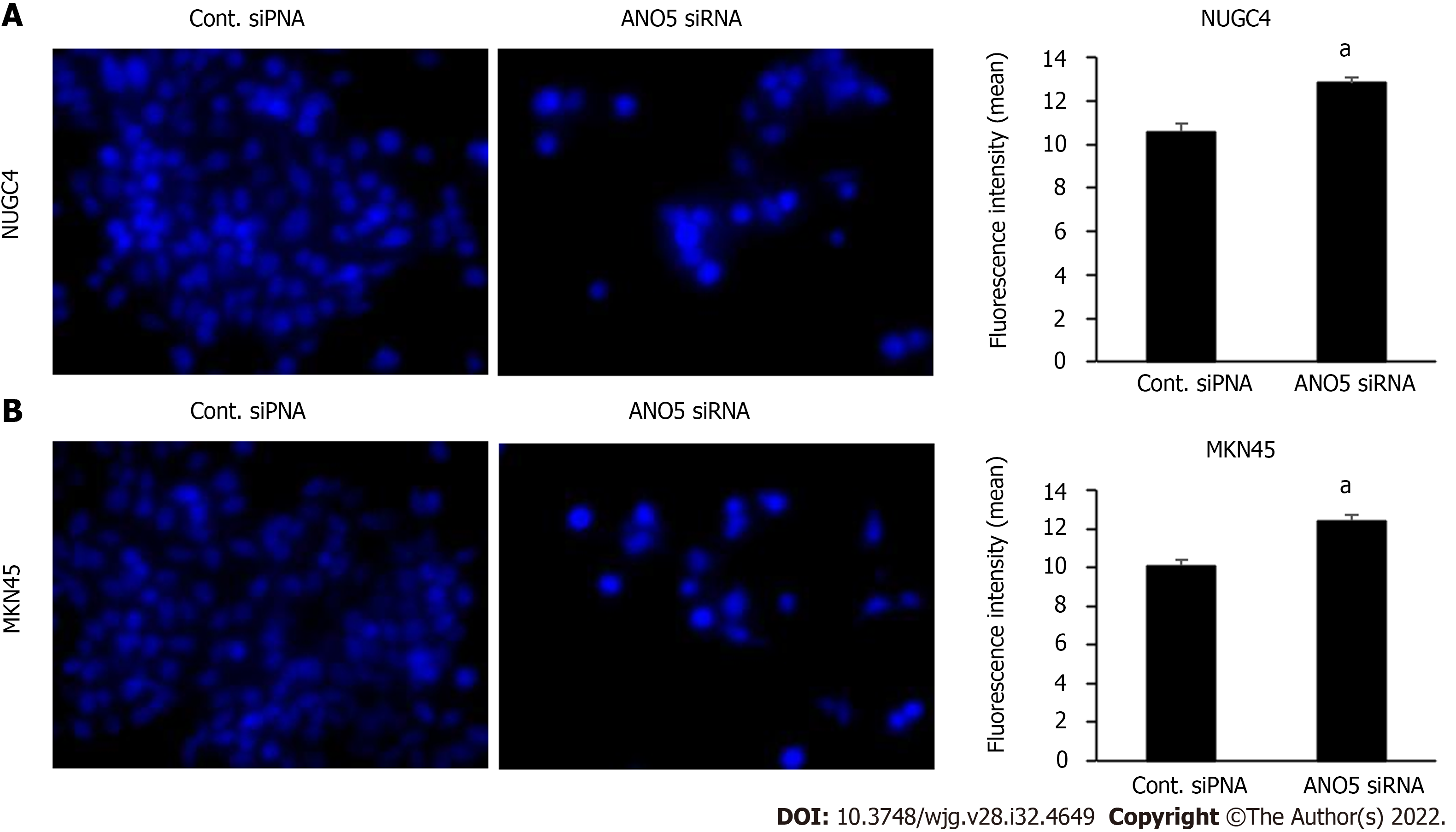
Figure 5 Immunofluorescent analysis of intracellular chloride concentration using MQAE reagent, a chloride-sensitive fluorescence probe.
The downregulation of anoctamin 5 increased the fluorescence intensity of MQAE in NUGC4 and MKN45 cells. A: NUGC4 cell; B: MKN45 cell. n = 3, mean ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05 (significantly different from control small interfering RNA). ANO5: Anoctamin 5; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; Cont.: Control.
