©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2020; 26(15): 1775-1791
Published online Apr 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i15.1775
Published online Apr 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i15.1775
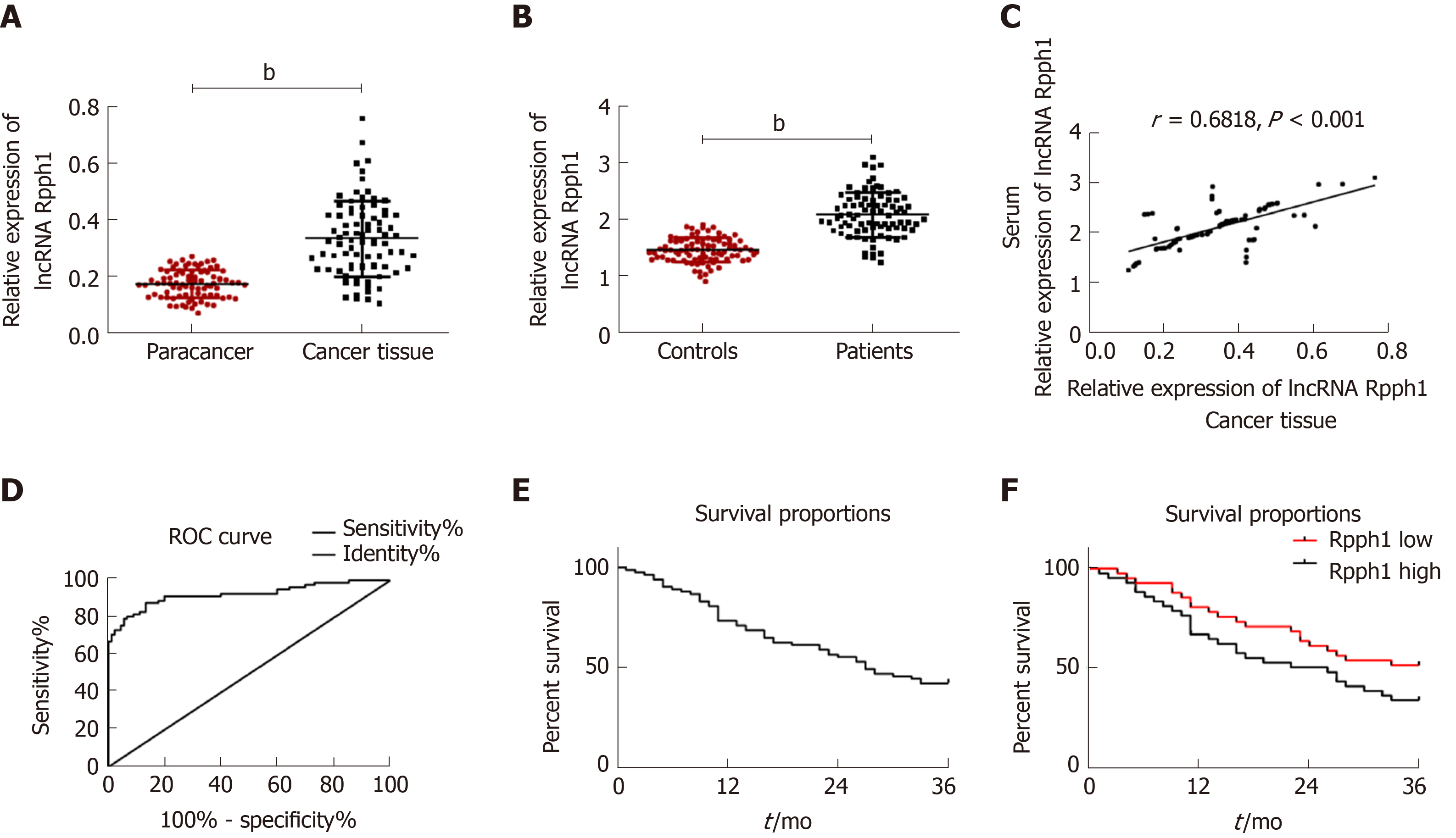
Figure 1 Expression of long non-coding RNA Rpph1 in esophageal cancer and its clinical value.
A: Expression of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) Rpph1 in esophageal cancer tissues and adjacent tissues; B: Serum expression of lncRNA Rpph1 in esophageal cancer patients and healthy participants; C: Correlation between serum lncRNA Rpph1 expression and lncRNA Rpph1 expression in tissue; D: ROC analysis of the diagnostic value of serum lncRNA Rpph1 for patients with esophageal cancer; E: Survival curve analysis of patients with esophageal cancer; F: Survival curves of the Rpph1 high expression group and low expression group.
