©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2020; 26(21): 2810-2820
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2810
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2810
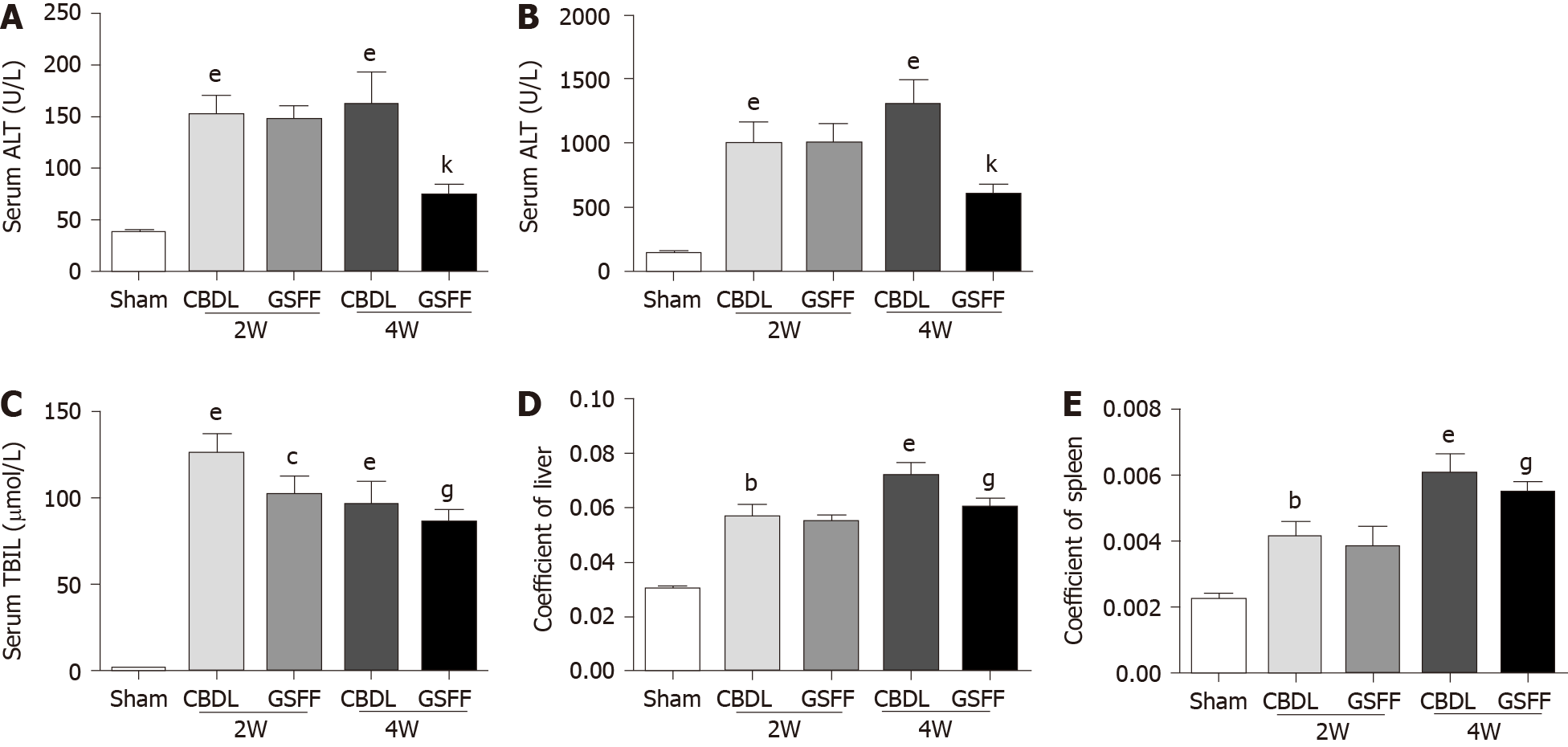
Figure 1 Gan Shen Fu Fangdecreased serum levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase and total bilirubin in common bile duct-ligated rats and the liver and spleen coefficients (n = 8).
A: Alanine aminotransferase level; B: Aspartate aminotransferase level; C: Total bilirubin level; D:Liver coefficient; E: Spleen coefficient. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001, compared with the sham group; cP < 0.05, compared with the 2W-CBDL rats; gP < 0.05, kP < 0.001, compared with the 4W-CBDL rat. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TBIL: Total bilirubin; CBDL: Common bile duct-ligated; GSFF: Gan Shen Fu Fang.
