©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2021; 27(29): 4862-4878
Published online Aug 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i29.4862
Published online Aug 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i29.4862
Figure 1 Main definitions of the presented topic.
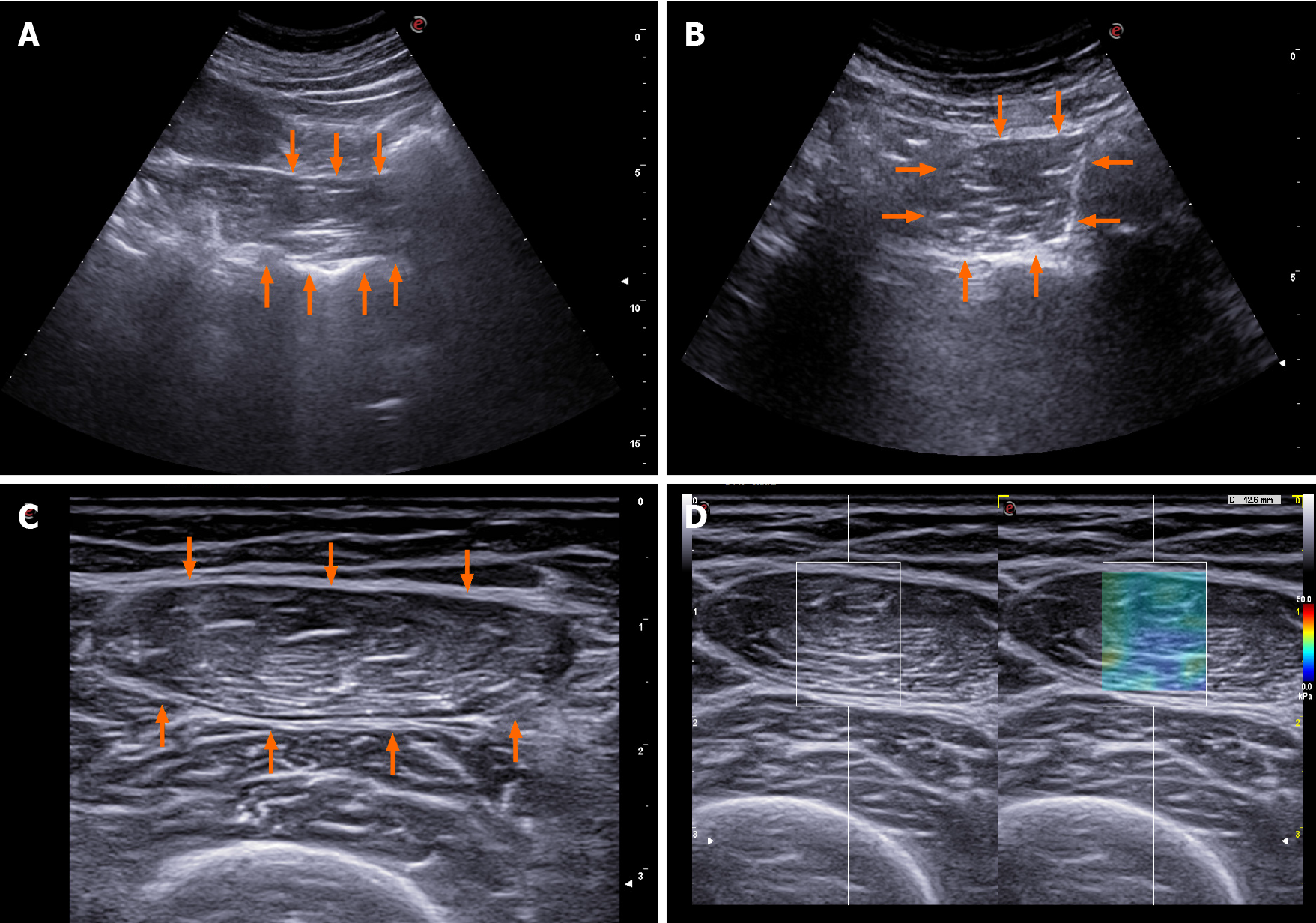
Figure 2 Reported options for ultrasound muscle mass assessment in cirrhosis.
