©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2021; 27(26): 4160-4171
Published online Jul 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i26.4160
Published online Jul 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i26.4160
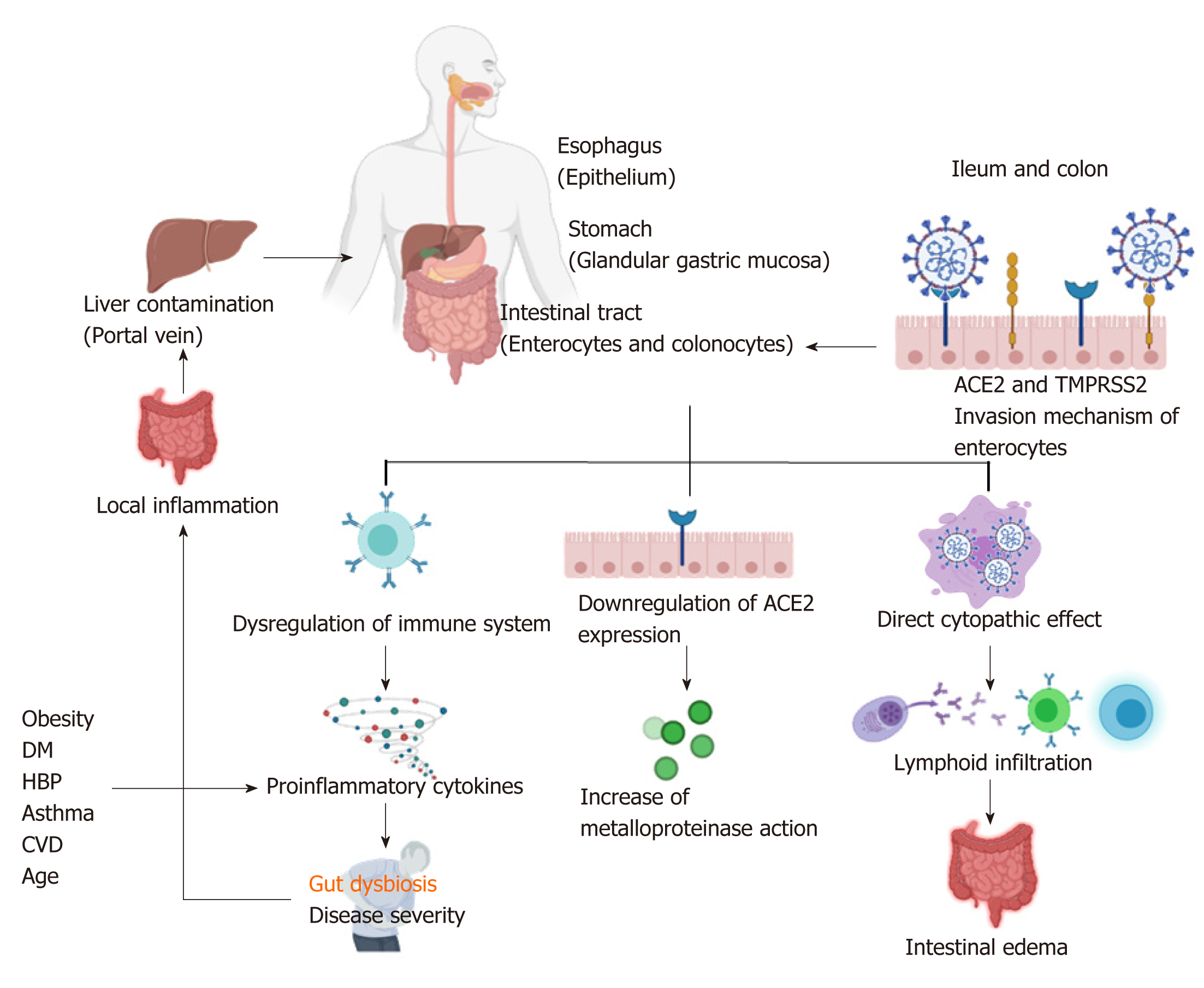
Figure 1 Mechanisms of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 gastrointestinal infection.
The same receptors mediate infections of the gastrointestinal system as in the respiratory system. This situation could begin at the intestinal tract by enterocyte invasion, which possesses angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and transmembrane protease serine 2 receptors recognized by severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2. Once in cells, the virus can induce cell death-mediated dysregulation of the immune system by downregulation of ACE2 receptor expression and a direct cytopathic effect. All three mechanisms induce immune dysregulation and increase the inflammation mechanism. Some risk factors that accelerate immune inflammation are obesity, diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure, asthma, cardiovascular disease, and advanced age. Moreover, the virus could enter the liver by the portal vein and induce hepatic failure. ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; TMPRSS2: Transmembrane protease serine 2; DM: Diabetes mellitus; HPB: High blood pressure; CVD: Cardiovascular disease.