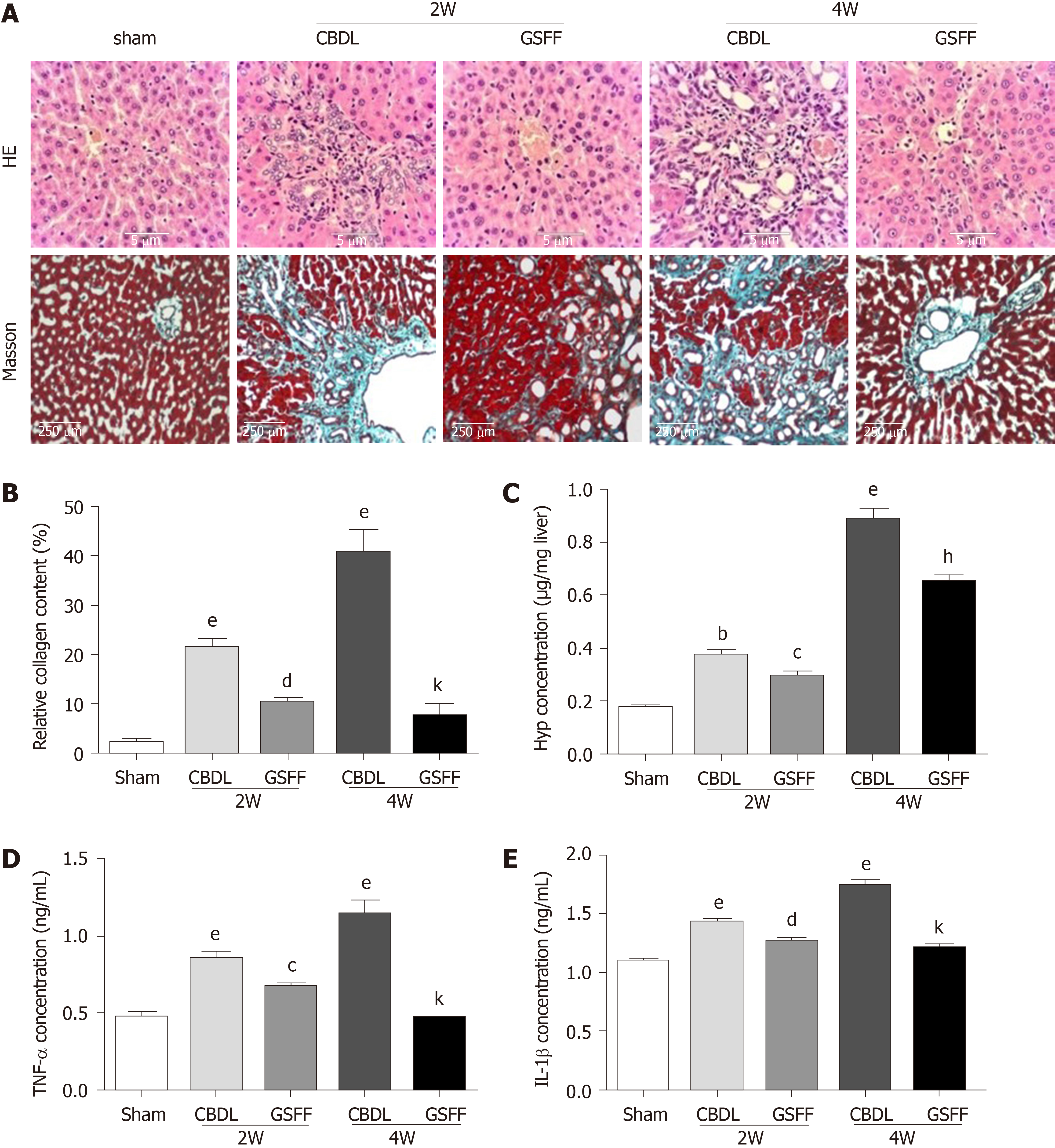
Figure 2 Gan Shen Fu Fang inhibited liver fibrosis and alleviated the inflammatory response.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining and Masson staining of the liver tissue; B: The collagen content was measured by quantitative histomorphometry; C: Hydroxyproline concentration in the liver; D and E: Tumour necrosis factor-α and IL-1β levels in the liver. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001, compared with the sham group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, compared with the 2W-CBDL rats; hP < 0.01, kP < 0.001, compared with the 4W-CBDL rats. HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; CBDL: Common bile duct-ligated; GSFF: Gan Shen Fu Fang; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; Hyp: Hydroxyproline.
