©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2021; 27(22): 2944-2962
Published online Jun 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i22.2944
Published online Jun 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i22.2944
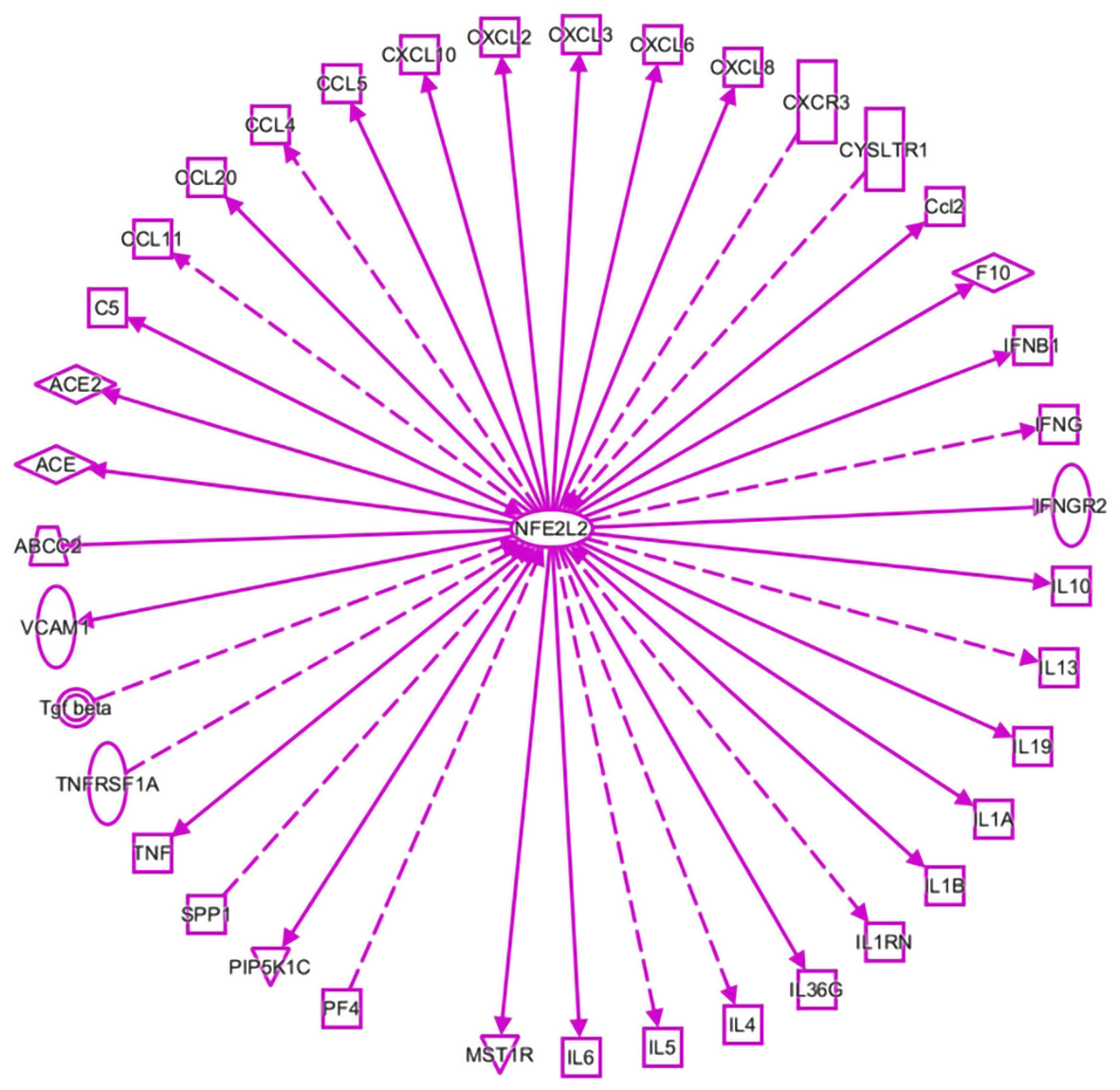
Figure 1 An interaction network analysis (ingenuity pathway analysis) was performed to predict nuclear factor, erythroid 2-like 2-mediated inflammatory cytokine-related genes in viral infections.
