©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2020; 26(21): 2740-2757
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2740
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2740
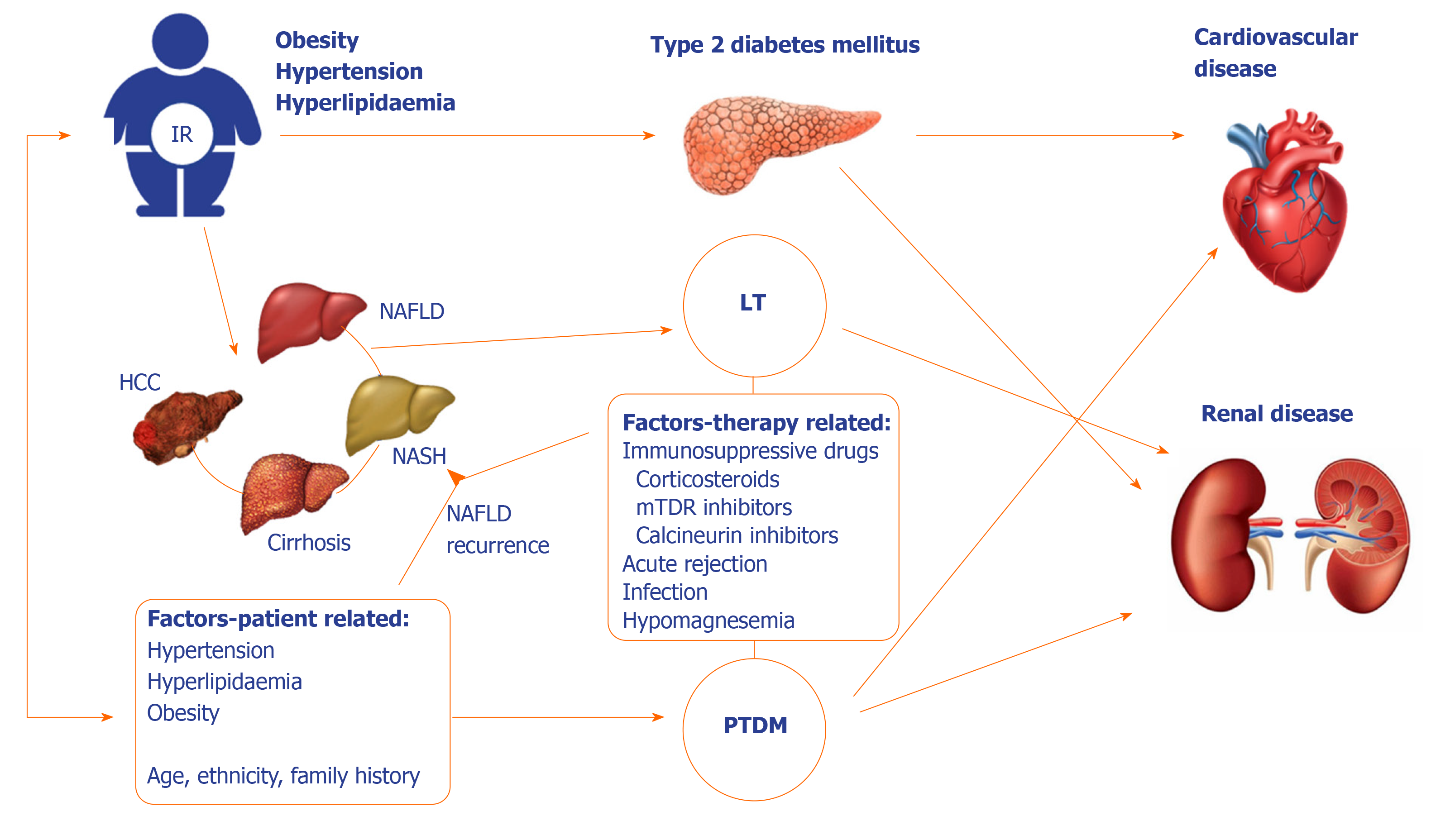
Figure 1 A complex relationship between liver disease and diabetes mellitus.
Although in case of diabetes mellitus following liver cirrhosis glycemia might improve after liver transplantation (LT), this may not be the case in the preexisting type 2 diabetes mellitus. Moreover, diabetes can develop following LT (post-transplant diabetes mellitus) due to different patient and procedure-related factors. Both diabetes and liver disease after transplant increase the cardiovascular risk, which is the main cause of mortality in the long-term follow-up. LT: Liver transplantation; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; PTDM: Post-transplant diabetes mellitus; IR: Insulin resistance; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Cigrovski Berkovic M, Virovic-Jukic L, Bilic-Curcic I, Mrzljak A. Post-transplant diabetes mellitus and preexisting liver disease - a bidirectional relationship affecting treatment and management. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(21): 2740-2757
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i21/2740.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2740