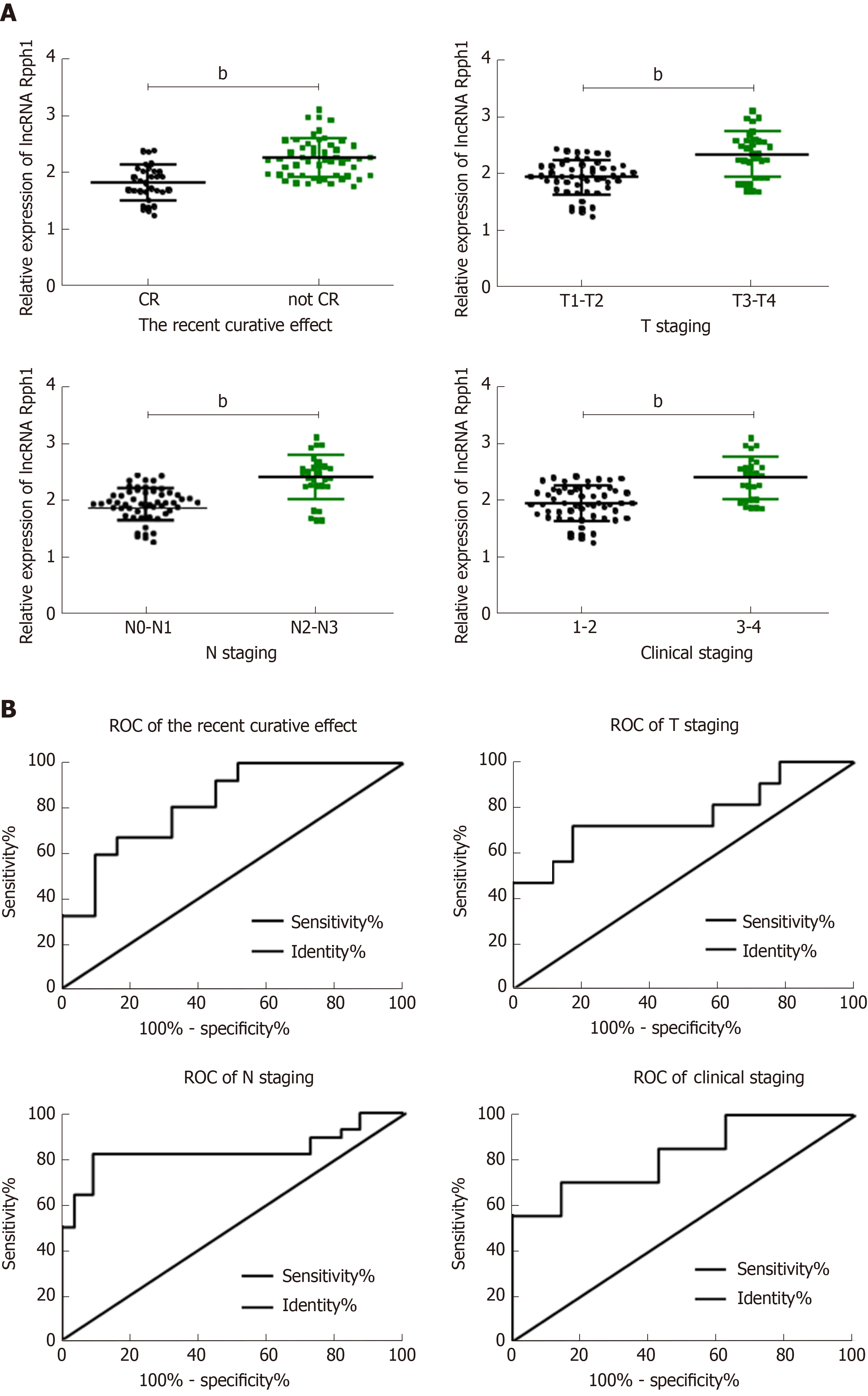
Figure 2 Relationship between long non-coding RNA Rpph1 expression and clinicopathological features of esophageal cancer.
A: Relationship between long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) Rpph1 and short-term response, T stage, N stage, and clinical stages; B: Diagnostic value of lncRNA Rpph1 for short-term response, T stage, N stage, and clinical stages. Note: b indicates bP < 0.001 when the two groups were compared.
