©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2019; 25(48): 6890-6901
Published online Dec 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i48.6890
Published online Dec 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i48.6890
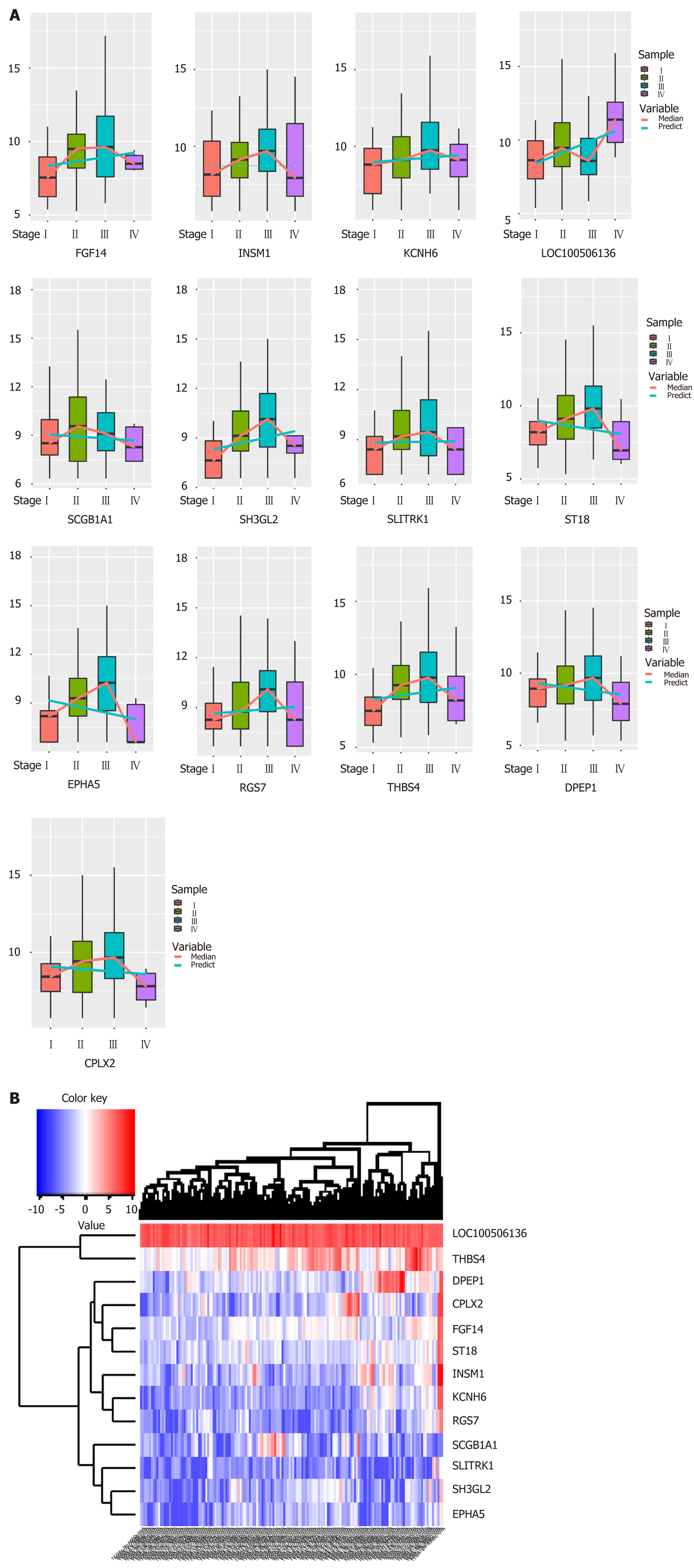
Figure 1 Synergistic expression of differential genes in four samples of esophageal cancer in patient samples.
A: Continuous regulation of common genes in differentially expressed genes in four stages; B: Expression heat map of common genes in samples of differentially expressed genes in four stages.
