©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2022; 28(13): 1315-1328
Published online Apr 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i13.1315
Published online Apr 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i13.1315
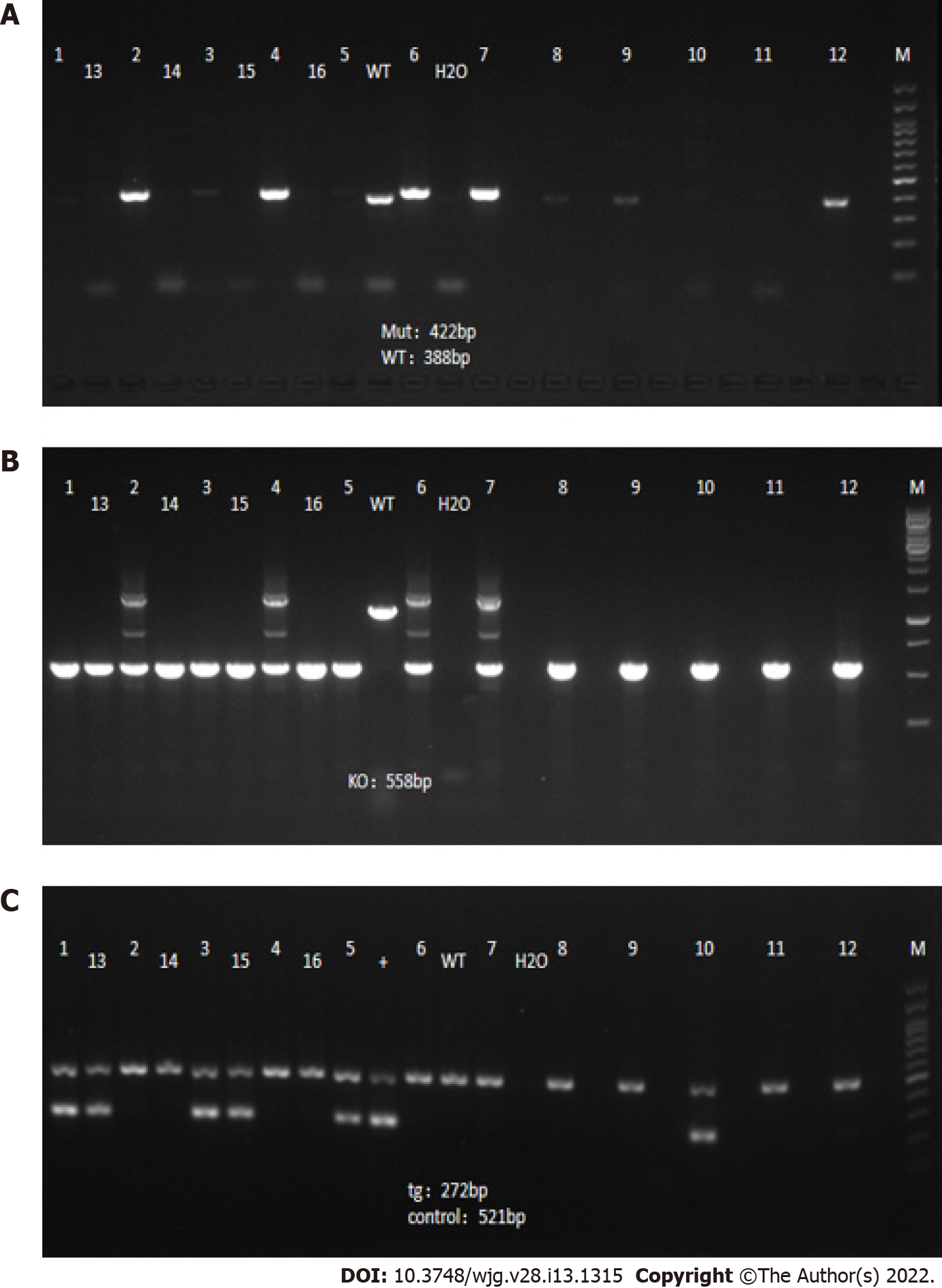
Figure 1 Gene detection results in F6-generation mice.