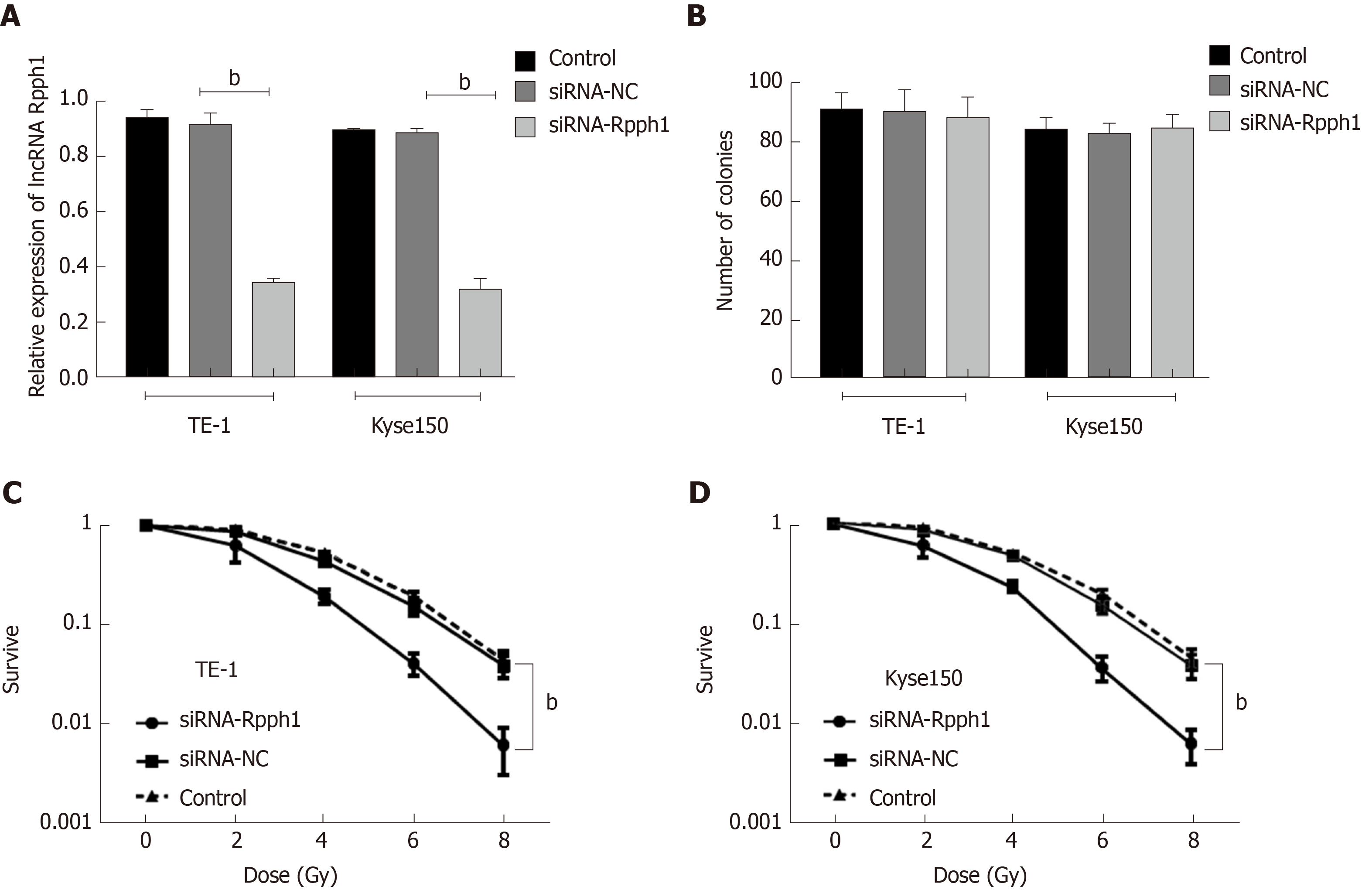
Figure 3 Effect of long non-coding RNA Rpph1 on cancer cell sensitivity to radiotherapy.
A: Expression of Rpph1 in esophageal cancer cell lines TE-1 and Kyse150 in different transfection groups; B: Role of Rpph1 on cell colonies; C: Effect of Rpph1 on the survival of TE-1 and Kyse150 cells after radiotherapy. bP < 0.001 when the two groups were compared.