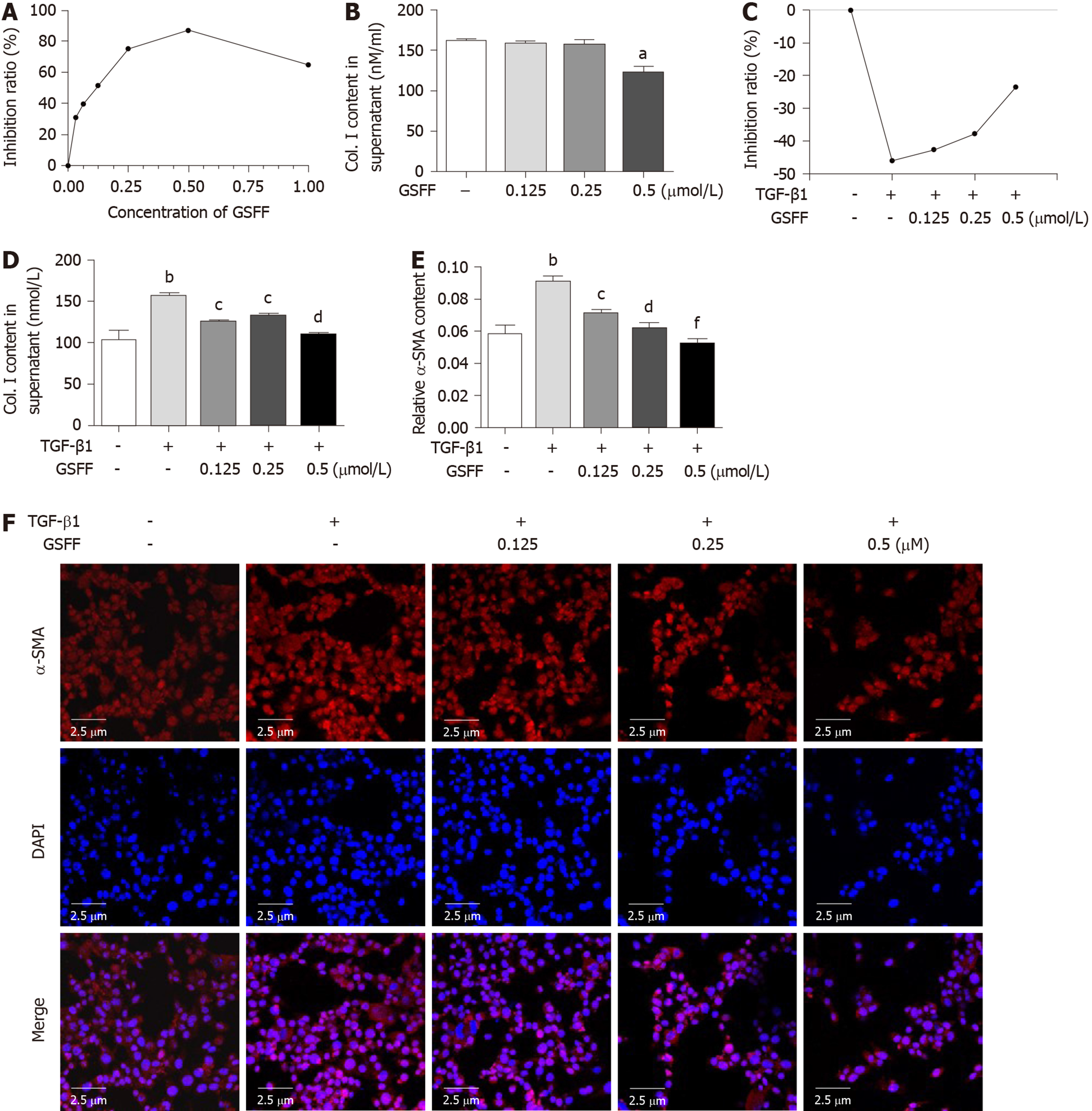
Figure 3 Gan Shen Fu Fang inhibited HSC-T6 cell viability and collagen synthesis.
A and B: GSFF inhibited HSC-T6 cell viability and Col. I release; C and D: GSFF inhibited the viability and Col. I release of HSC-T6 cells stimulated with transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1); E and F: TGF-β1 promoted α-SMA expression in HSC-T6 cells, which was decreased by GSFF. The relative α-SMA content was measured by quantitative histomorphometry, and the results are shown in panel E. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, compared with the control cells. cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, fP < 0.001, compared with cells stimulated with TGF-β1 only. GSFF: Gan Shen Fu Fang; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor β1.
