©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2019; 25(41): 6273-6288
Published online Nov 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i41.6273
Published online Nov 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i41.6273
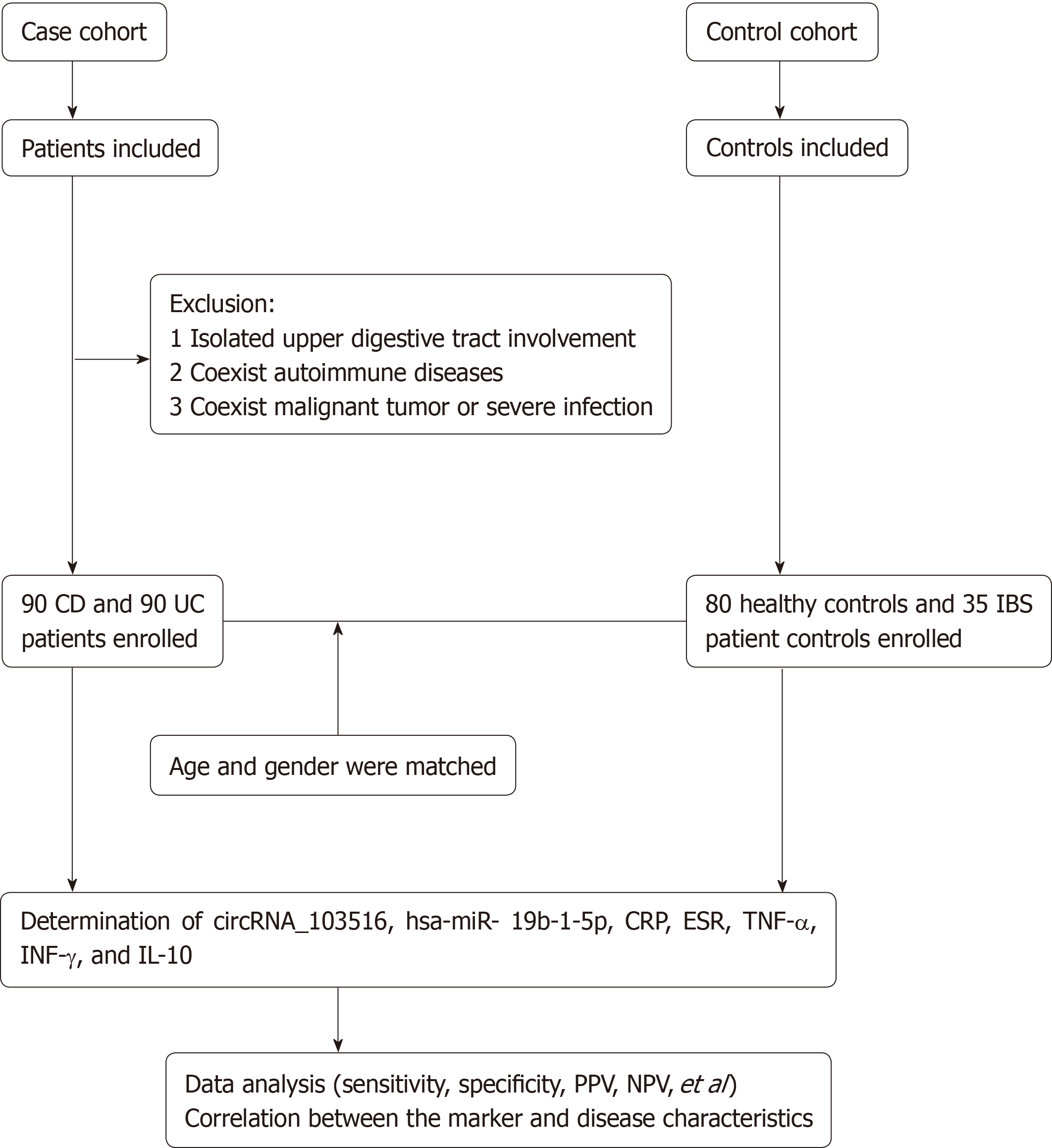
Figure 1 Flow chart of patient selection in the study and main study procedures.
CD: Crohn’s disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; CRP: C reactive protein; ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; INF-γ: Interferon γ; IL-10: Interleukin-10; PPV: Positive predictive value; NPV: Negative predictive value.