A: Psoas muscle evaluation as proposed by Hari et al[43]; B: Psoas muscle evaluation as proposed by Kobayashi et al[42]; C: Femoral muscle evaluation as proposed by Tandon et al[40]; D: 2D-shearwave elastography of the femoral muscle.
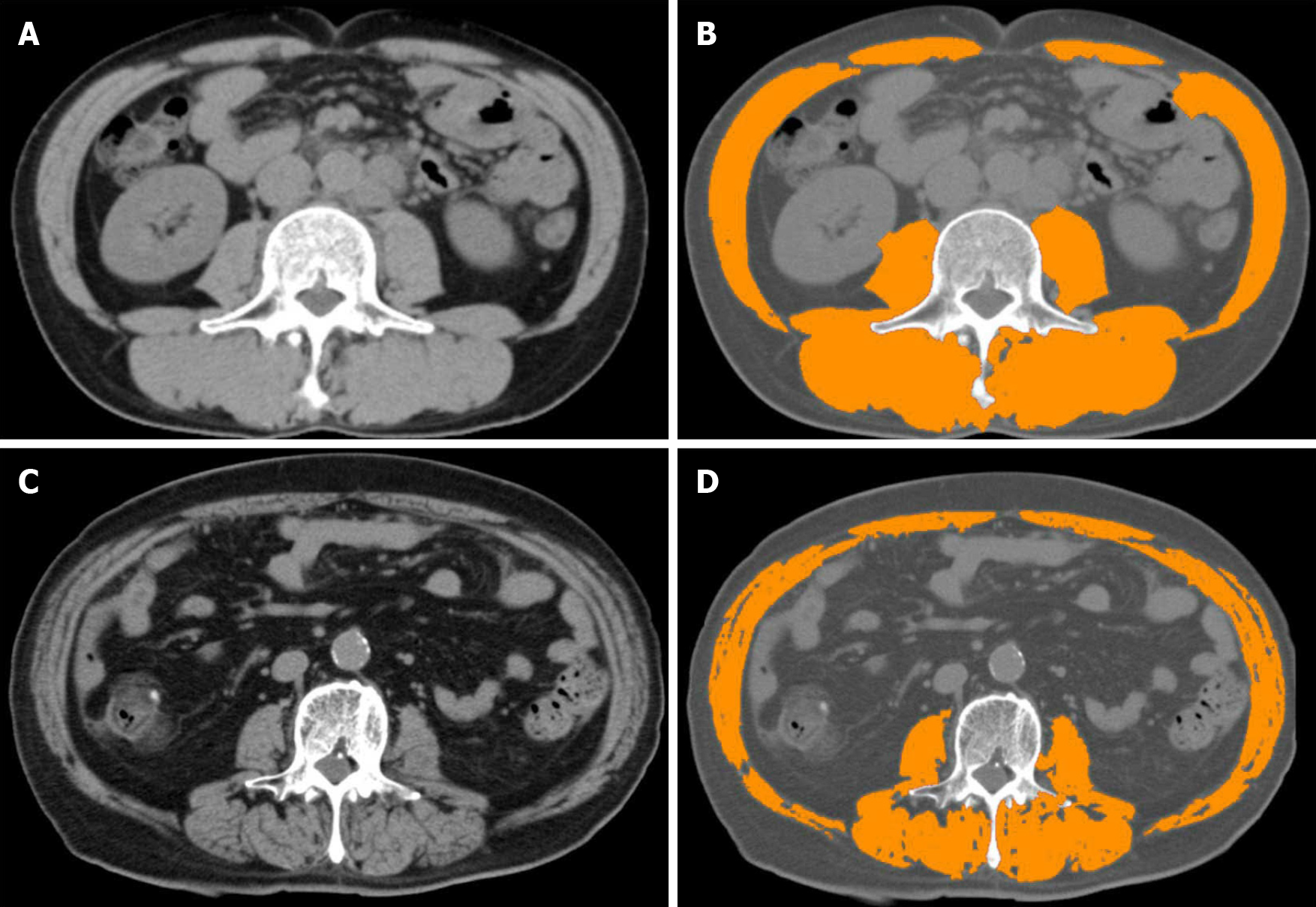
Figure 3 Computed tomography modality and skeletal muscle index.
