©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2020; 26(24): 3495-3516
Published online Jun 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i24.3495
Published online Jun 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i24.3495
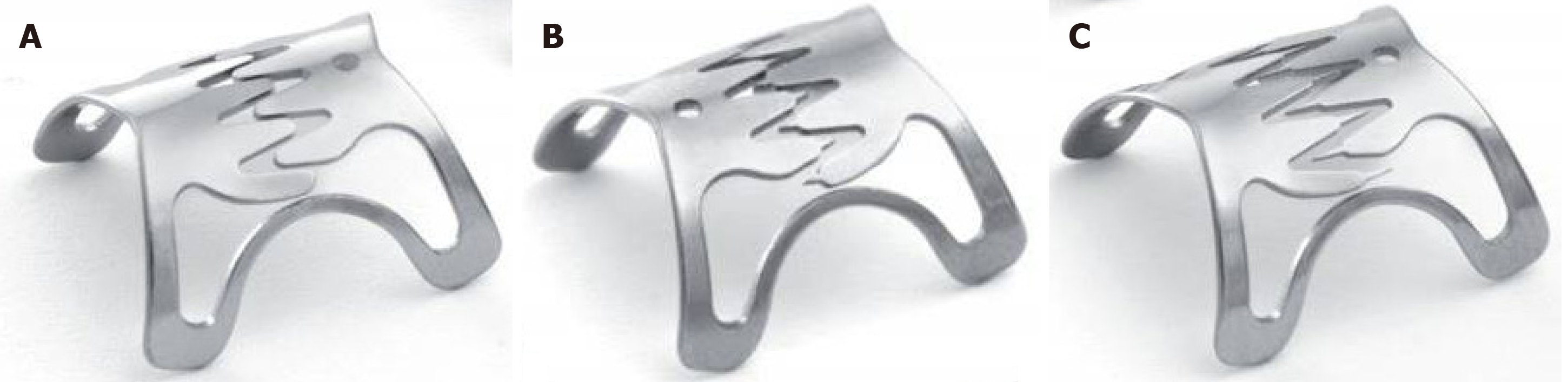