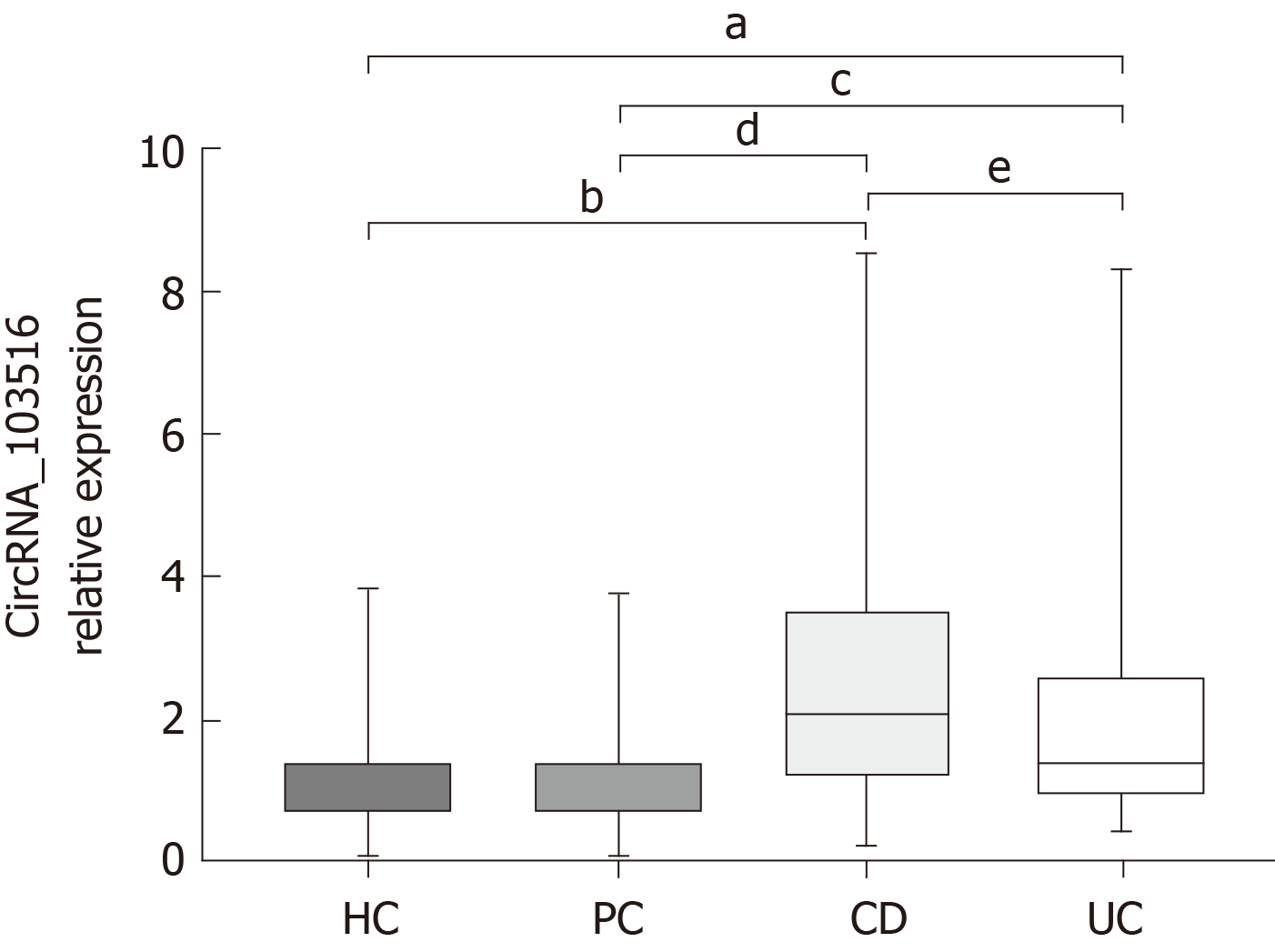
Figure 2 Circular RNA_103516 relative expression in patients with Crohn’s disease, patients with ulcerative colitis, healthy controls, and patient controls.
Circular RNA (circRNA)_103516 was increased in Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) patients compared with healthy controls (HC) and patient controls (PC). A significant difference in circRNA_103516 was detected between CD and UC groups. Comparing the relative circRNA levels between two groups was performed by the Mann Whitney U-test. aP < 0.05 vs HC and bP < 0.001 vs HC; cP < 0.05 vs PC; dP < 0.001 vs PC; eP < 0.05 vs UC. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. CD: Crohn’s disease, UC: Ulcerative colitis, HC: Healthy controls, PC: Patient controls; CircRNA: Circular RNA.