A: Interleukin (IL)-10 conditional knockout; B: IL-10 knockout; C: Dppa3-cre.
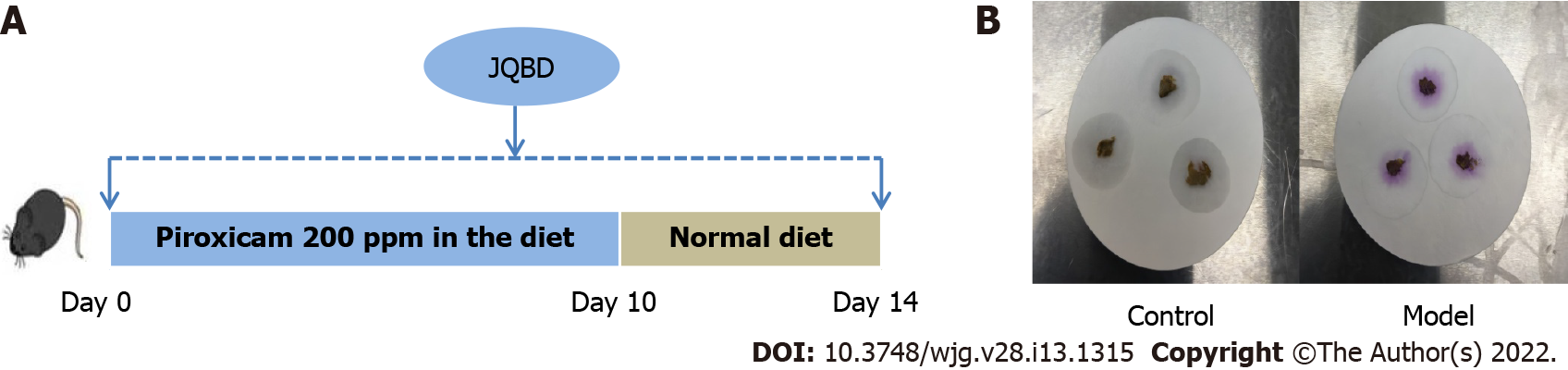
Figure 2 Animal experimental flow and fecal occult blood test.
A: An experimental bone loss inflammatory bowel disease model was induced by peroral administration of piroxicam for 10 d in interleukin-10-/- mice. Normal saline or Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction (JQBD; 16.5 g/kg/d) was given intragastrically to the control/model groups and JQBD group, respectively (n = 6, each); B: Fecal occult blood test of control and