Figure 1 Over-the-scope clip types.
A: Type “atraumatic”; B: Type “traumatic”; C: Type “gastric closure”. Use of images with permission from Ovesco Endoscopy AG (Tübingen, Germany).
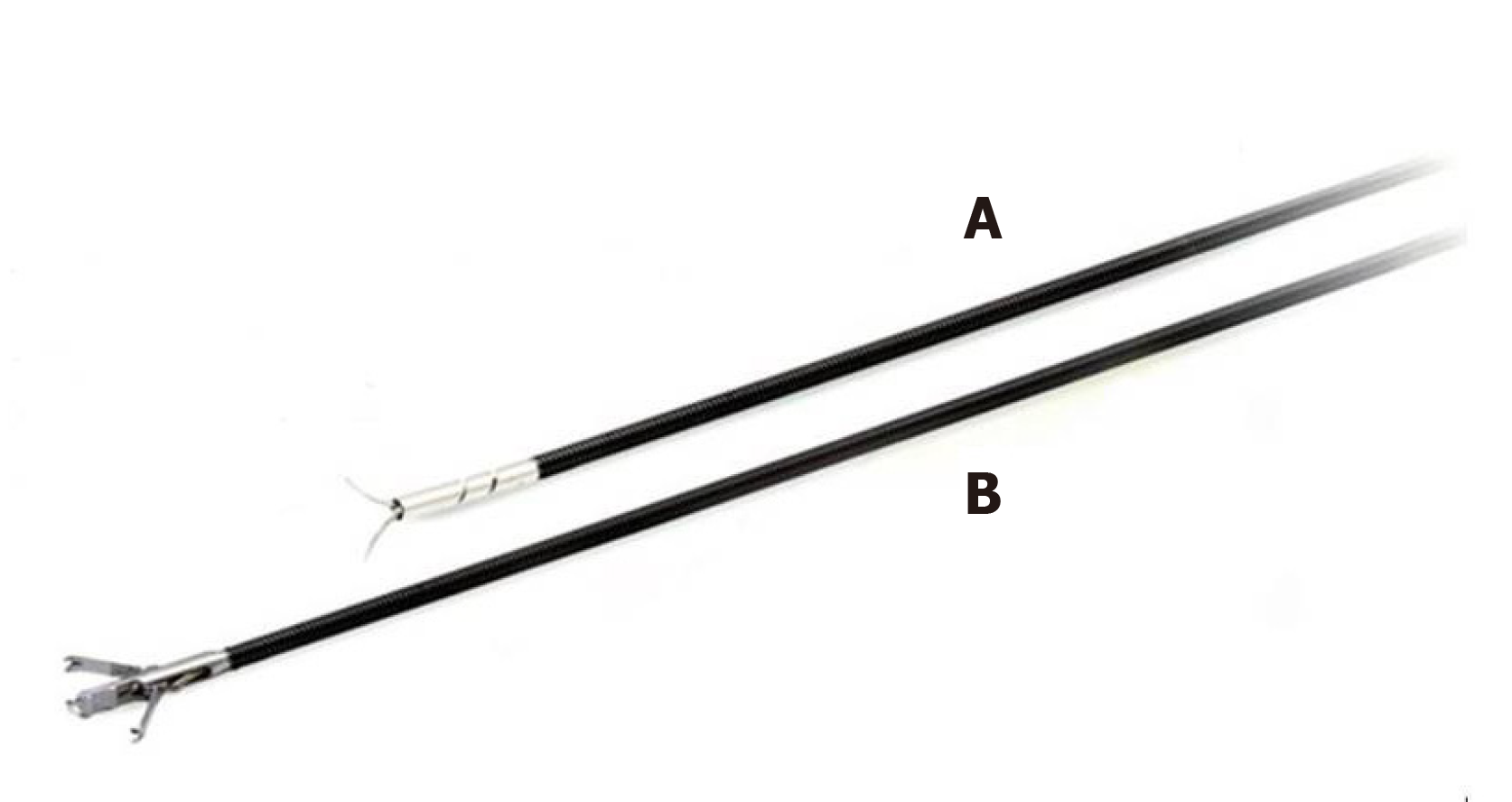
Figure 2 Over the scope clip accessories.
A: Over-the-scope clip Anchor; B: Over-the-scope clip Twin Grasper.