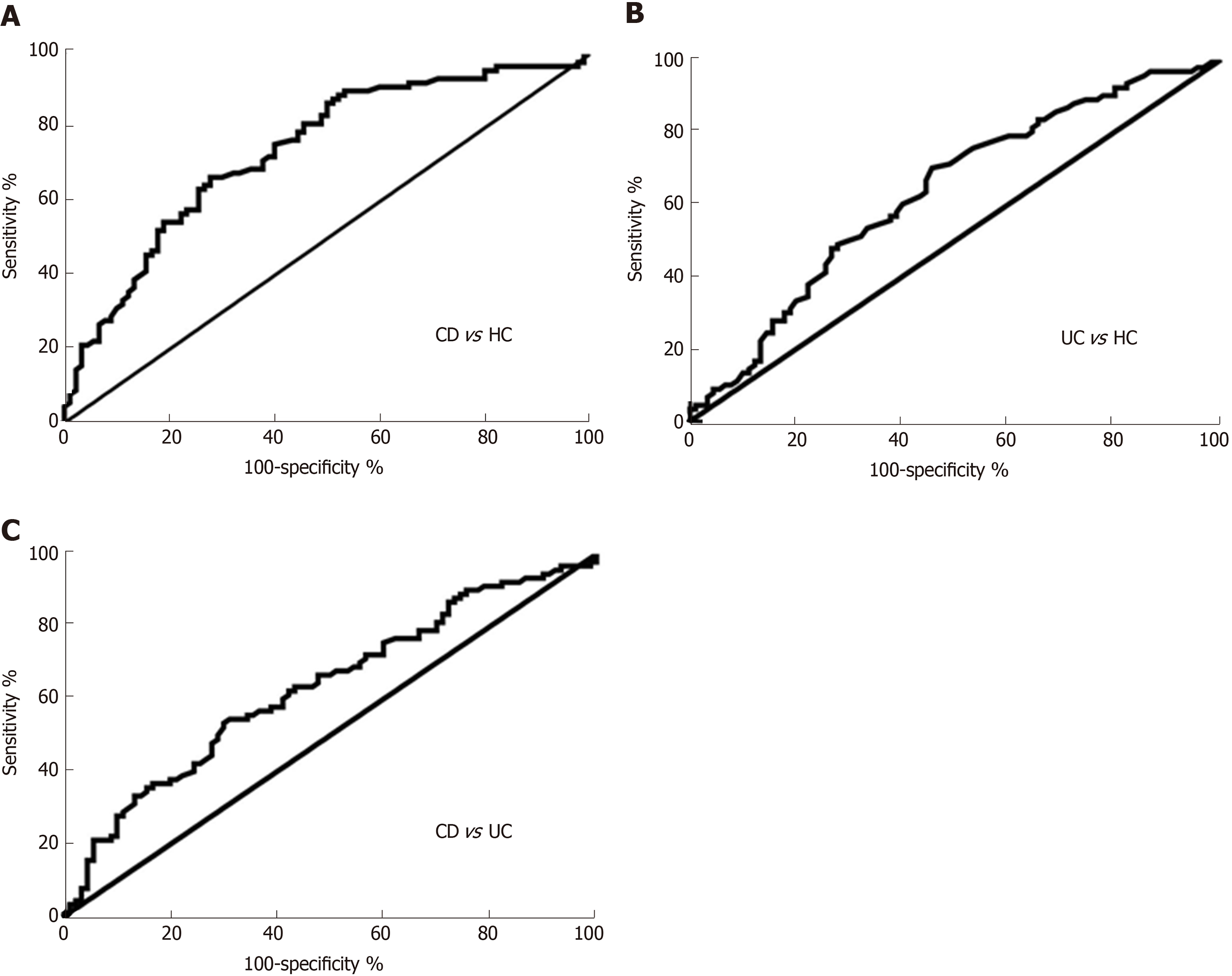
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic analysis of circular RNA_103516 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
A: Circular RNA (circRNA)_103516 was able to differentiate CD from HC; B: CircRNA_103516 could differentiate UC from HCs; C: CircRNA_103516 was able to differentiate CD from UC. CD: Crohn’s disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; HCs: Healthy controls.
