©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2020; 26(19): 2349-2373
Published online May 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2349
Published online May 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2349
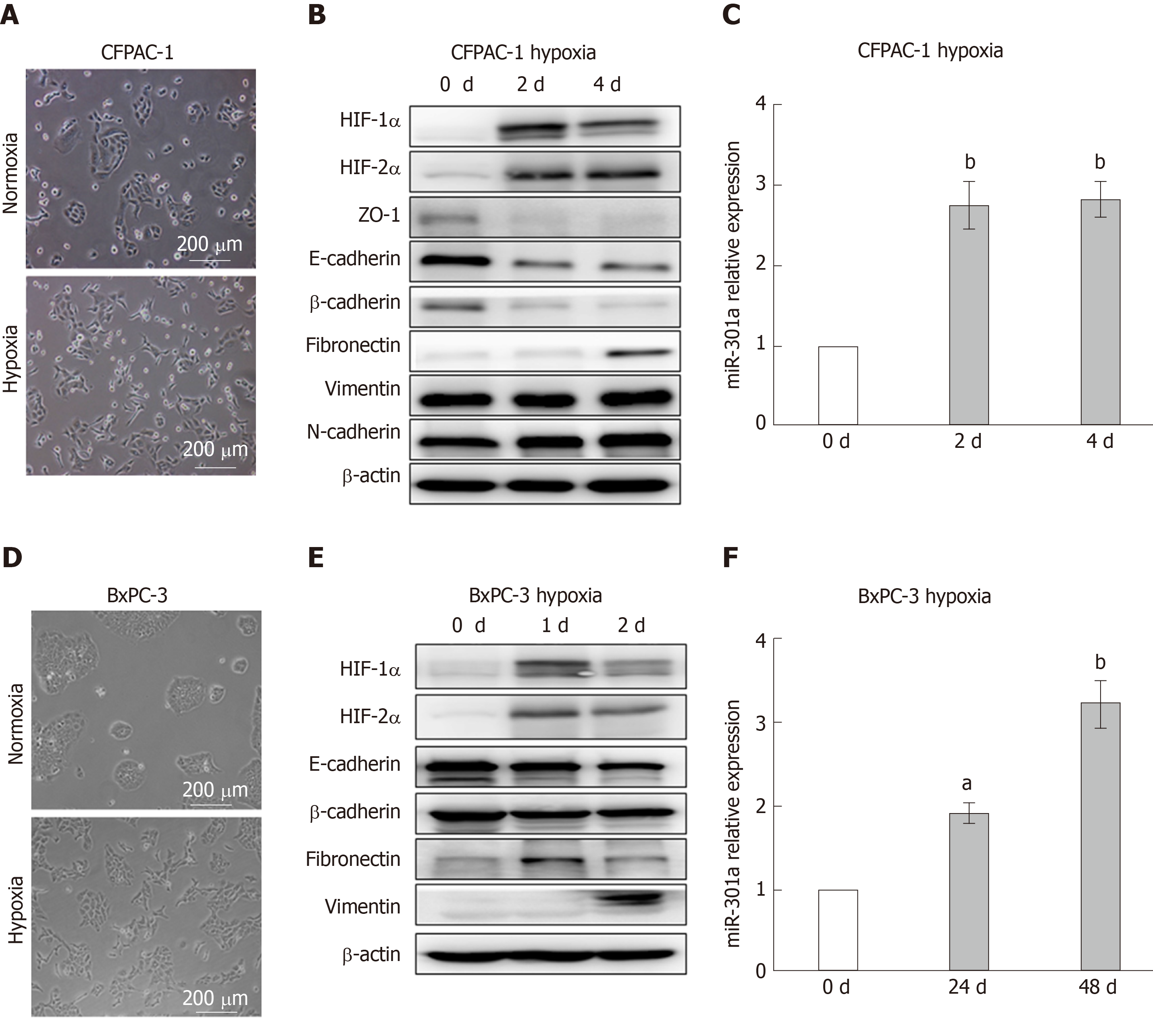
Figure 1 Hypoxia induces pancreatic cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increases miR-301a expression.
A and D: Phase-contrast photomicrographs. Notably, CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 cells cultured under normoxia exhibit a typical epithelial morphology, whereas cells cultured under hypoxia for 48 h exhibit a typical mesenchymal morphology; B and E: Western blot analysis was performed to detect hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, HIF-2α, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers. The expression levels of HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and the mesenchymal markers (Vimentin and Fibronectin) in hypoxia-cultured CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 cells were higher than the levels in normoxia-cultured cells, while the expression levels of the epithelial markers (E-cadherin and β-catenin) were lower under hypoxia than under normoxia; C and F: qRT-PCR was used to measure the expression of miR-301a. The expression of miR-301a was higher in hypoxia-cultured CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 cells than in the normoxia-cultured cells. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor.