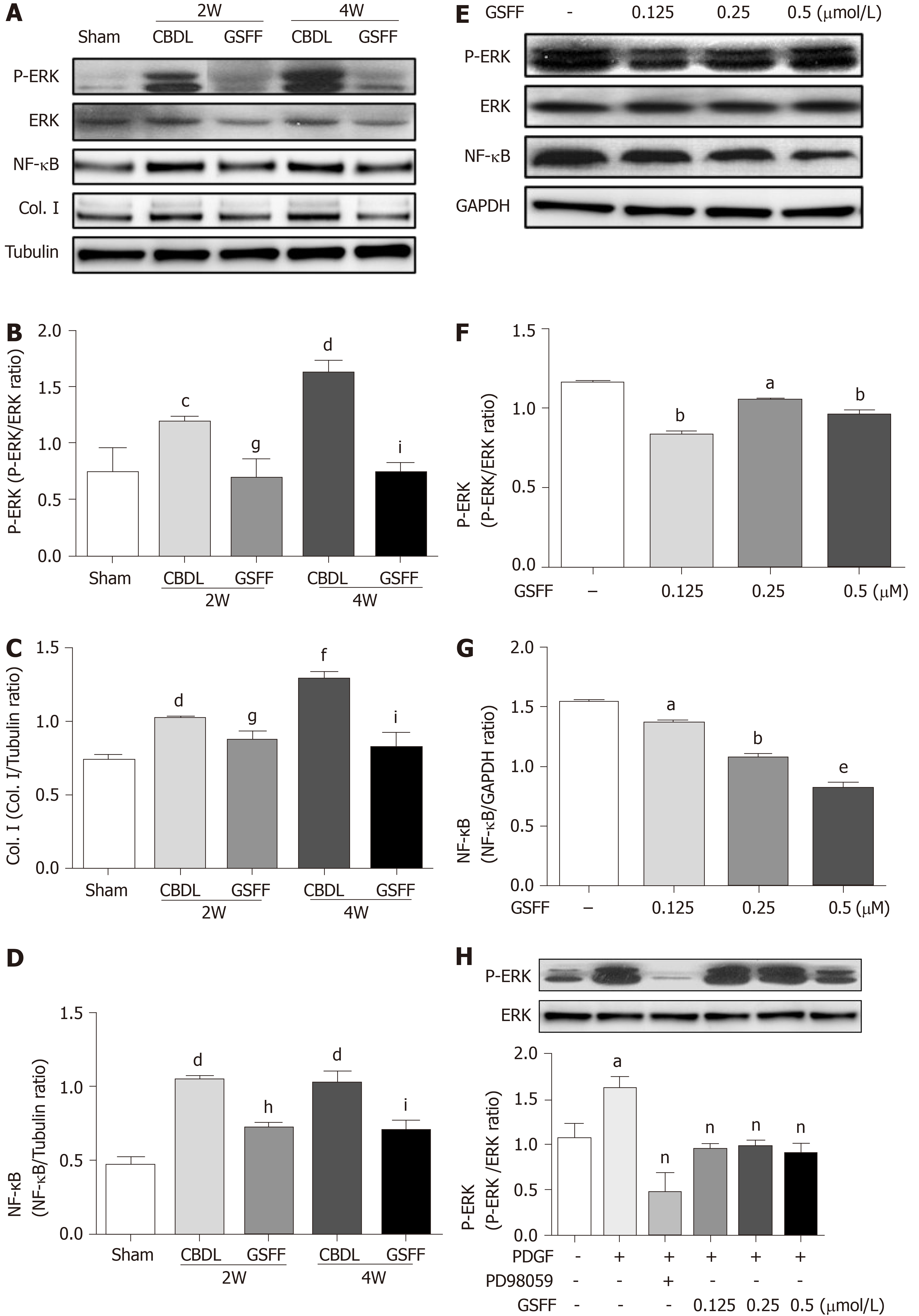
Figure 4 Gan Shen Fu Fang reduced extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation and NF-κB expression in common bile duct-ligated rats and HSC-T6 cells.
A-D: Liver tissue homogenates were subjected to immunoblotting as indicated. Representative bans and quantitative data are shown. N = 4; E-G: HSC-T6 cells were not stimulated, and whole-cell lysates were used. Representative images and quantitative data are shown; H: HSC-T6 cells were stimulated with platelet-derived growth factor-BB to further evaluate the effect of GSFF on extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001, compared with control cells; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 compared with sham rats. gP < 0.05, hP < 0.01 compared with the 2W-CBDL rats; iP < 0.05, lP < 0.001, compared with the 4W-CBDL rats; nP <0.01, compared with cells stimulated with only platelet-derived growth factor-BB. PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; GSFF: Gan Shen Fu Fang; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; CBDL: Common bile duct-ligated.
- Citation: Du QH, Zhang CJ, Li WH, Mu Y, Xu Y, Lowe S, Han L, Yu X, Wang SY, Li Y, Li J. Gan Shen Fu Fang ameliorates liver fibrosis in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting the inflammatory response and extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(21): 2810-2820
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i21/2810.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2810