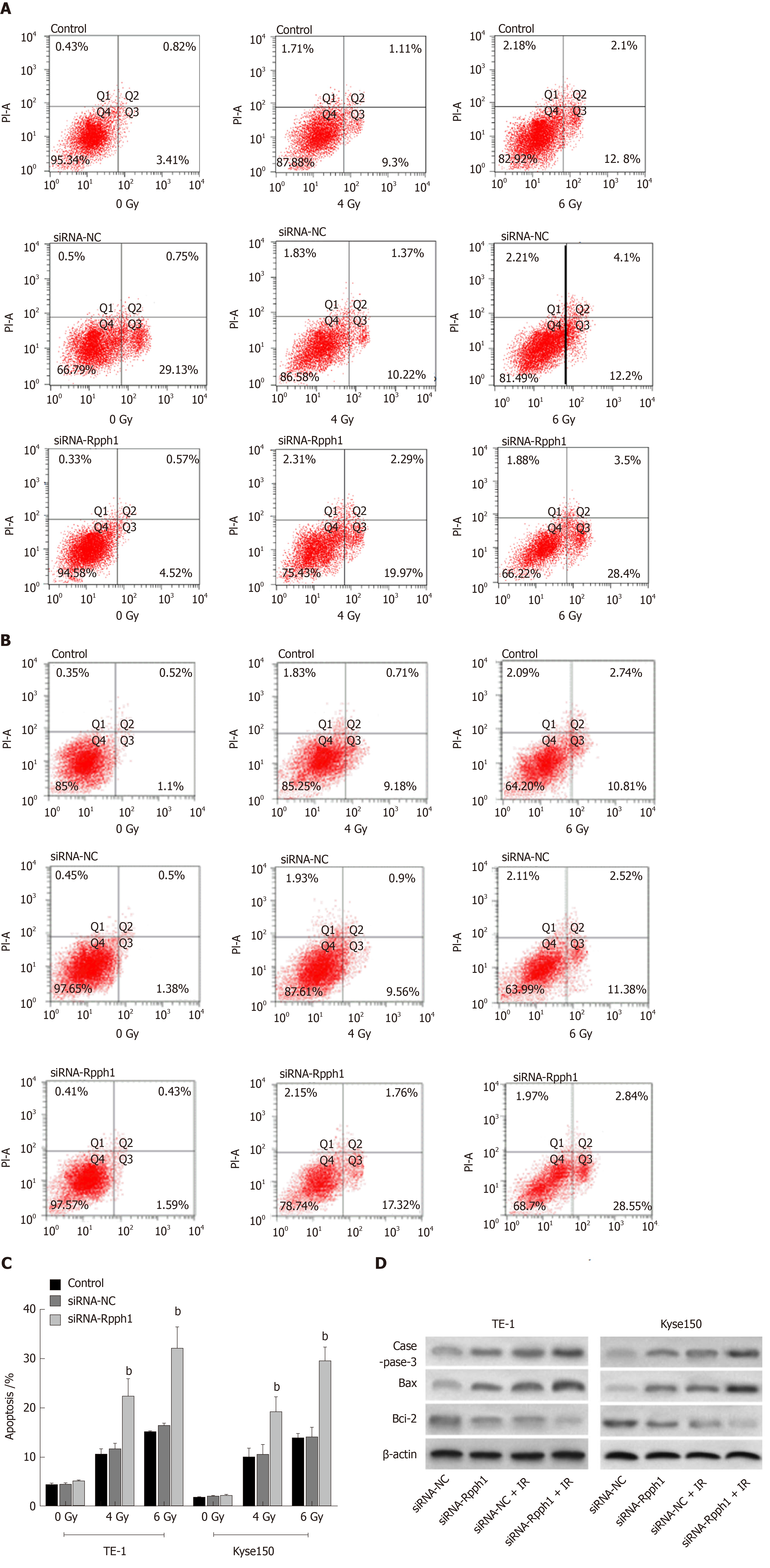
Figure 4 Effect of long non-coding RNA Rpph1 on radiation-induced apoptosis and apoptosis proteins.
A: Apoptosis of TE-1 cells after irradiation; B: Apoptosis of Kyse150 cells after irradiation; C: Comparison of apoptosis rate in esophageal cancer cells between different transfection groups; D: Expression of apoptosis-related proteins in esophageal cancer cells after irradiation. bP < 0.001 when the two groups were compared.