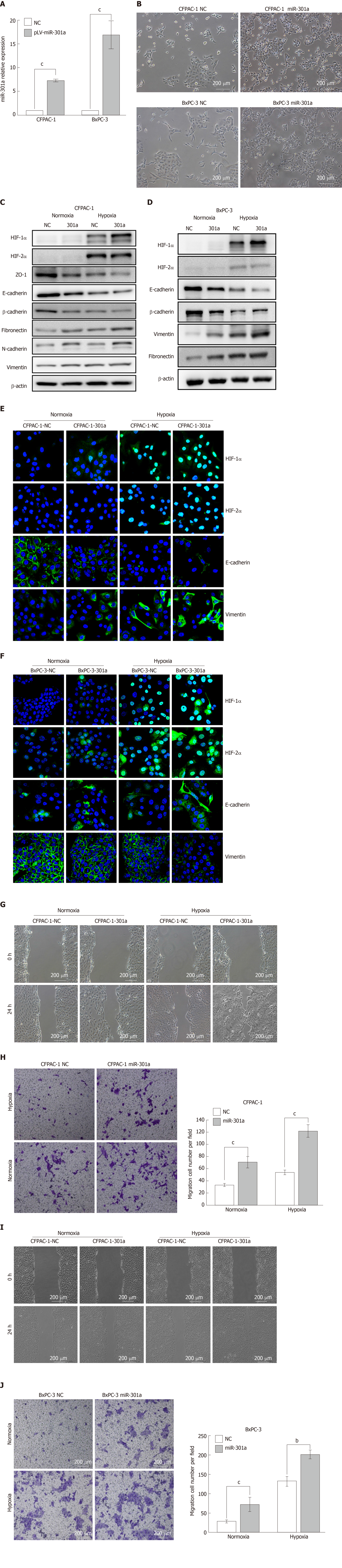
Figure 2 Upregulation of miR-301a promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells.
A: MiR-301a was upregulated in CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 cells; B: MiR-301a upregulation promoted the transition of the CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 cells from an epithelial morphology to a mesenchymal morphology; C and D: Western blot analysis was performed to detect the protein expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, HIF-2α, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers; the expression of HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and the epithelial markers (E-cadherin and β-catenin) was upregulated in miR-301a-overexpressing cells, while the expression of the mesenchymal markers was downregulated; E and F: Immunofluorescence was performed to detect the protein expression of HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 cells; the expression of HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and E-cadherin was upregulated in miR-301a-overexpressing cells, while the expression of the mesenchymal markers (Vimentin) was downregulated. HIF-1α protein accumulation in the nuclei of the tumor cells was more obvious in the miR-301a-overexpressing group than in the control group; G-J: Wound healing assays and Transwell assays were performed to measure CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 migration; miR-301a overexpression improved CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 migration under normoxia and hypoxia. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor.
Figure 3 MiR-301a knockout results in the suppression of hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
A: To identify miR-301a knockout cell lines, the amplification product was tested by gel electrophoresis after amplifying the miR-301a flanking sequence; B: Sanger sequencing showed that the No. 2 monoclonal cell line had 169 bases, including the miR-301a sequence, deleted from the genome; C: qRT-PCR was used to measure miR-301a expression in PANC-1 cells after miR-301a knockout; D: HIF-1α was downregulated in the miR-301a knockout cells cultured under hypoxia for 48 h; miR-301a knockout in PANC-1 cells promoted the expression of the epithelial markers (E-cadherin and ZO-1) and inhibited the expression of the mesenchymal markers (Fibronectin and Vimentin); E: The mesenchymal morphological changes of the pancreatic cancer cells under hypoxia were blocked after miR-301a was knocked out; F and G: Transwell assays and wound healing assays showed that PANC-1 cell migration was suppressed after miR-301a was knocked out. cP < 0.001.