model groups: The control group was negative, and the model group was strongly positive for occult blood. JQBD: Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction Group.
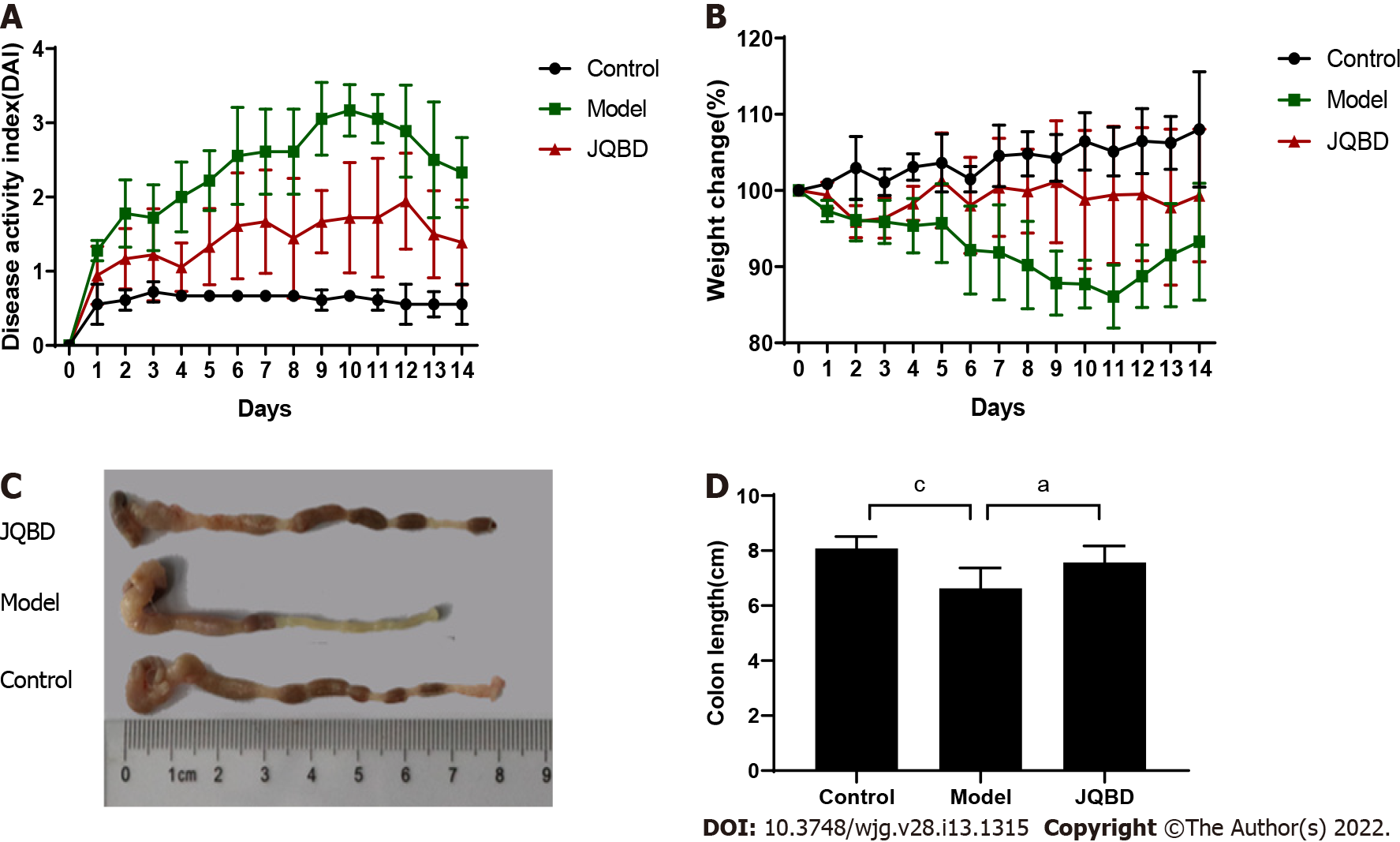
Figure 3 General condition of the mice.
A: Disease activity index scores gauged daily (n = 6 per group); B: Body weight measured daily (n = 6 per group); C and D: Colon length measurement and graph presenting the statistical analysis results. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001 (n = 6 per group).
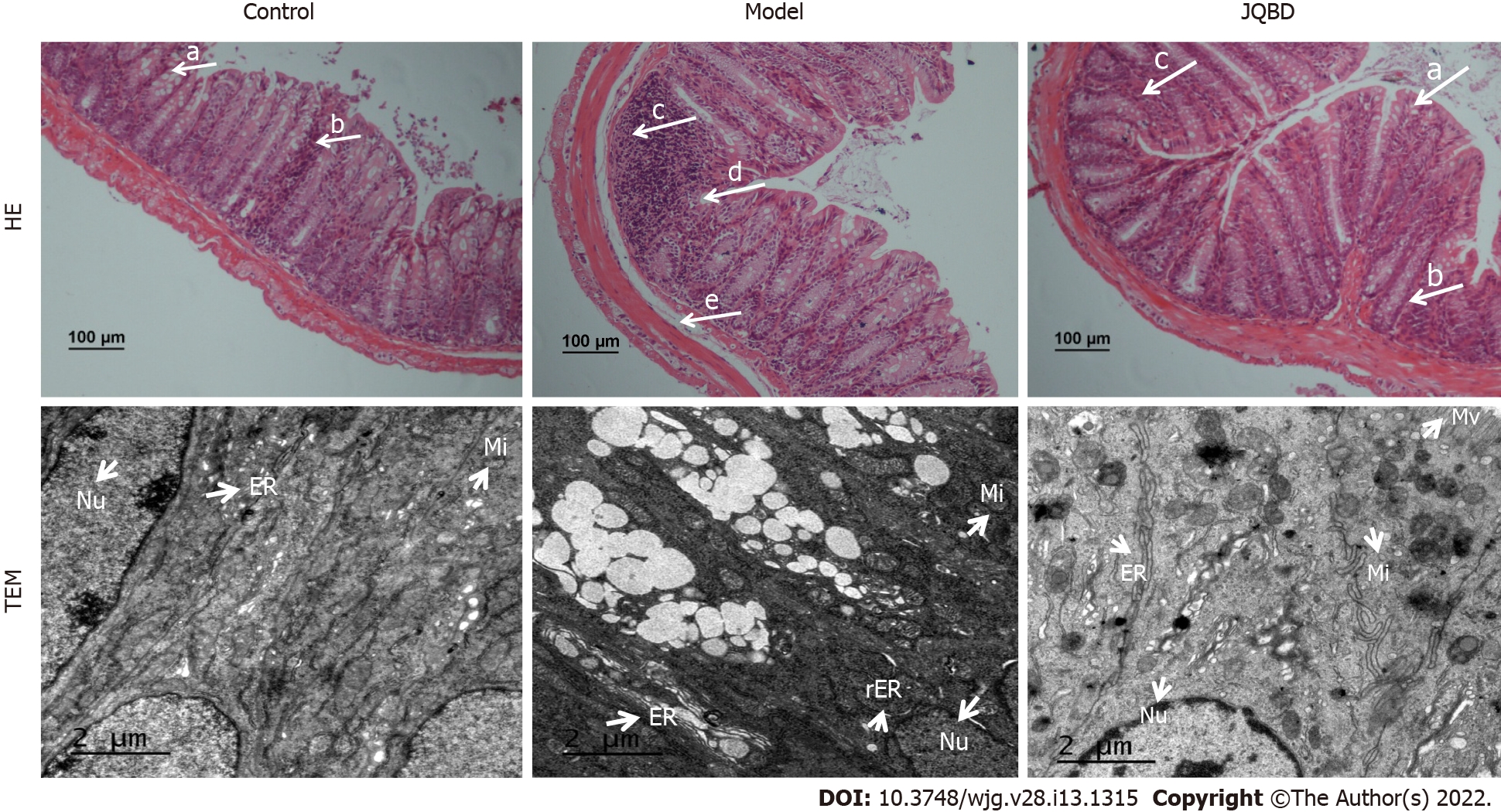
Figure 4 Histological evaluation of the colonic mucosa following hematoxylin and eosin staining (× 100) and ultrastructure of the colonic epithelium by transmission electron microscopy (× 6000).
Arrows indicate goblet cells (a), crypts (b), inflammatory cells infiltration (c), epithelium surface erosion (d), and submucosal oedema (e). Control: Control group; Model: Model group; JQBD: Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction Group; Nu: Nucleus; Mi: Mitochondrial; ER: Endoplasmic Reticulum; rER: Rough endoplasmic reticulum; Mv: Microvillus.