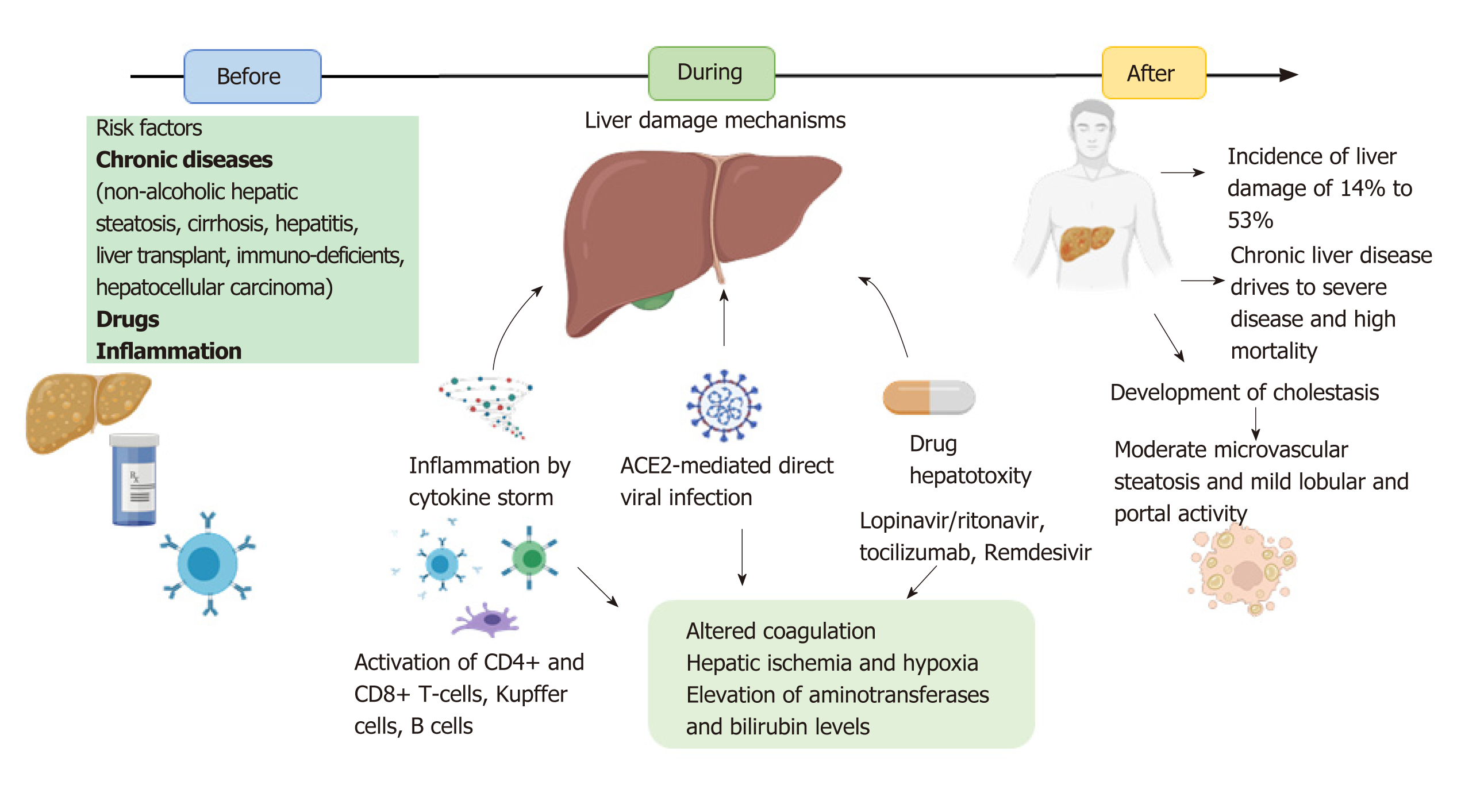
Figure 2 Proposed process of liver damage.
Before severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 infection, there are risk factors considered that could be poor prognostic factors, such as chronic diseases, the use of drugs that affect the liver and the inflammation process. The virus can infect the liver through the portal vein. There are three proposed mechanisms of liver damage: inflammation induced by cytokine storm and activation of hepatic immunity, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-mediated direct viral infection of hepatocytes, epithelial cells, and cholangiocytes, and drug hepatotoxicity mediated by some antivirals employed for coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) treatment. The three mechanisms culminate in altered coagulation, hepatic ischemia, and elevation of aminotransferases and bilirubin levels. Following this, the incidence of liver damage derived from COVID-19 is up to 53%, which could develop cholestasis and reach high mortality risk. ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.
- Citation: Delgado-Gonzalez P, Gonzalez-Villarreal CA, Roacho-Perez JA, Quiroz-Reyes AG, Islas JF, Delgado-Gallegos JL, Arellanos-Soto D, Galan-Huerta KA, Garza-Treviño EN. Inflammatory effect on the gastrointestinal system associated with COVID-19. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(26): 4160-4171
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i26/4160.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i26.4160