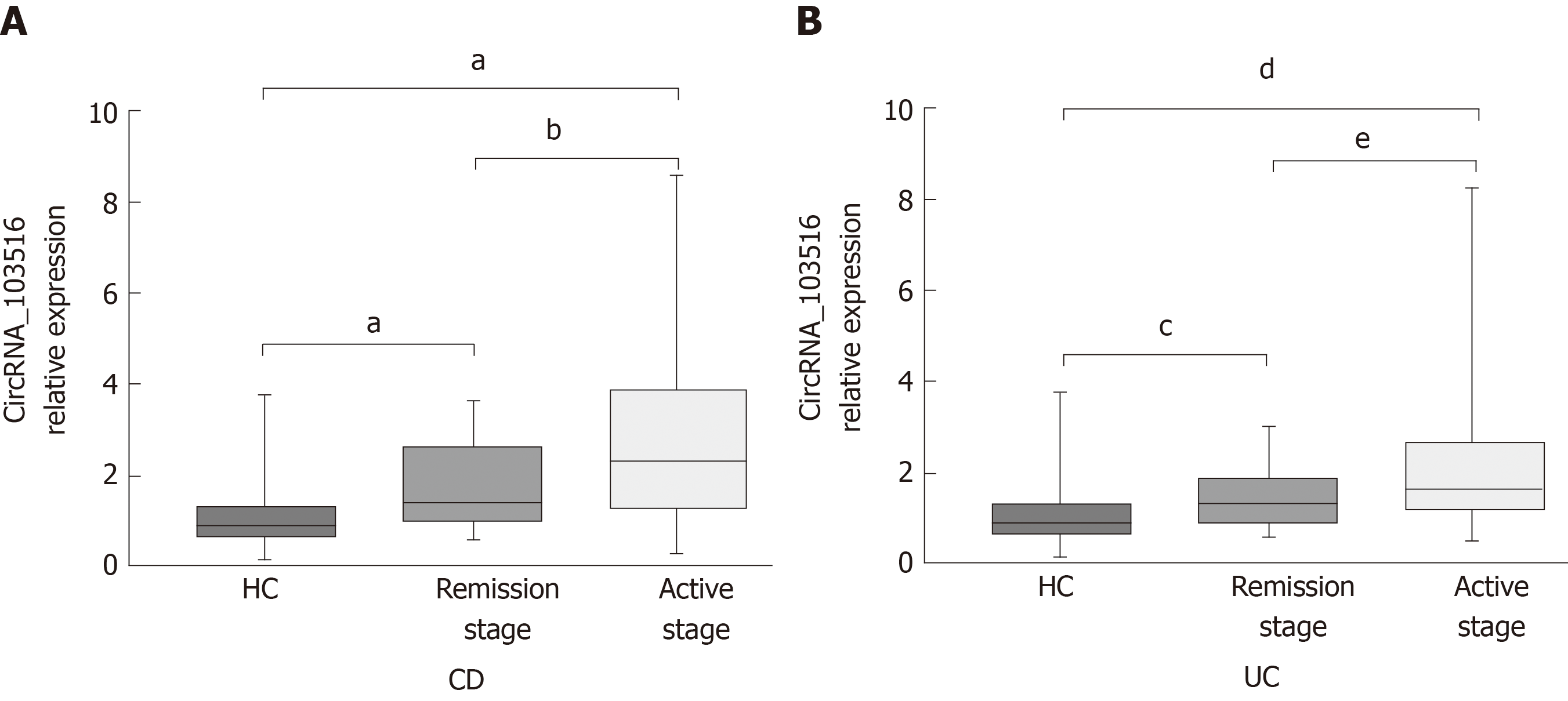
Figure 4 Expression of circular RNA_103516 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from inflammatory bowel disease patients at different stages.
A: Circular RNA (circRNA)_103516 in CD patients at different stages. aP < 0.001 vs HCs; bP < 0.05, remission stage vs active stage. B: CircRNA_103516 in UC patients at different stage. cP < 0.05 vs HCs; dP < 0.001 vs HCs; eP < 0.05, remission stage vs active stage. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. CD: Crohn’s disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CircRNA: Circular RNA.