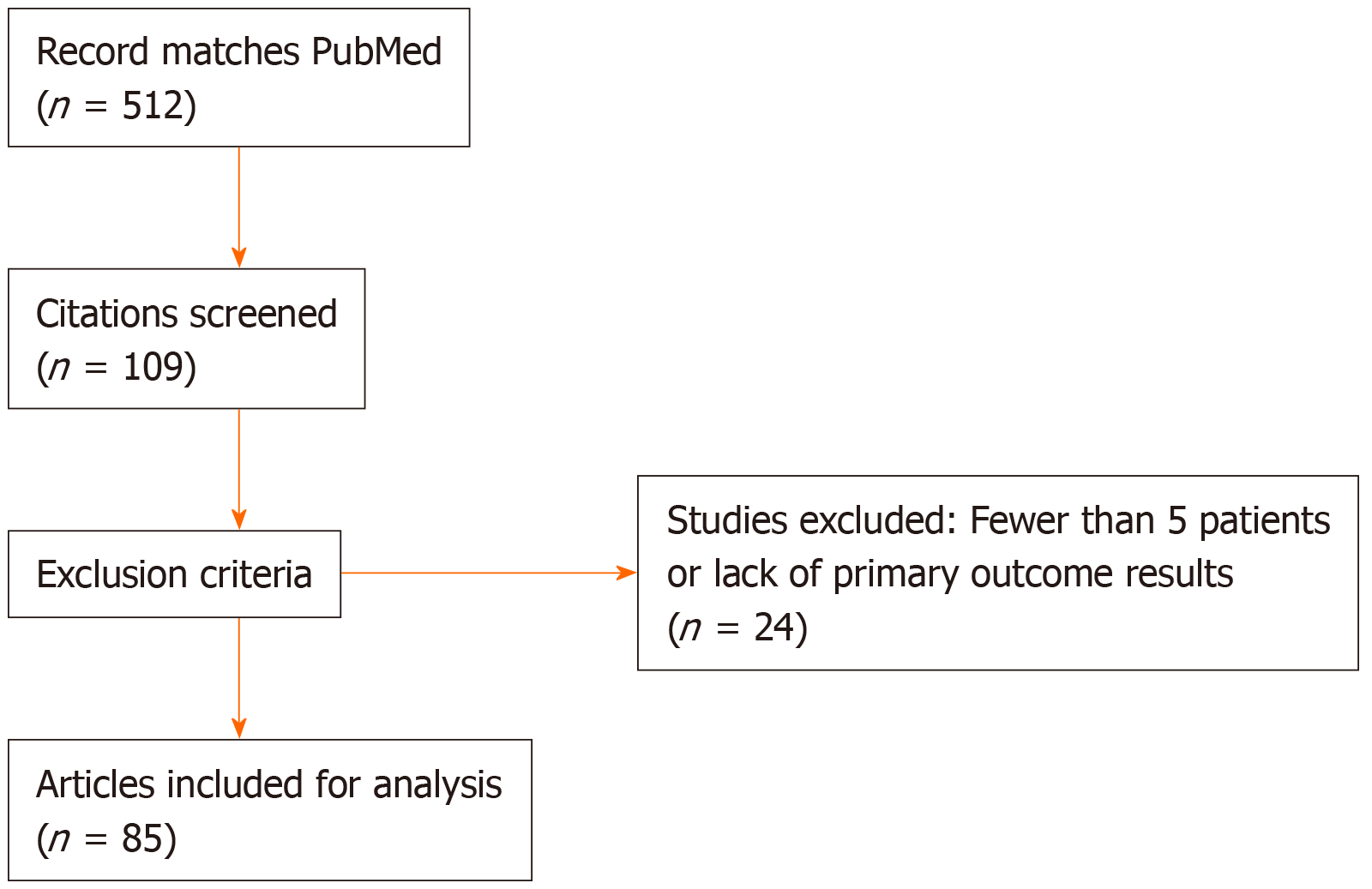
Figure 3 Article selection process, per preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis guideline.
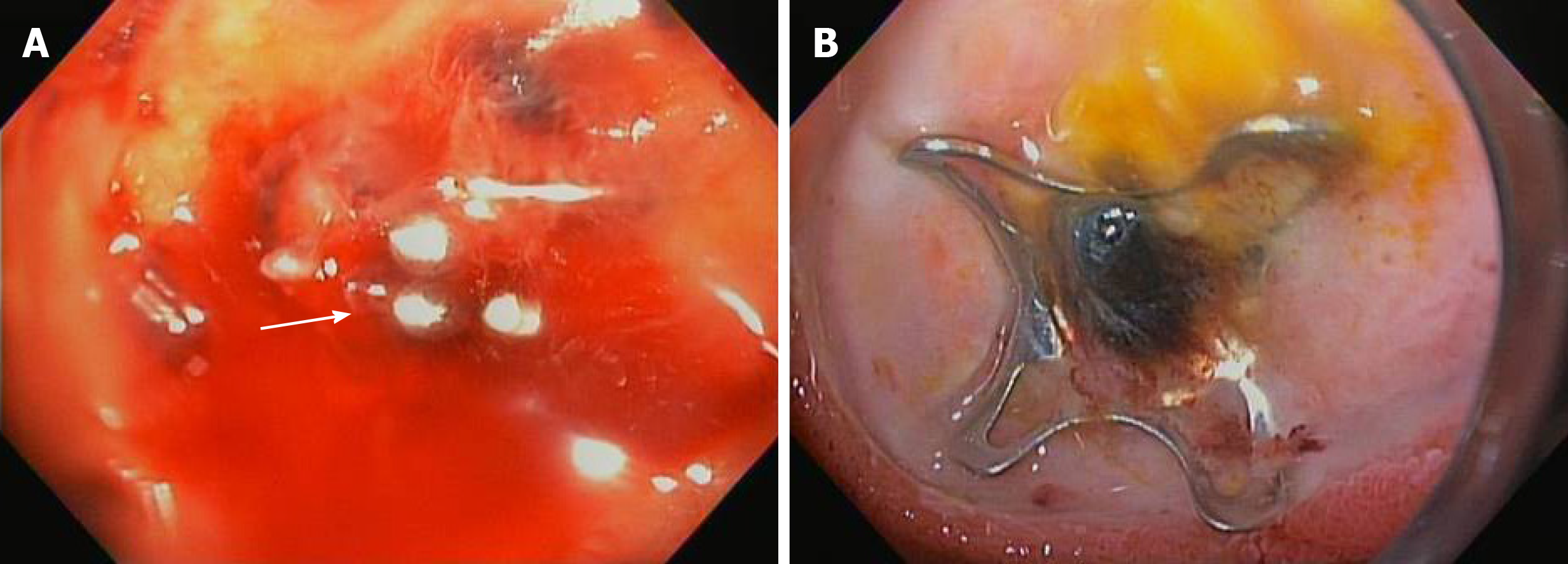
Figure 4 Over the scope clip used in management of gastrointestinal bleeding.