Solid lines indicate direct regulation, and dotted lines depict indirect interactions. ABCC2: ATP-binding cassette subfamily C member 2; ACE: Angiotensin I-converting enzyme; ACE2: Angiotensin I-converting enzyme 2; C5: Complement C5; Ccl2: Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2; CCL: C-C motif chemokine ligand; CXCR3: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3; CYSLTR1: Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1; F10: Coagulation factor X; IFNB1: Interferon beta 1; IFNG: Interferon gamma; IFNGR2: Interferon gamma receptor 2; IL: Interleukin; IL1A: Interleukin 1 alpha; IL1B: Interleukin 1 beta; IL1RN: Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist; IL36G: Interleukin 36 gamma; MST1R: Macrophage-stimulating 1 receptor; NFE2L2: Nuclear factor, erythroid 2-like 2; PF4: Platelet factor 4; PIP5K1C: Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type 1 gamma; SPP1: Secreted phosphoprotein 1; TGF-beta: Transforming growth factor beta; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNFRSF1A: TNF receptor superfamily member 1A; VCAM1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.
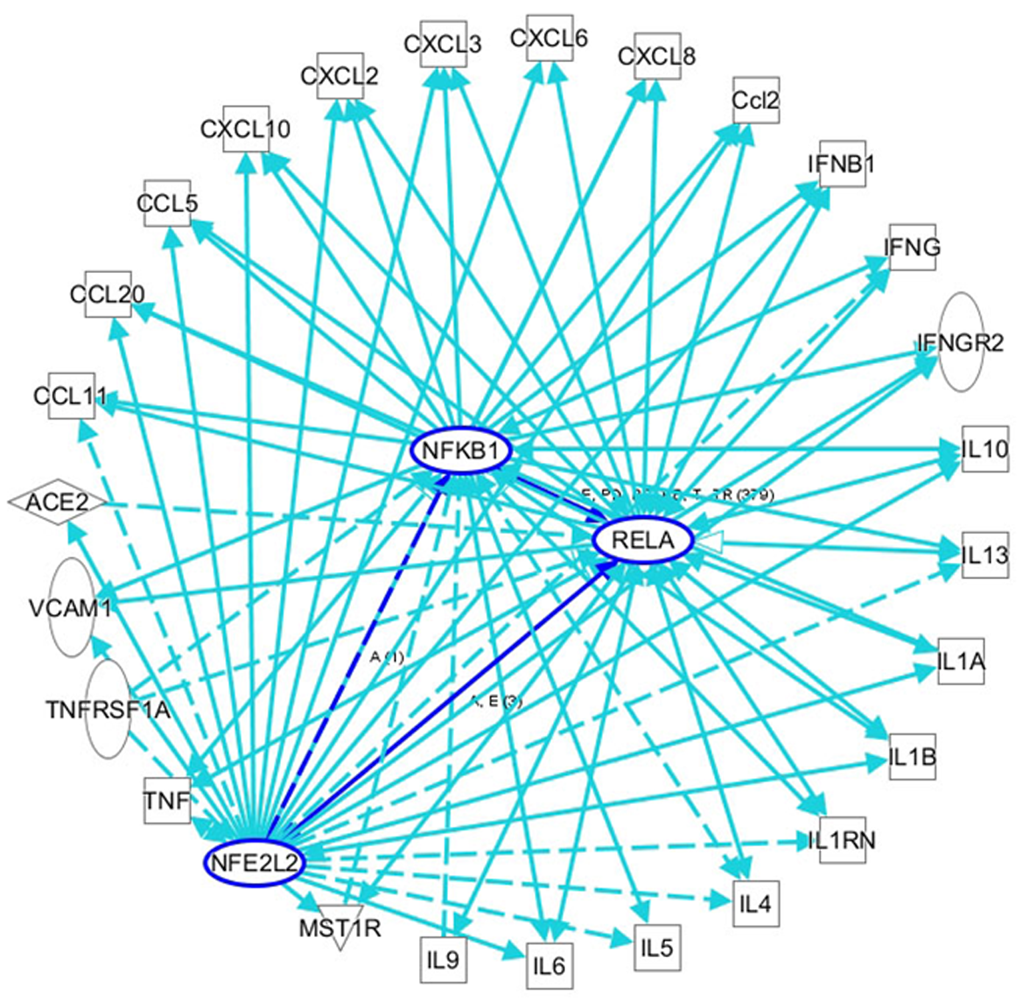
Figure 2 An ingenuity pathway analysis was performed to predict nuclear factor, erythroid 2-like 2/nuclear factor kappa B-mediated inflammatory cytokine-related genes in viral infections.