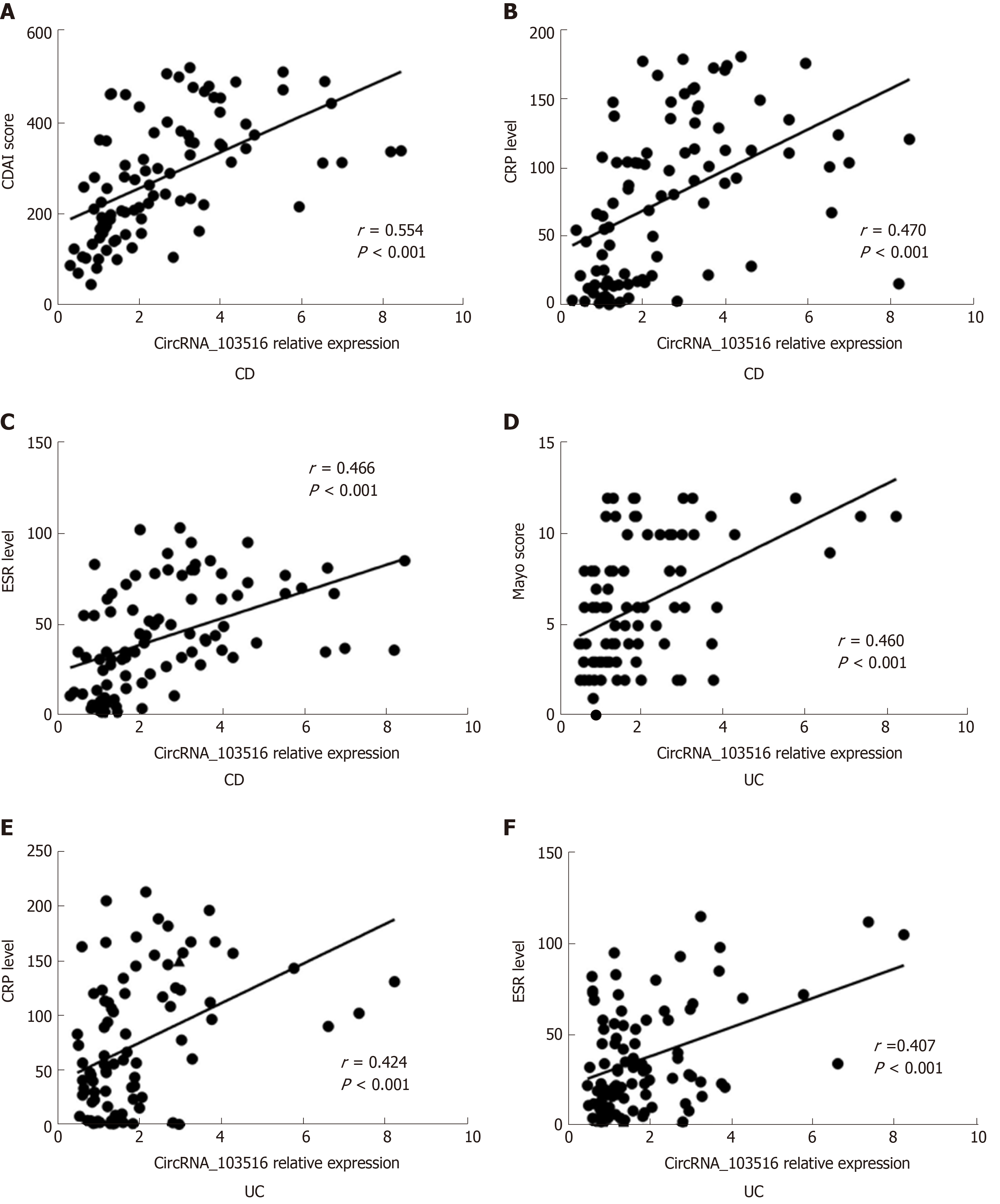
Figure 5 Correlations of circular RNA_103516 expression with Crohn's disease activity index, Mayo score, C reactive protein, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in inflammatory bowel disease patients.
Spearman’s analysis was applied to test the correlation of circular RNA (circRNA)_103516 expression with disease activity. A-C: Correlations of circRNA_103516 expression with disease activity in patients with CD; D-F: Correlations of circRNA_103516 expression with disease activity in patients with UC. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. CD: Crohn’s disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CDAI: Crohn's disease activity index; CRP: C reactive protein; ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CircRNA: Circular RNA.
