©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2021; 27(5): 377-390
Published online Feb 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i5.377
Published online Feb 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i5.377
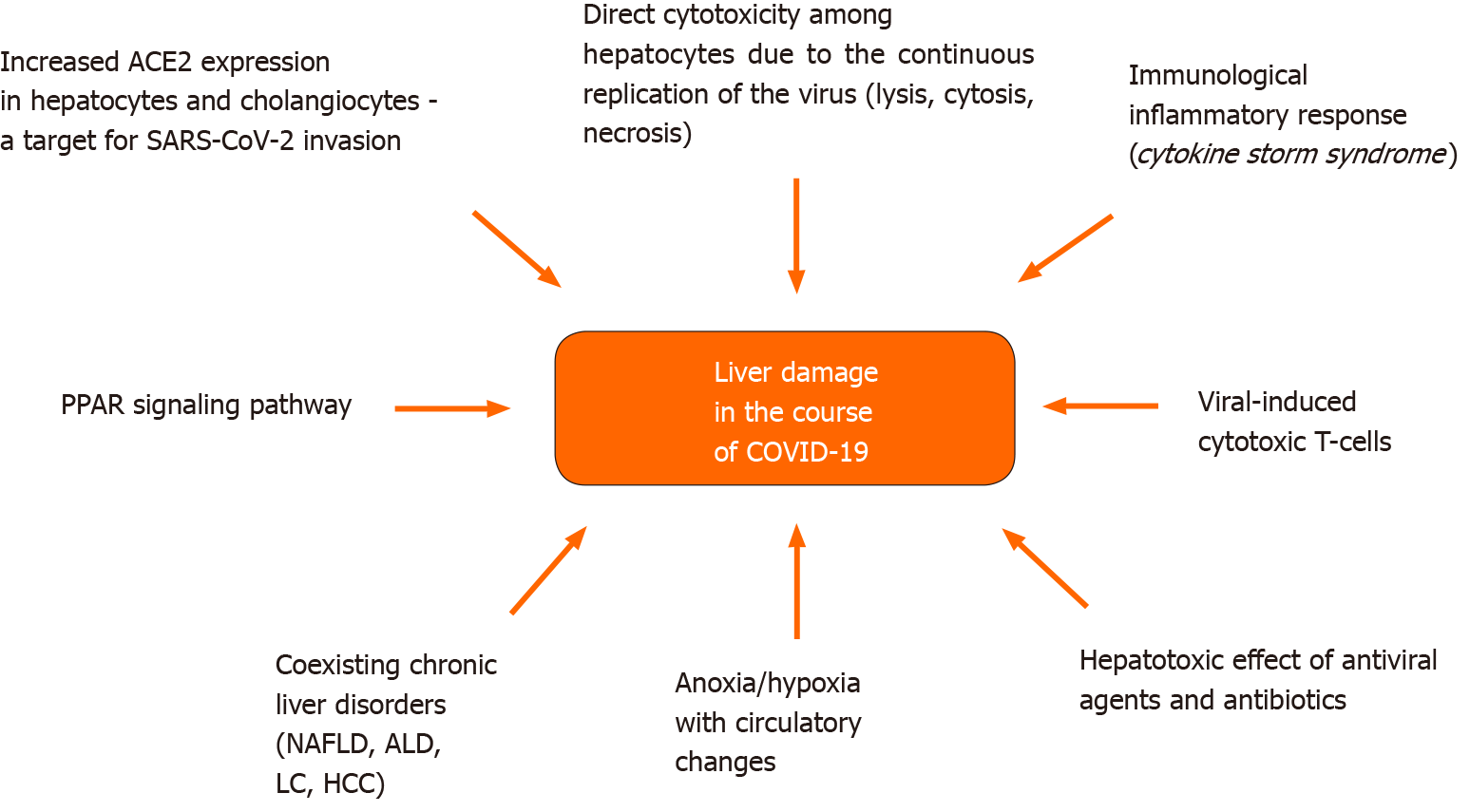
Figure 1 Mechanisms of coronavirus disease 2019-related liver injury.
ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; ALD: Alcohol-related liver disease; LC: Liver cirrhosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
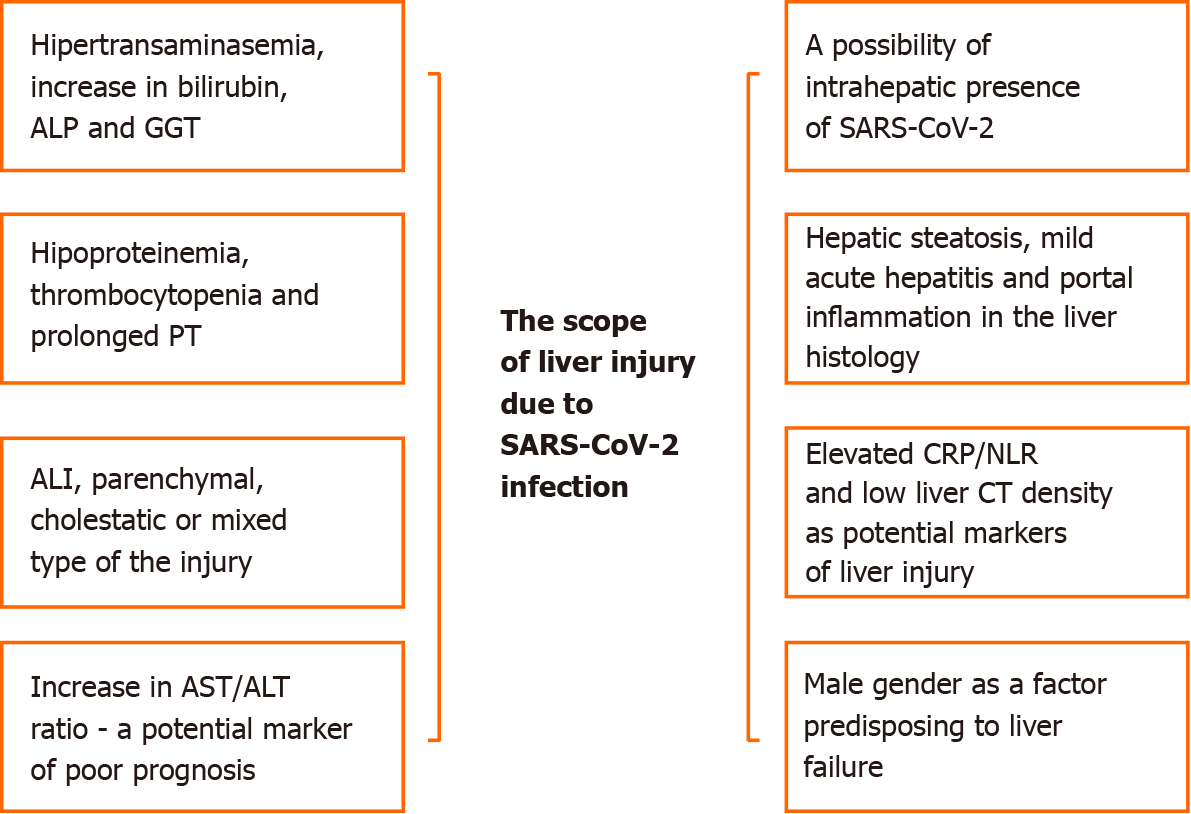
Figure 2 Characteristics of liver injury during the course of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection.
ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transferase; PT: Prothrombin time; ALI: Acute liver failure; AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALT: Alanine transaminase; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; CRP: C-reactive protein; NLR: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; CT: Computed tomography.
- Citation: Cichoż-Lach H, Michalak A. Liver injury in the era of COVID-19. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(5): 377-390
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i5/377.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i5.377