Solid lines indicate direct regulation, and dotted lines depict indirect interactions. ACE: Angiotensin I-converting enzyme; Ccl2: Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2; CXCL: C-X-C motif ligand; IL: Interleukin; IL1B: Interleukin 1 beta; IFNG: Interferon gamma; IL1RN: Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist; NFKB1: Nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1 (p50); RELA: RELA proto-oncogene, NF-κB subunit (p65); TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNFRSF1A: TNF receptor superfamily member 1A; VCAM1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.
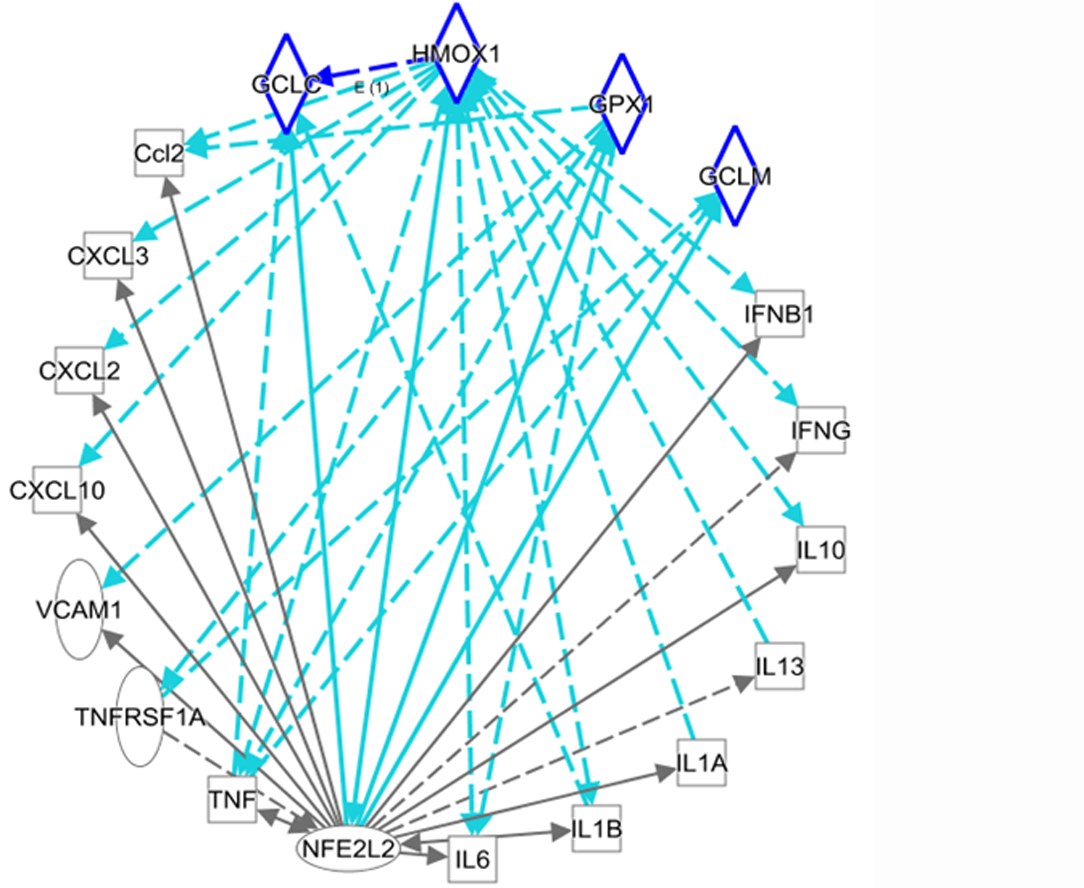
Figure 3 An ingenuity pathway analysis was performed to predict NRF2/redox-related genes and inflammatory cytokine-related gene expression in viral infections.