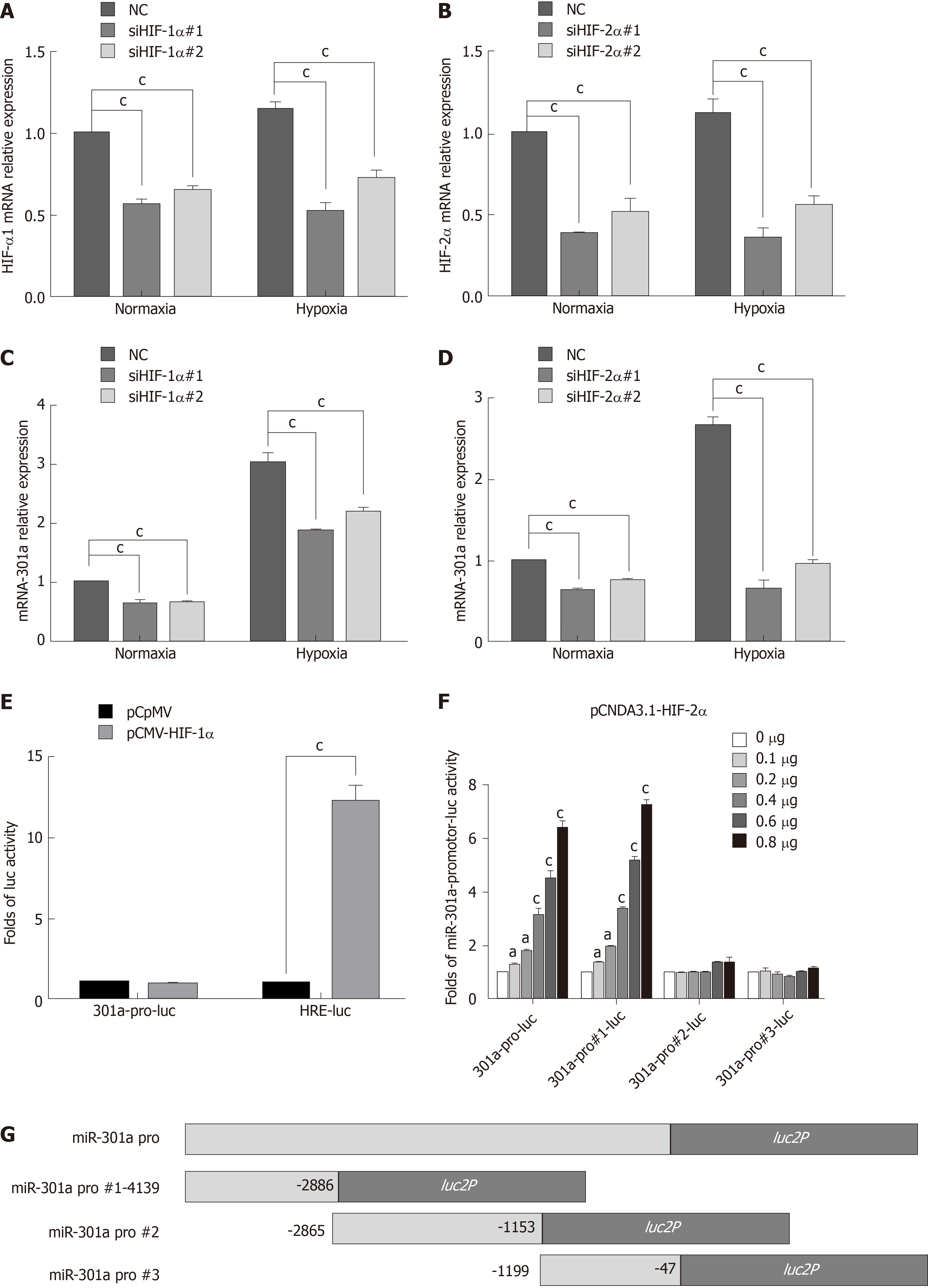
Figure 4 Knockdown of HIF-1α or HIF-2α by siRNA interference and detection of miR-301a expression by qRT-PCR.
A and B: After cells were transfected with siRNA, real-time PCR was performed to measure the mRNA expression levels of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α in CFPAC-1 cells; C and D: Real-time RCR was performed to measure miR-301a expression after the knockdown of HIF-1α and HIF-2α; E: HIF-1α significantly promoted luciferase activity in the positive control group (HRE-Luc) but had no effect on the activity of the miR-301a promoter; F: Transfections with different doses of the HIF-2α plasmids significantly promoted miR-301a promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner; G: Transfection with HIF-2α significantly promoted the transcriptional activity of the truncated No. 1 miR-301a promoter in a dose-dependent manner but had no effect on the truncated No. 2 and No. 3 promoters. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. HIF: Hypoxia-inducible factor.
Figure 5 MiR-301a directly targets TP63 in pancreatic cancer.