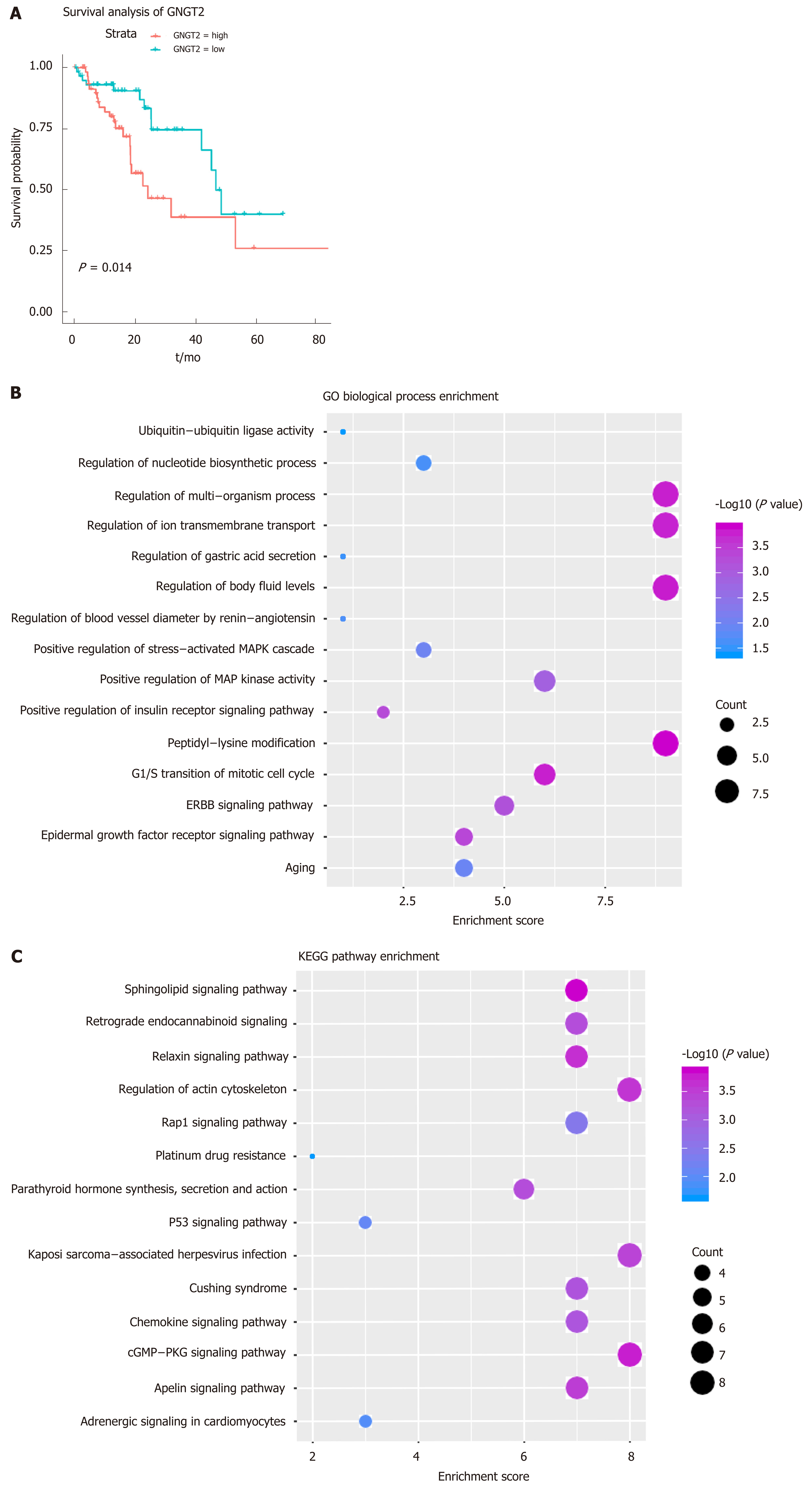
Figure 2 Dysfunctional modules.
A: Survival analysis of G protein subunit gamma transducin 2; B and C: Module gene function and pathway enrichment analysis. The larger the circle, the greater the proportion of the gene in the Gene Ontology/Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. GNGT2: G protein subunit gamma transducin 2; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERBB: Epidermal growth factor.