A: Massive gastrointestinal bleeding from duodenal bulb ulcer with an actively bleeding blood vessel; B: Successful hemostasis achieved using over-the-scope-clip.
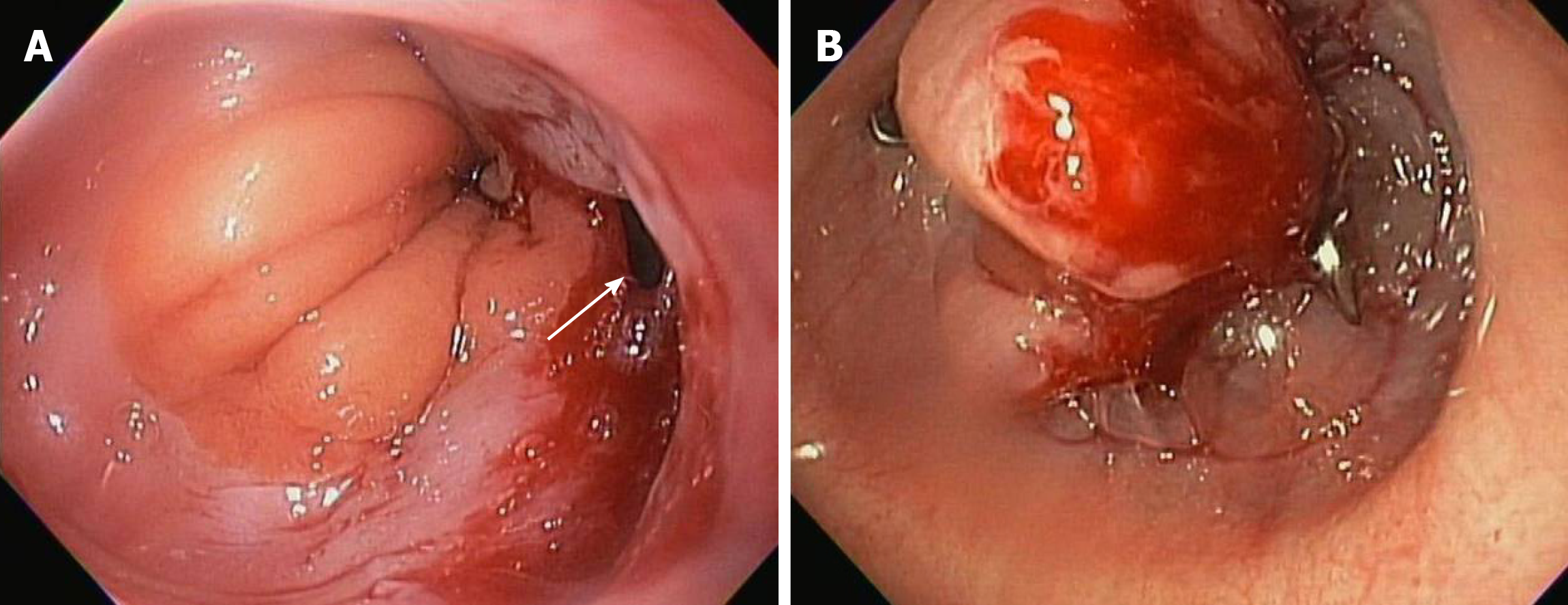
Figure 5 Over the scope clip used in management of gastrointestinal perforation.
A: Gastro-esophageal junction perforation caused during advancement of side viewing duodenoscope; B: Successful closure of perforation using over-the-scope-clip.