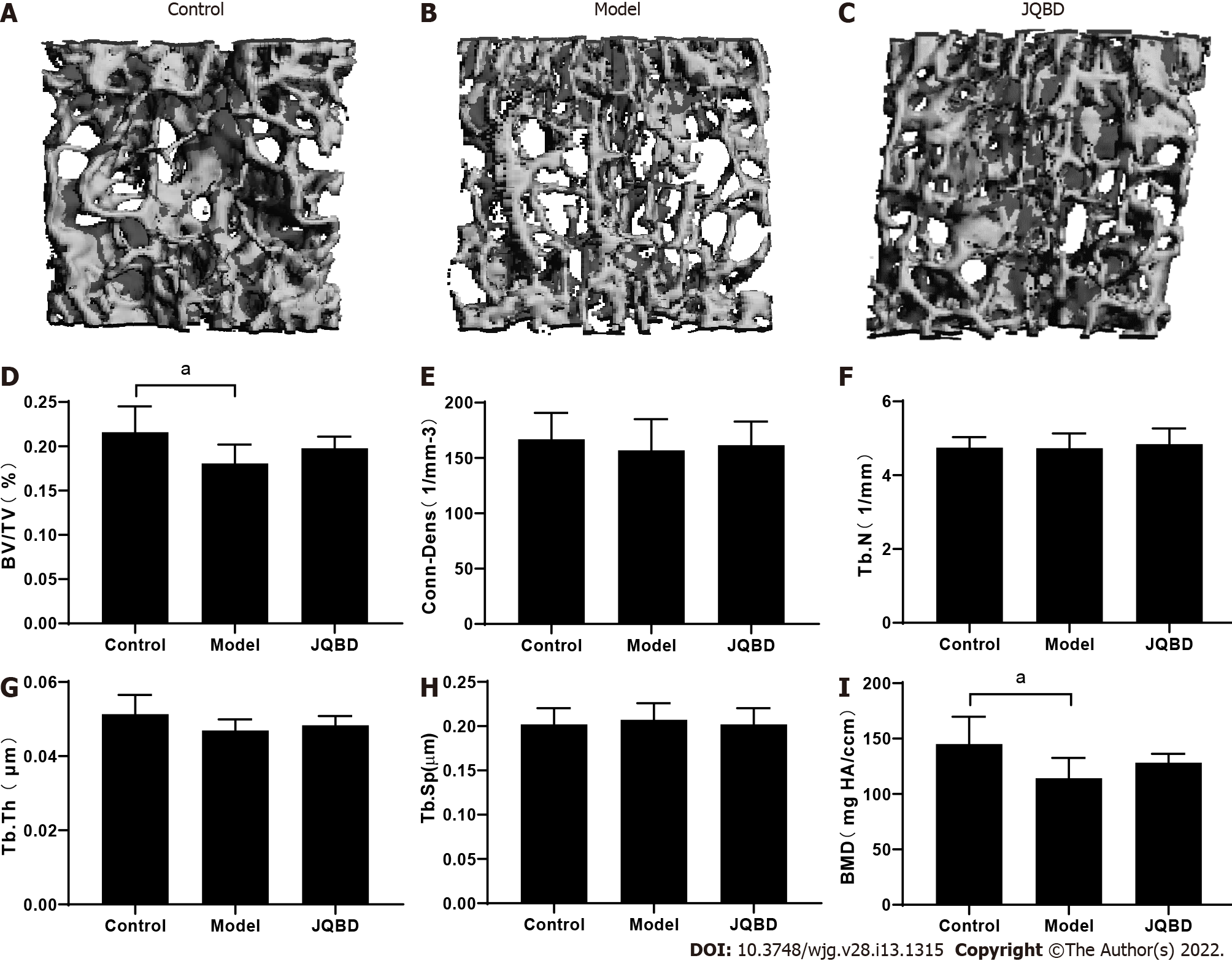
Figure 5 Three-dimensional reconstruction of the lumbar spine trabecular structure in mice and micro-computed tomographic analyses of the lumbar vertebral metaphysis.
Bone volume to total volume (BV/TV) ratio, Conn-Dens, trabecular number (Tb.N), trabecular thickness (Tb.Th), trabecular separation (Tb.Sp), and bone mineral density (BMD) were obtained for all mice. A: Control; B: Model; C: JQBD; D: BV/TV; E: Conn-Dens; F: Trabecular number; G: Trabecular thickness; H: Trabecular separation; I: Bone mineral density. Control: Control group; Model: Model group; JQBD: Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction Group; BV/TV: Bone volume to total volume ratio; Conn-Dens: Connectivity-density; Tb.N: Trabecular number; Tb.Th: Trabecular thickness; Tb.Sp: Trabecular separation; BMD: Bone mineral density. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. (n = 6 per group).