A and C: Analysing computed tomography slices obtained at the third lumbar vertebra level; B: Patient with normal skeletal muscle index (SMI) values; D: Patient with reduced SMI values. After using medical imaging software and analysing areas of predefined Hounsfield units, SMI values are calculated.
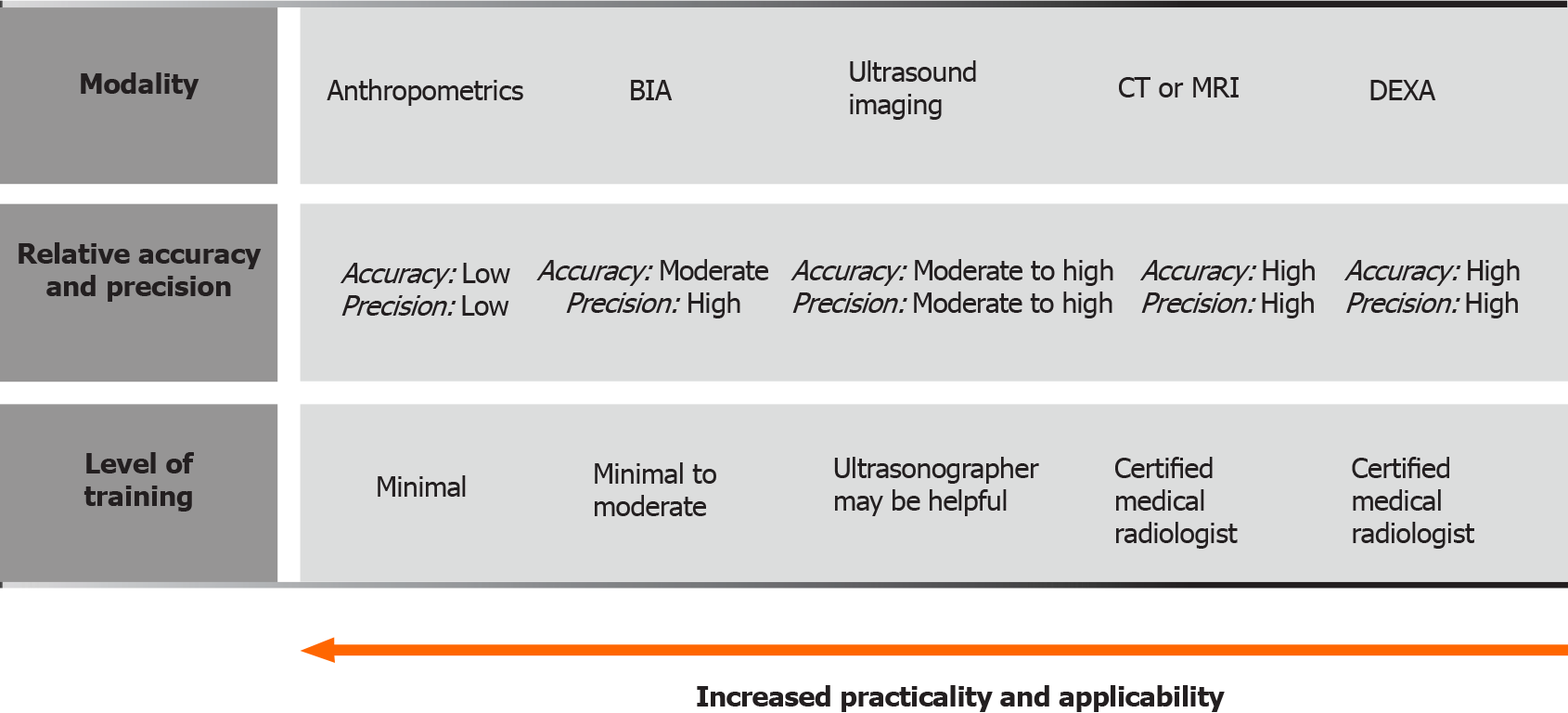
Figure 4 Sarcopenia evaluating methods.
Distinctions regarding required training, applicability, practicality, accuracy and precision are presented. Adapted from Tandon et al[55]. BIA: Bioelectrical impedance analysis; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; DEXA: Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry.
- Citation: Hari A. Muscular abnormalities in liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(29): 4862-4878
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i29/4862.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i29.4862