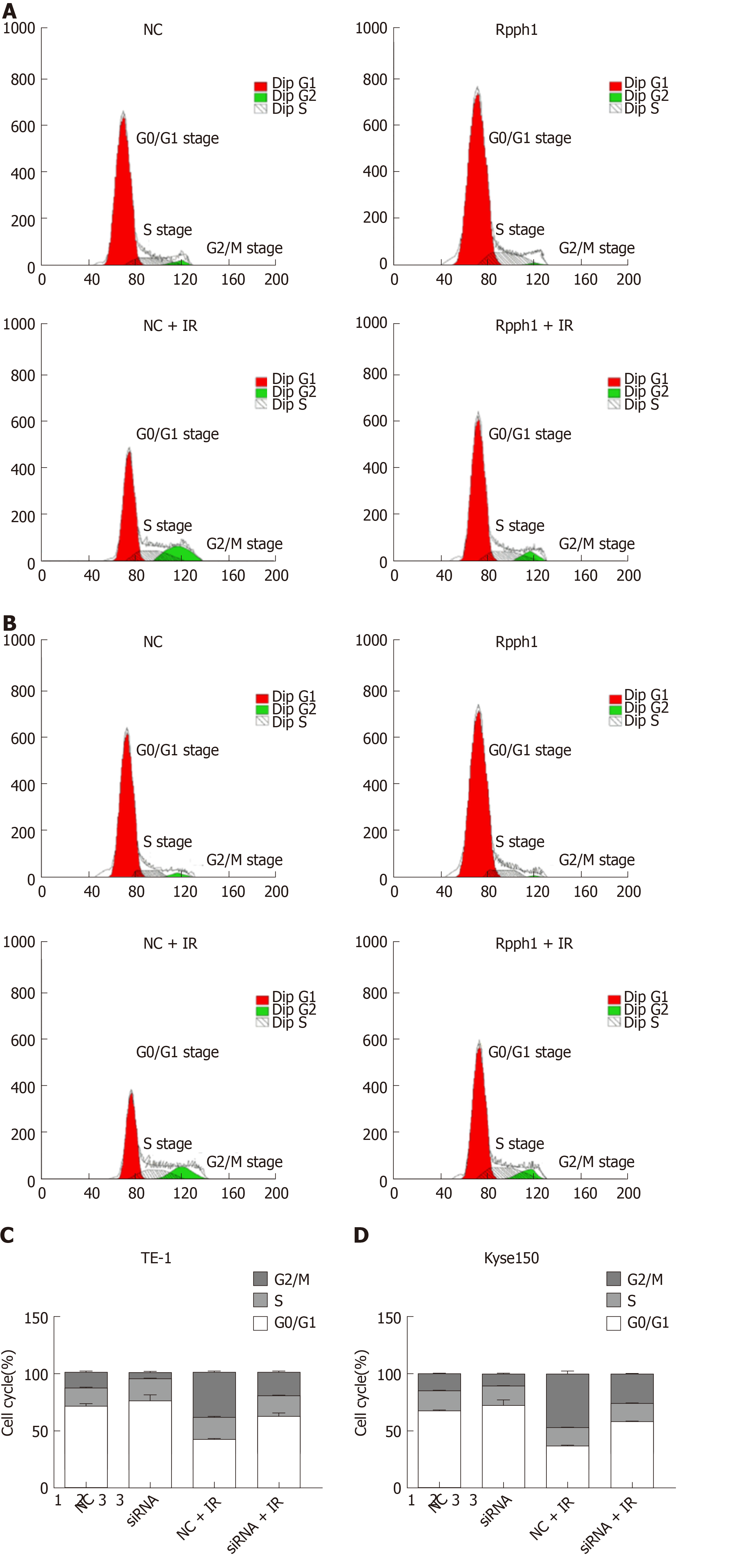
Figure 5 Effect of long non-coding RNA Rpph1 on radiation-induced cell cycle.
A: Changes in cell cycle of TE-1 cells; B: Changes in cell cycle of Kyse150 cells; C: Cell cycle distribution of TE-1 cells; D: Cell cycle distribution of Kyse150 cells.