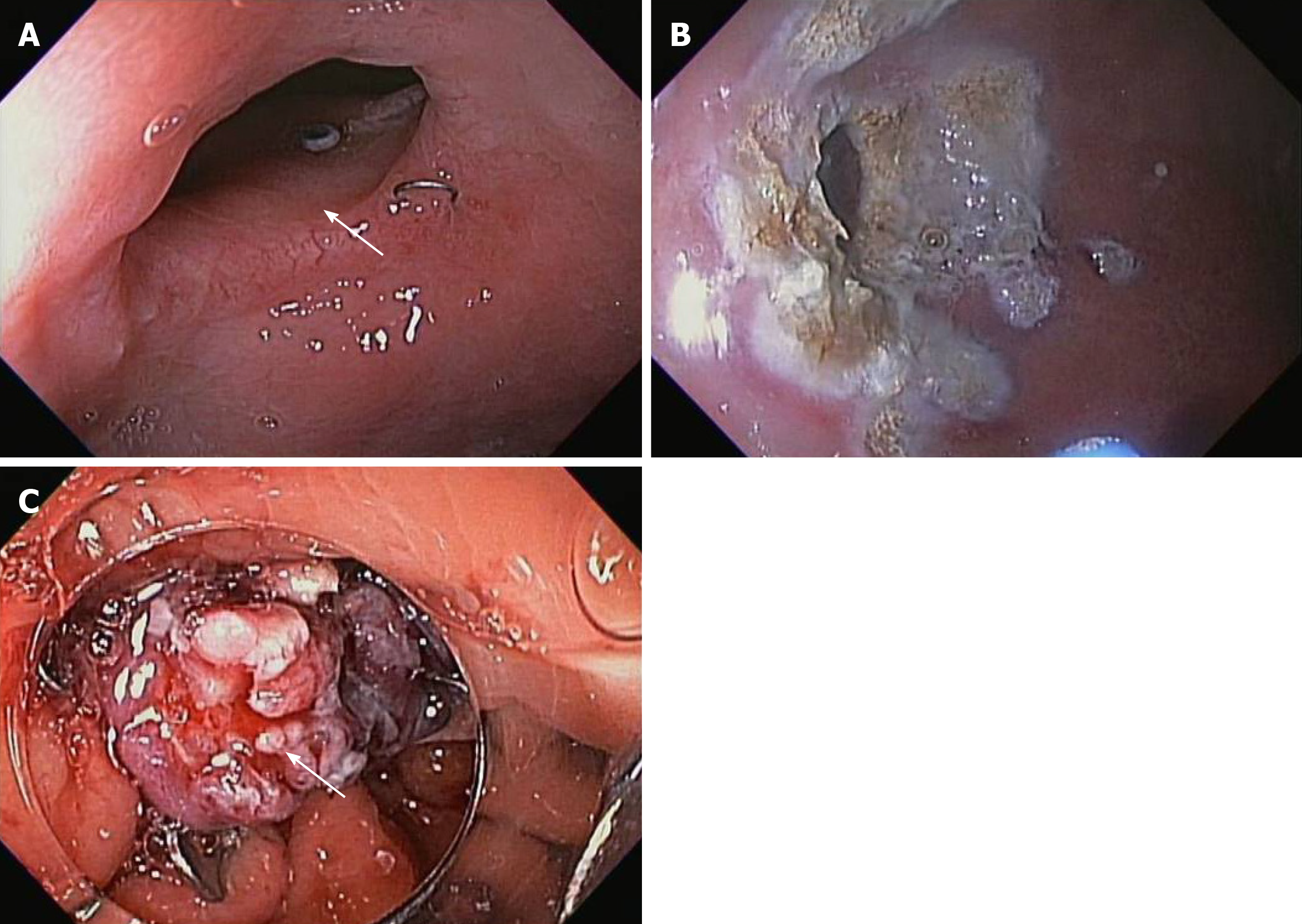
Figure 6 Over the scope clip used in management of gastrointestinal fistula.
A: Gastro-gastric fistula in a patient with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; B: Argon plasma coagulation ablation of the fistula margin; C: Successful closure of fistula using over-the-scope-clip.
- Citation: Bartell N, Bittner K, Kaul V, Kothari TH, Kothari S. Clinical efficacy of the over-the-scope clip device: A systematic review. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(24): 3495-3516
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i24/3495.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i24.3495