A: Prediction of miR-301a binding to the 3’ untranslated region (3’UTR) of TTP; B: Luciferase reporter assays confirmed that P63 was a miR-301a target gene; C: Immunofluorescence was performed to detect the expression of P63 in miR-301a-upregulated cell lines under normoxia and hypoxia; D and E: Western blot was performed to detect the expression of P63 protein after the overexpression and knockout of miR-301a; G: The expression of TP63 and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers were detected in the miR-301a-upregulated BxPC-3 cell line by Western blot, and (F) Transwell assays were performed to measure cell migration; H: TP63 was knocked down in the miR-301a knockout cell line PANC-1, and (F) Transwell assays were performed to measure cell migration. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
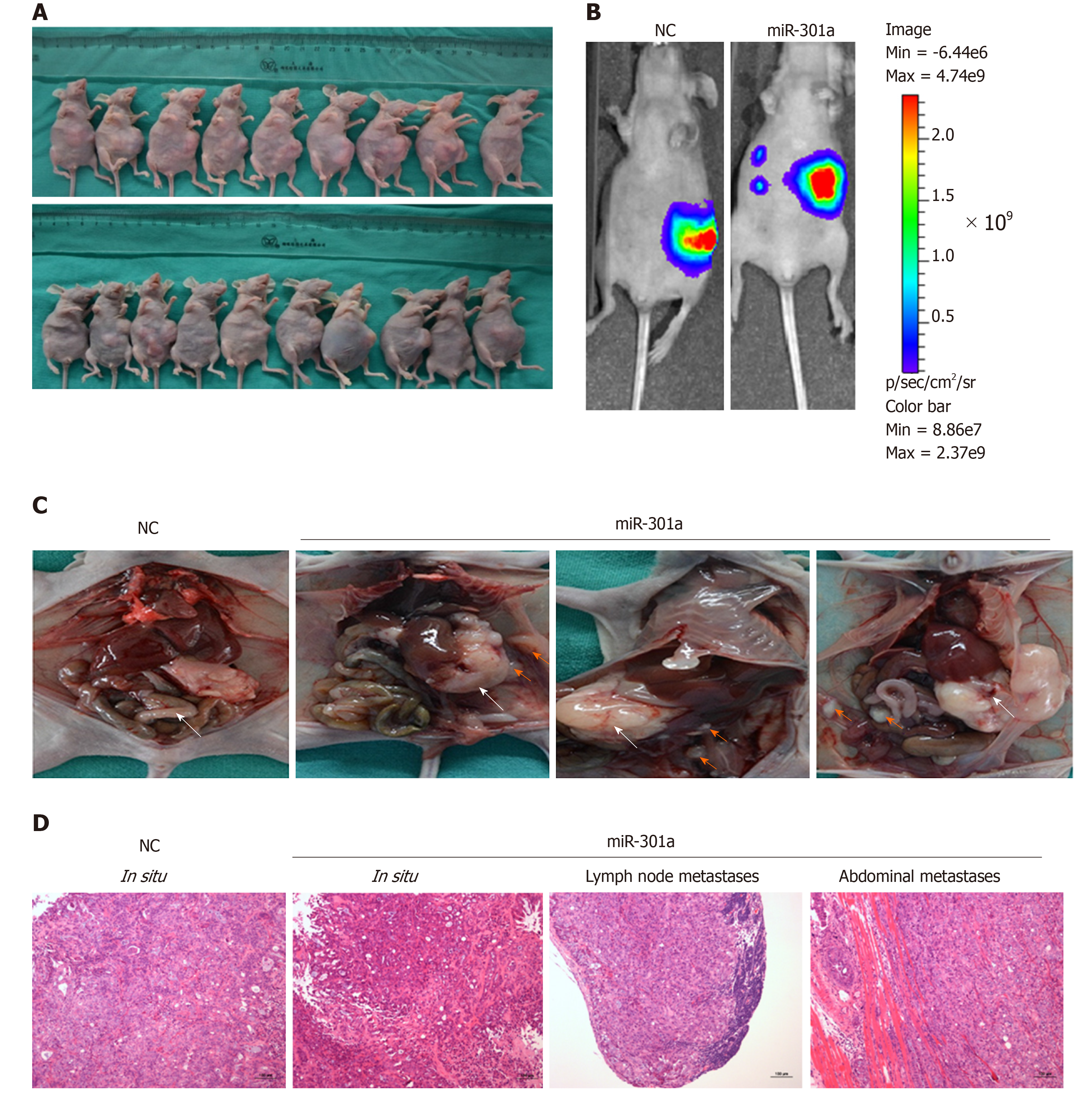
Figure 6 MiR-301a overexpression promotes the metastasis of CFPAC-1 cells in vitro.