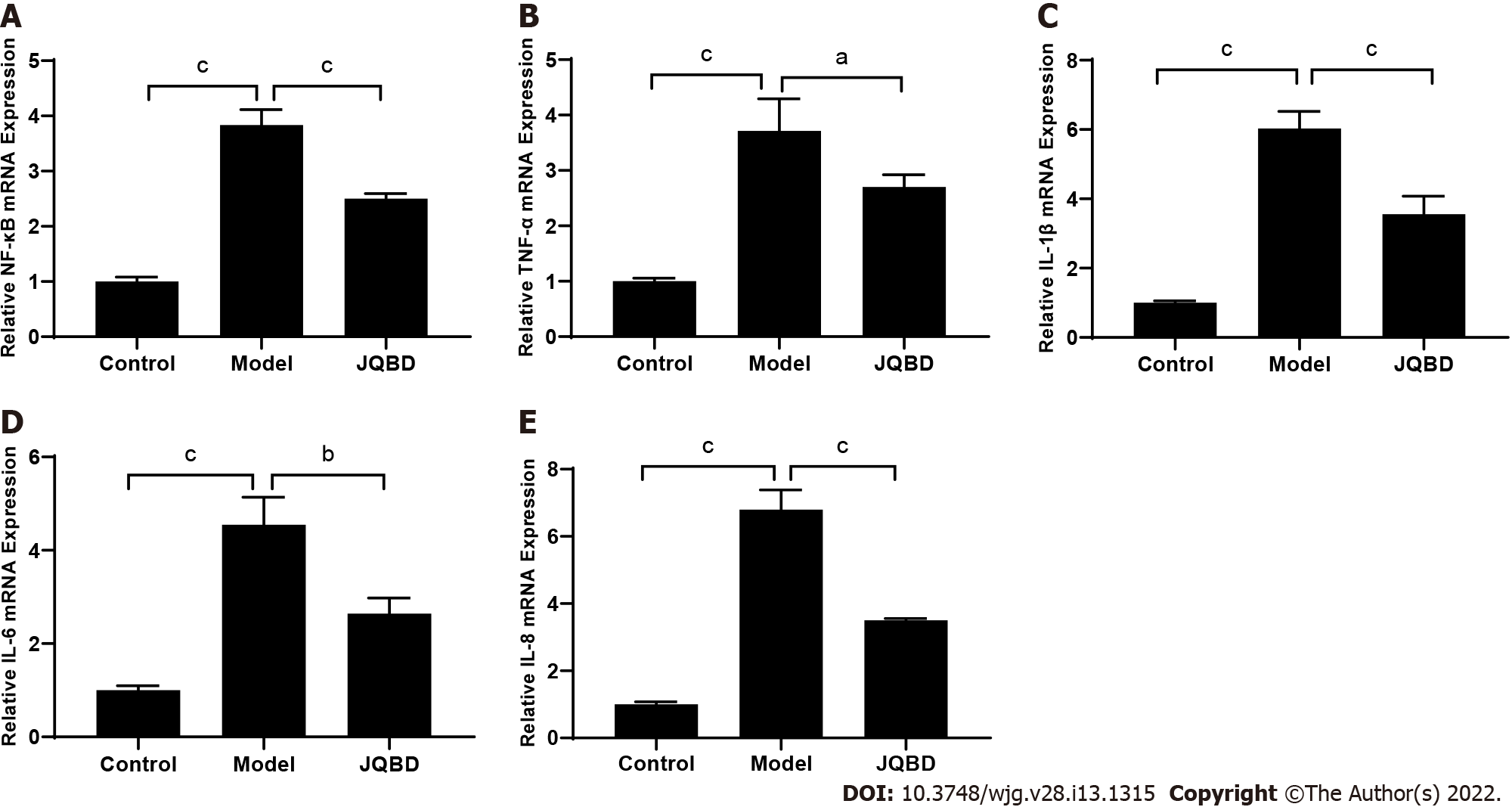
Figure 6 Effect of Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction on nuclear factor-kappaB, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and interleukin-8 gene expression.
The relative expression of these genes was quantified by real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction. A: NF-κB; B: TNF-α; C: IL-1β; D: IL-6; E: IL-8. Control: Control group; Model: Model group; JQBD: Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction Group; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappaB; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL: Interleukin. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001 (n = 3 per group).