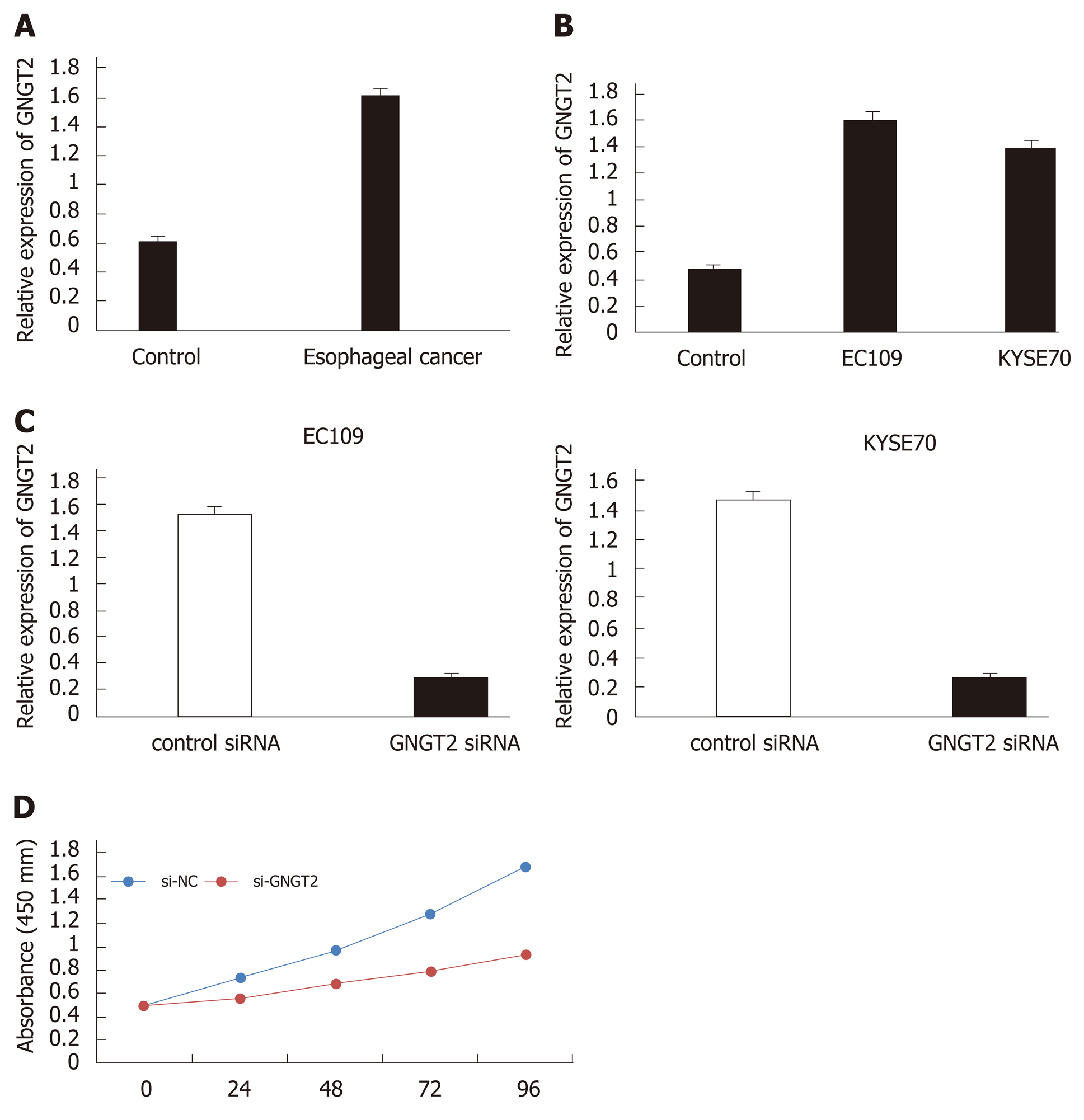
Figure 3 Molecular mechanism and expression of G protein subunit gamma transducin 2 in esophageal cancer.
A and B: The expression of G protein subunit gamma transducin 2 (GNGT2) in esophageal cancer patients and cell lines; C: Transfected of EC109 and KYSE70 cells; D: GNGT2 promote the proliferation of esophageal cancer cells.
- Citation: Liu GM, Ji X, Lu TC, Duan LW, Jia WY, Liu Y, Sun ML, Luo YG. Comprehensive multi-omics analysis identified core molecular processes in esophageal cancer and revealed GNGT2 as a potential prognostic marker. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(48): 6890-6901
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i48/6890.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i48.6890