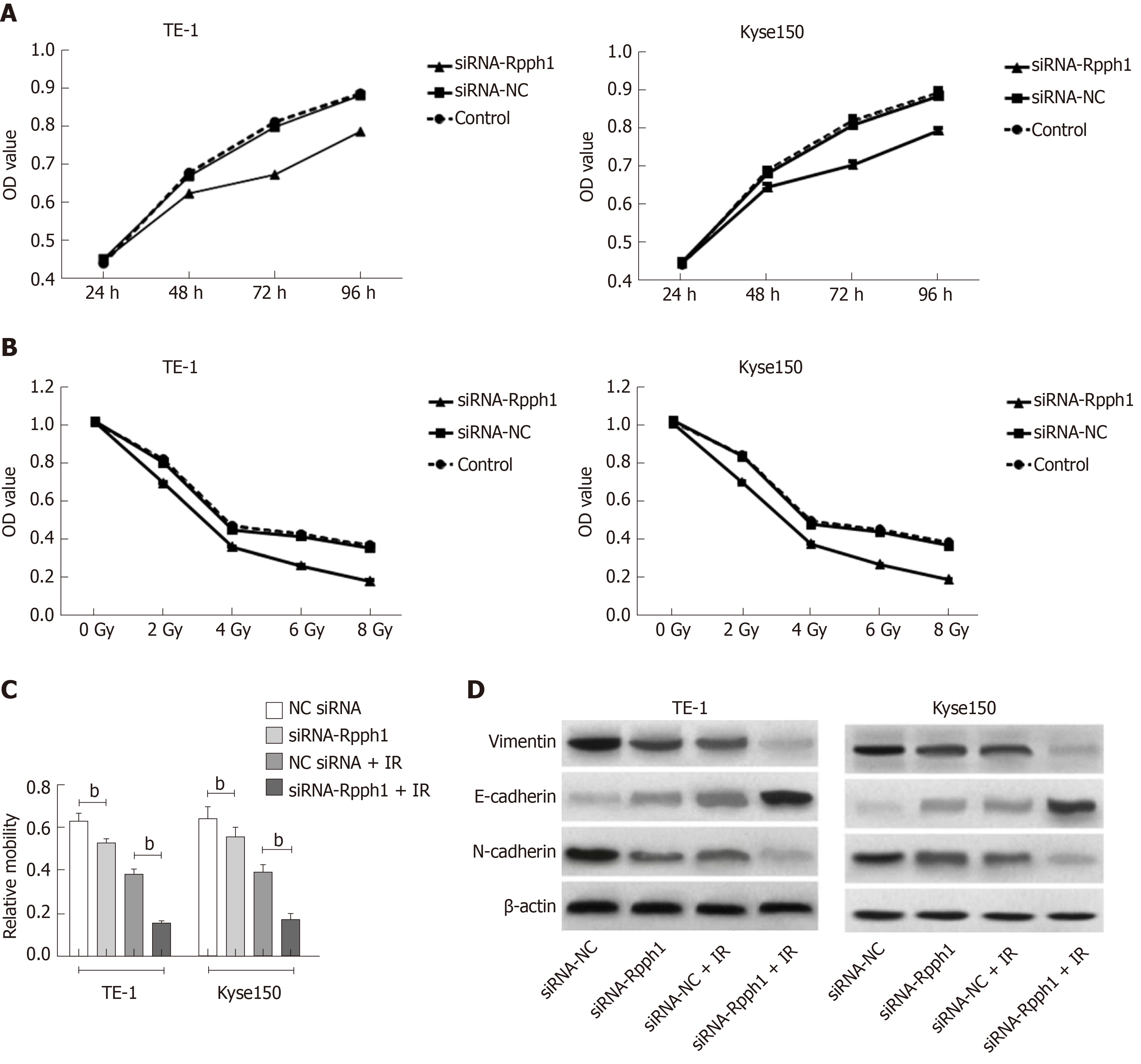
Figure 6 Effect of long non-coding RNA Rpph1 on radiation-induced cell proliferation, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
A: Cell growth curves of TE-1 and Kyse150 at different time points; B: Cell growth curves of TE-1 and Kyse150 at different radiotherapy doses; C: Comparison of cell migration of esophageal cancer cells; D: Expression of EMT-related proteins in esophageal cancer cells. Note: b indicates bP < 0.001 when the two groups were compared.
- Citation: Li ZY, Li HF, Zhang YY, Zhang XL, Wang B, Liu JT. Value of long non-coding RNA Rpph1 in esophageal cancer and its effect on cancer cell sensitivity to radiotherapy. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(15): 1775-1791
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i15/1775.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i15.1775