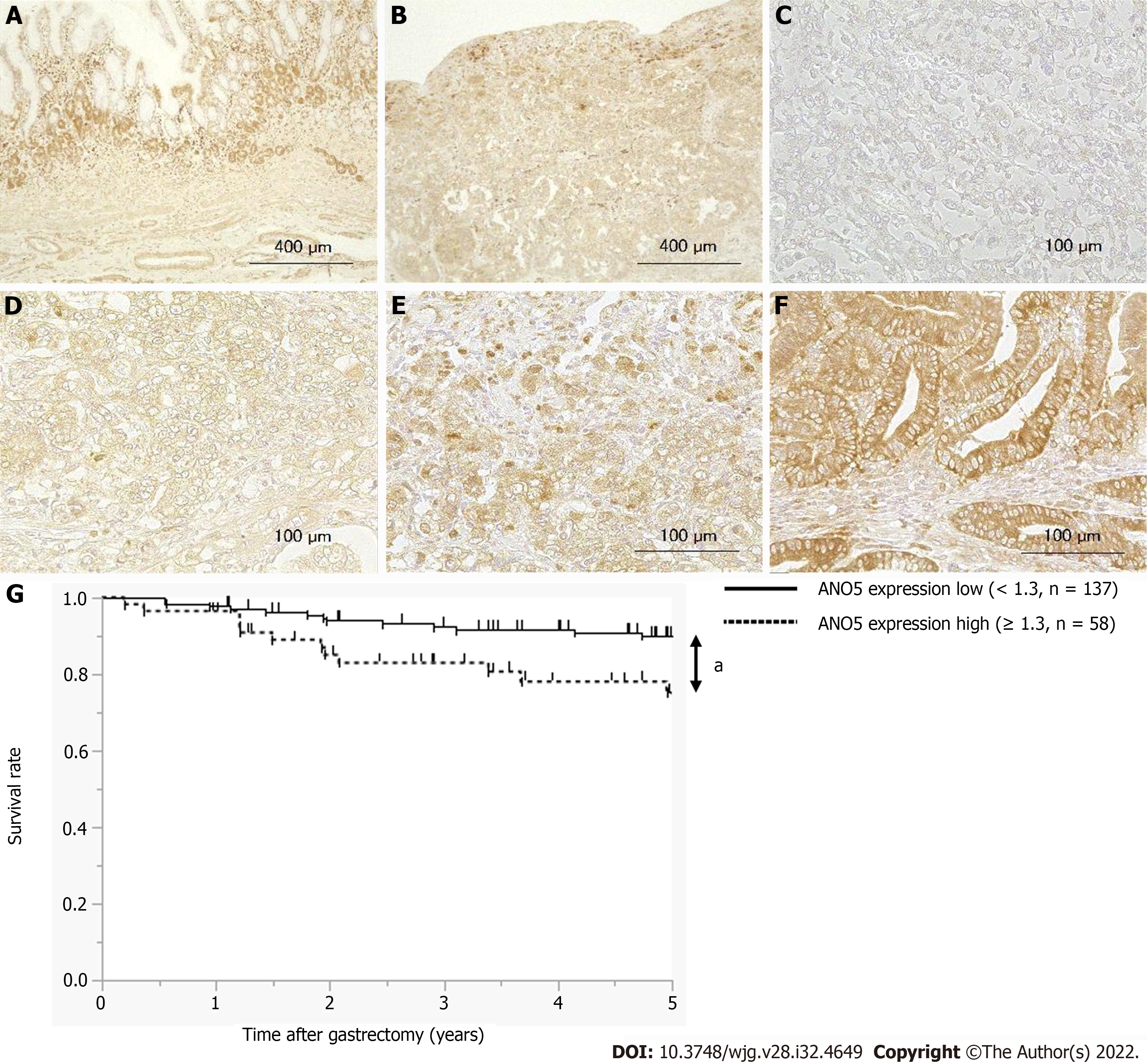
Figure 6 Anoctamin 5 protein expression levels in human gastric cancer tissues and a survival analysis based on anoctamin 5 expression.
A: Non-cancerous gastric epithelia were immunohistochemically stained using an anti-anoctamin 5 (ANO5) antibody. Magnification: × 100; B: Primary human gastric cancer samples were immunohistochemically stained using an anti-ANO5 antibody. Magnification: × 100; C: The immunohistochemical staining results of ANO5 are shown as intensity 0. Magnification: × 400; D: Intensity 1. Magnification: × 400; E: Intensity 2. Magnification: × 400; F: Intensity 3. Magnification: × 400; G: Gastric cancer patients were classified into two groups based on ANO5 expression: A low ANO5 expression group (< 1.3, n = 137) and high ANO5 expression group (≥ 1.3, n = 58). aP < 0.05 (significant difference). ANO5: Anoctamin 5.
- Citation: Fukami T, Shiozaki A, Kosuga T, Kudou M, Shimizu H, Ohashi T, Arita T, Konishi H, Komatsu S, Kubota T, Fujiwara H, Okamoto K, Kishimoto M, Morinaga Y, Konishi E, Otsuji E. Anoctamin 5 regulates the cell cycle and affects prognosis in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(32): 4649-4667
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i32/4649.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4649