A: Photographs of the orthotopic implantation of pancreatic cancer cells in nude mice; B: Tumor formation and metastasis were assessed with BLI measurements. Metastasis occurred in the miR-301a overexpression group; C: MiR-301a accelerated the local invasion, lymph node metastasis, and distant metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells; D: HE staining of tumor tissues and metastatic tissues.
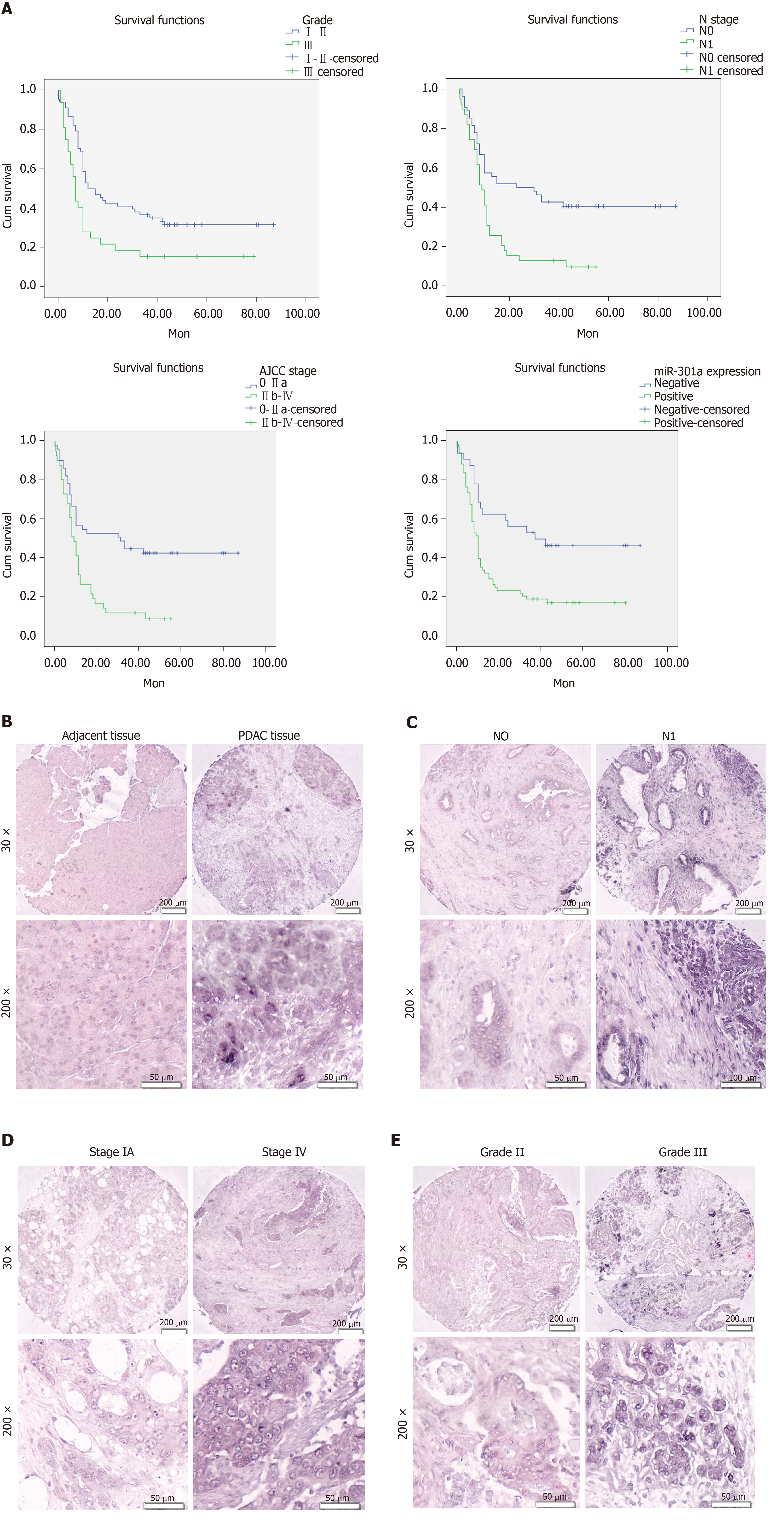
Figure 7 Prognostic significance of miR-301a expression and clinicopathological features (A), and in situ hybridization detecting the expression of miR-301a in a pancreatic cancer tissue microarray (B-E).
- Citation: Zhang KD, Hu B, Cen G, Yang YH, Chen WW, Guo ZY, Wang XF, Zhao Q, Qiu ZJ. MiR-301a transcriptionally activated by HIF-2α promotes hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting TP63 in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(19): 2349-2373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i19/2349.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2349