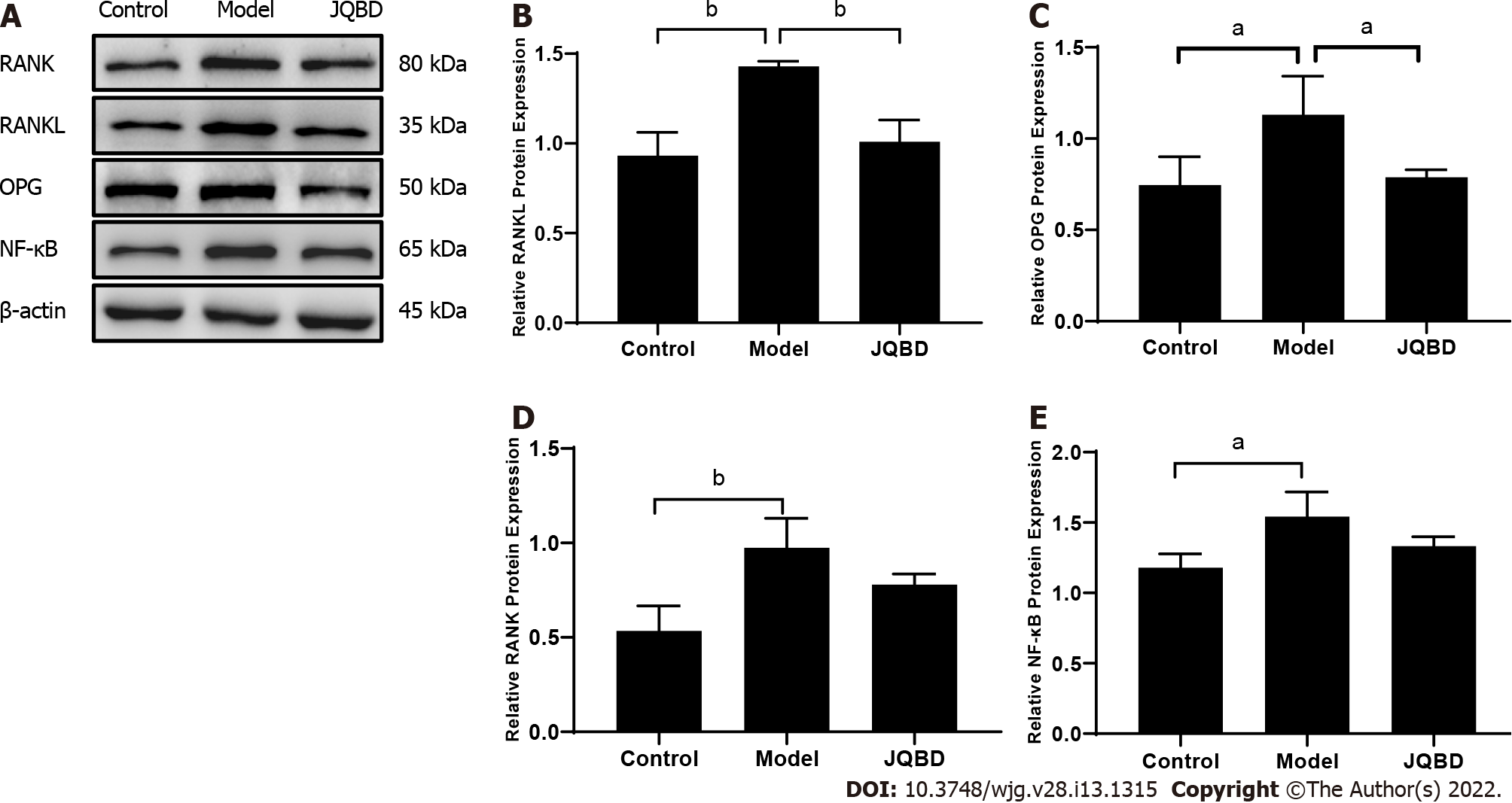
Figure 7 Effect of Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction on receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand, osteoprotegerin, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B, and nuclear factor-kappaB protein expression.
A: Protein expression quantified by Western blot; B: RANKL; C: OPG; D: RANK; E: NF-κB. Control: Control group; Model: Model group; RANK: Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B; RANKL: Receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand; JQBD: Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction Group. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001 (n = 3 per group).