Solid lines indicate direct regulation, and dotted lines depict indirect interactions. Ccl2: Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2; CXCL: C-X-C motif ligand; GCLC: Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GCLM: Glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit; GPX1: Glutathione peroxidase 1; HMOX1: Heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1); IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNFRSF1A: TNF receptor superfamily member 1A; VCAM1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.
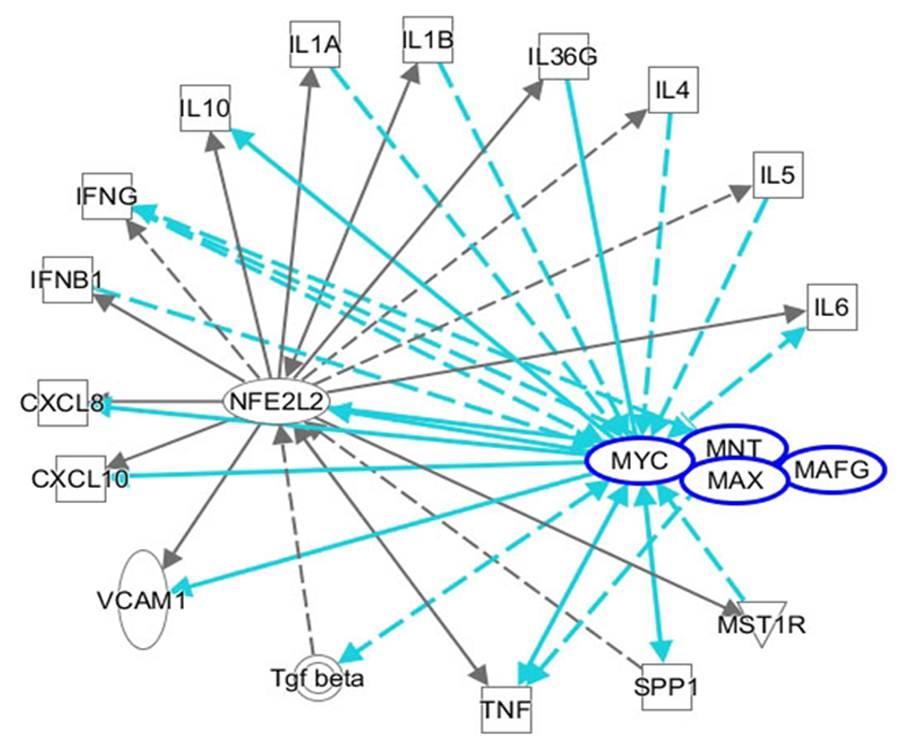
Figure 4 An ingenuity pathway analysis was performed to predict that nuclear factor, erythroid 2-like 2/MYC proto-oncogene, bHLH transcription factor/MAX network transcriptional repressor/MAF bZIP transcription factor G regulates the corresponding inflammatory cytokines.
Solid lines indicate direct regulation, and dotted lines depict indirect interactions. CXCL: C-X-C motif ligand; MAFG: MAF bZIP transcription factor G; MAX: MYC-associated factor X; MNT: MAX network transcriptional repressor; MYC: MYC proto-oncogene, bHLH transcription factor; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; TGF-beta: Transforming growth factor beta; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNFRSF1A: TNF receptor superfamily member 1A; VCAM1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.
