©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2020; 26(37): 5543-5560
Published online Oct 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i37.5543
Published online Oct 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i37.5543
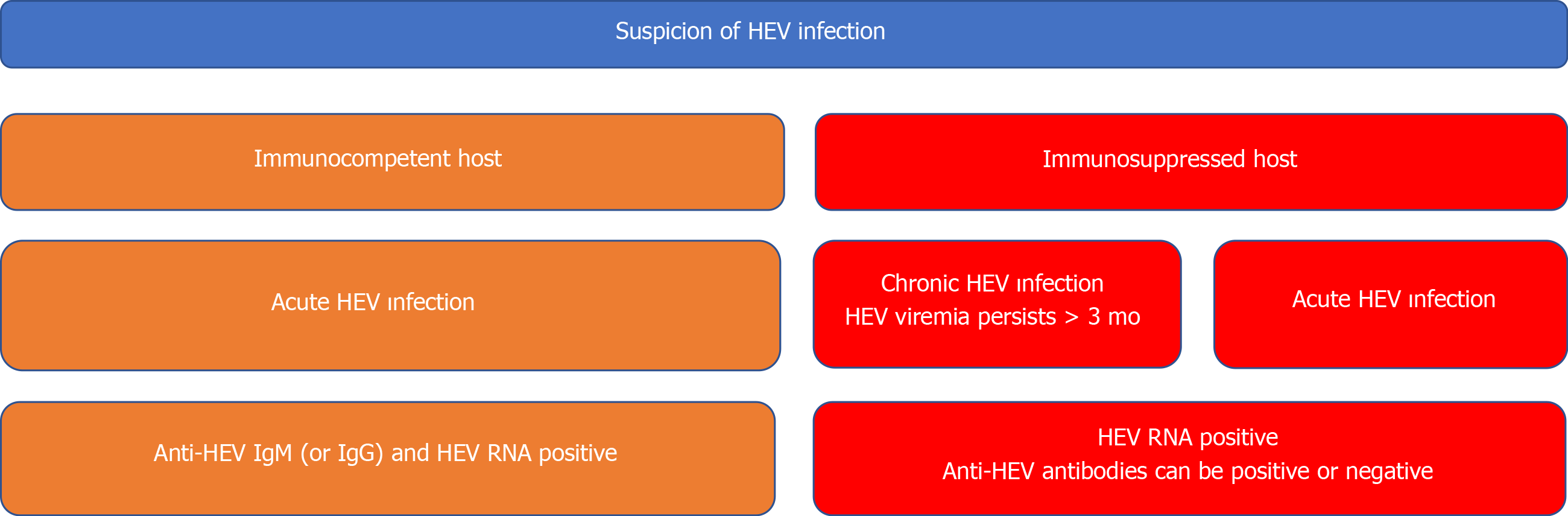
Figure 1 Diagnostic algorithm of hepatitis E virus infection.
For diagnosis of acute hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection in immunocompetent patients, both serologic assays and nucleic acid amplification tests (PCR) should be used in combination. Negative PCR results can be seen in early period of acute infection. On the other hand, serologic tests are not reliable tools in immunosuppressed patients. Therefore, PCR results are much more important in diagnosis of acute infection among these patients. In addition, HEV RNA positivity that is lasting at least 3 mo is accepted as a diagnostic marker for chronic HEV infection in some immunocompromised patients (e.g., solid-organ transplant recipients, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients). HEV: Hepatitis E virus; RNA: Ribonucleic acid; Ig: Immunoglobulin.
- Citation: Aslan AT, Balaban HY. Hepatitis E virus: Epidemiology, diagnosis, clinical manifestations, and treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(37): 5543-5560
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i37/5543.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i37.5543