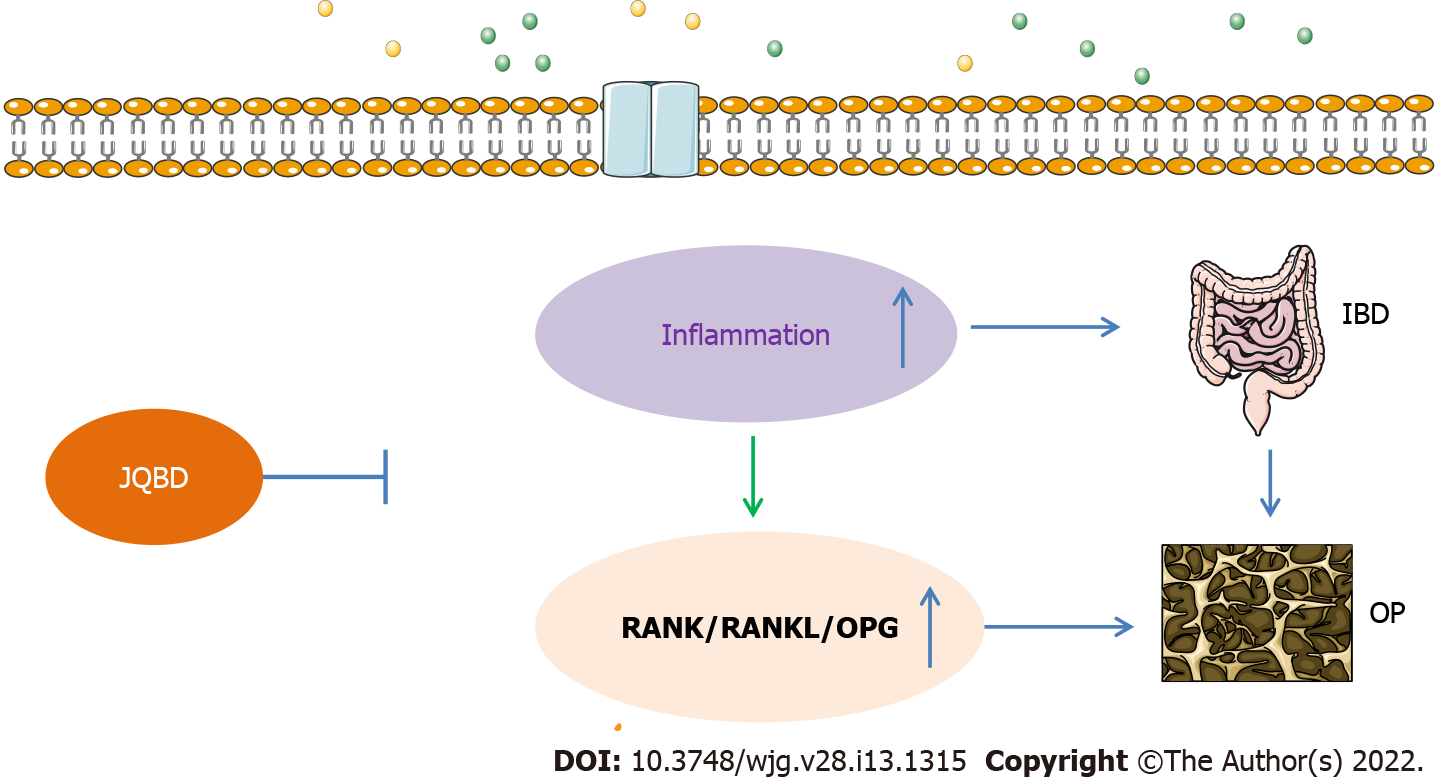
Figure 8 Possible mechanisms of bone loss in inflammatory bowel disease.
IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; OPG: Osteoprotegerin; RANK: Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B; RANKL: Receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand; JQBD: Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction Group.
- Citation: Zhang YL, Chen Q, Zheng L, Zhang ZW, Chen YJ, Dai YC, Tang ZP. Jianpi Qingchang Bushen decoction improves inflammatory response and metabolic bone disorder in inflammatory bowel disease-induced bone loss. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(13): 1315-1328
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i13/1315.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i13.1315