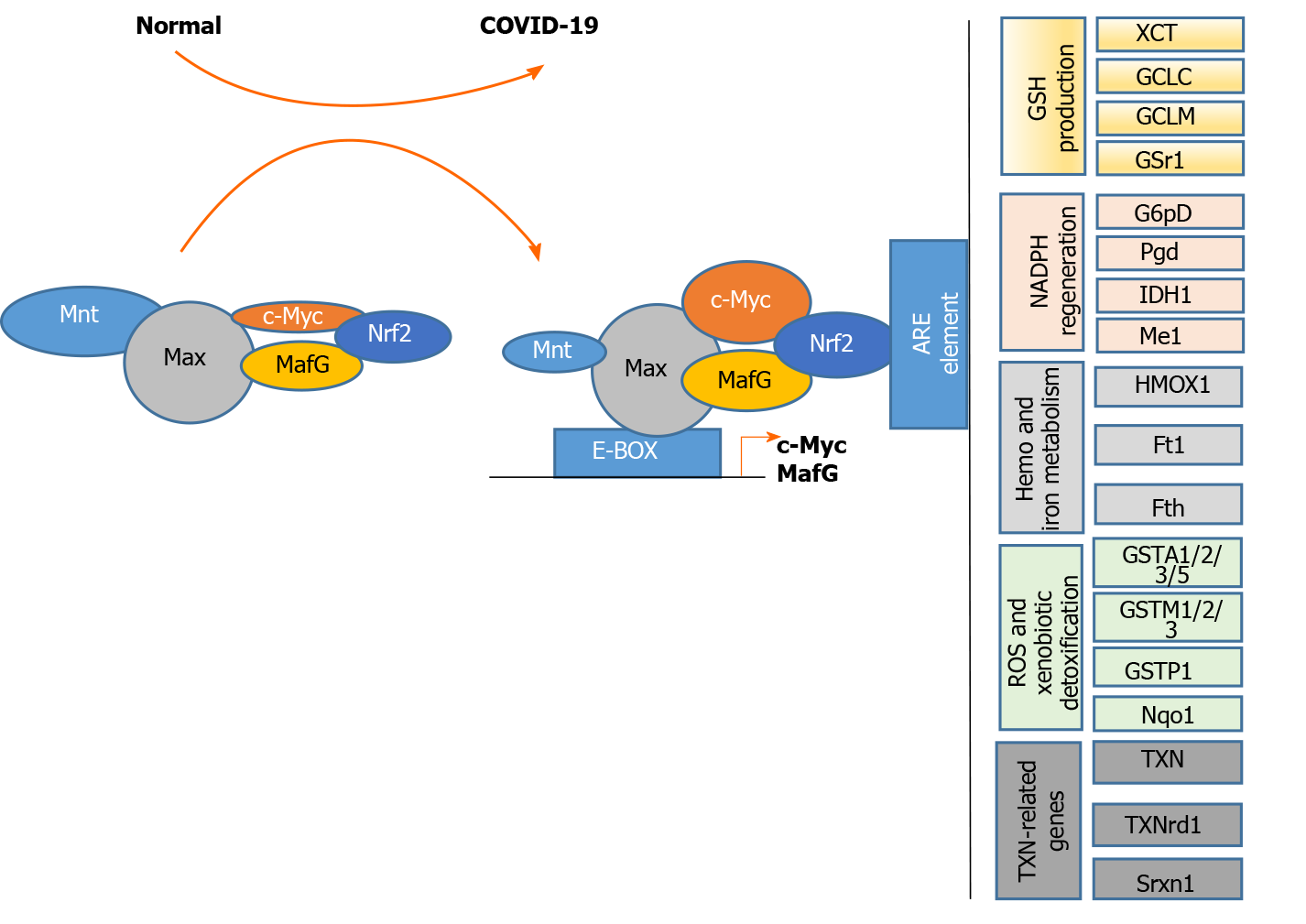
Figure 5 Interplay between c-MYC, MAX network transcriptional repressor, MAF bZIP transcription factor G, and nuclear factor, erythroid 2-like 2 proteins in viral infections.
MAX network transcriptional repressor (MAX) directly interacts with c-MYC and MAX network transcriptional repressor proteins, while c-MYC and MAF bZIP transcription factor G (MAFG) interact with nuclear factor, erythroid 2-like 2 (NRF2). These complexes bind to E-box elements in the promoters of c-MYC and MAFG genes, regulating their activation. In addition, c-MYC and MAFG interact with NRF2, and their complexes bind to antioxidant response elements, regulating downstream gene expression. COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019.
- Citation: Zhu DD, Tan XM, Lu LQ, Yu SJ, Jian RL, Liang XF, Liao YX, Fan W, Barbier-Torres L, Yang A, Yang HP, Liu T. Interplay between nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and inflammatory mediators in COVID-19-related liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(22): 2944-2962
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i22/2944.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i22.2944