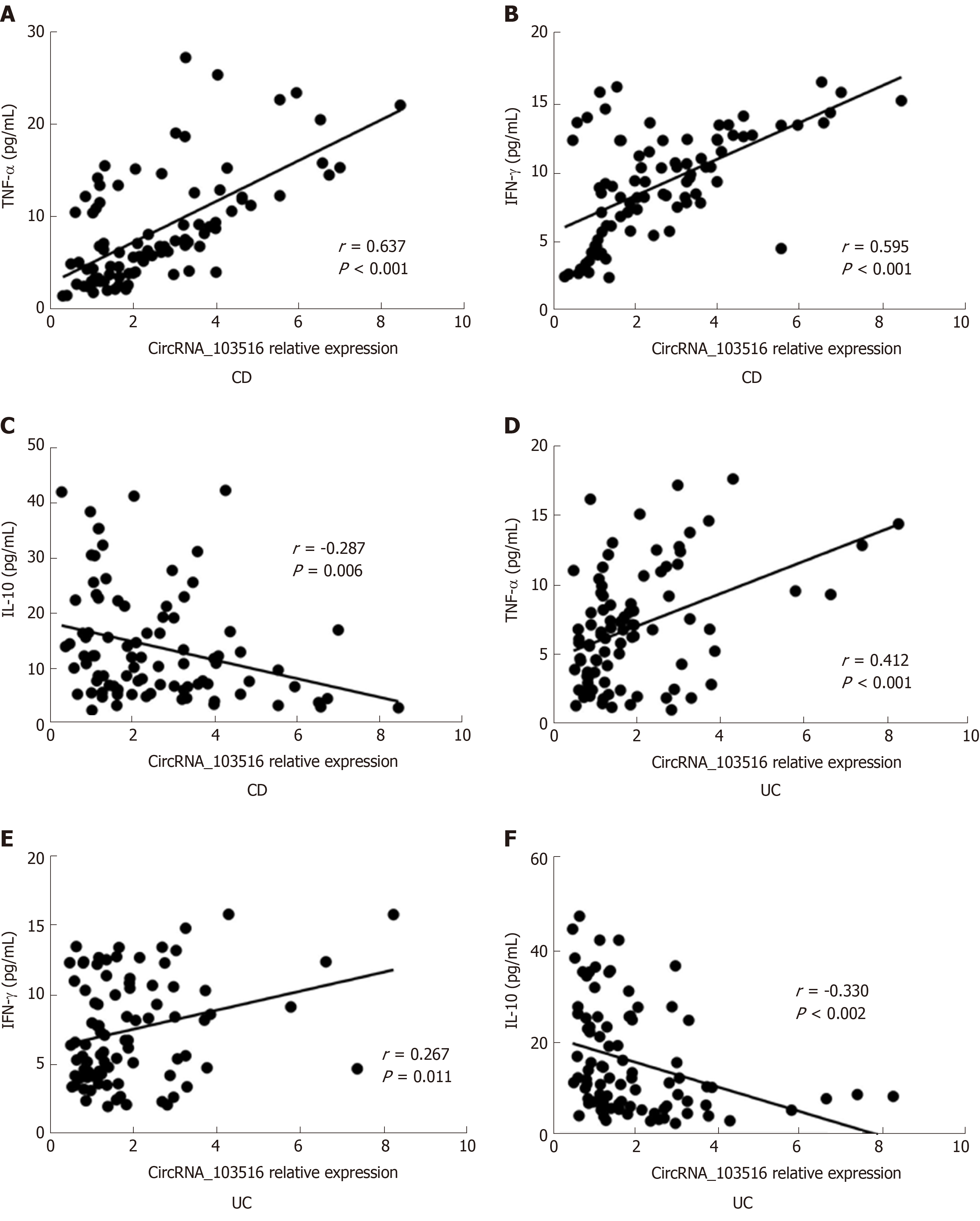
Figure 6 Correlations of circular RNA_103516 expression with inflammatory cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease.
A-C: Correlations of circular RNA (circRNA)_103516 expression with TNFα, IFN-γ, and IL-10 in CD; D-F: Correlations of circRNA_103516 expression with TNFα, IFN-γ, and IL-10 in UC. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. CD: Crohn’s disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; INF-γ: Interferon γ; IL-10: Interleukin-10; CircRNA: Circular RNA.
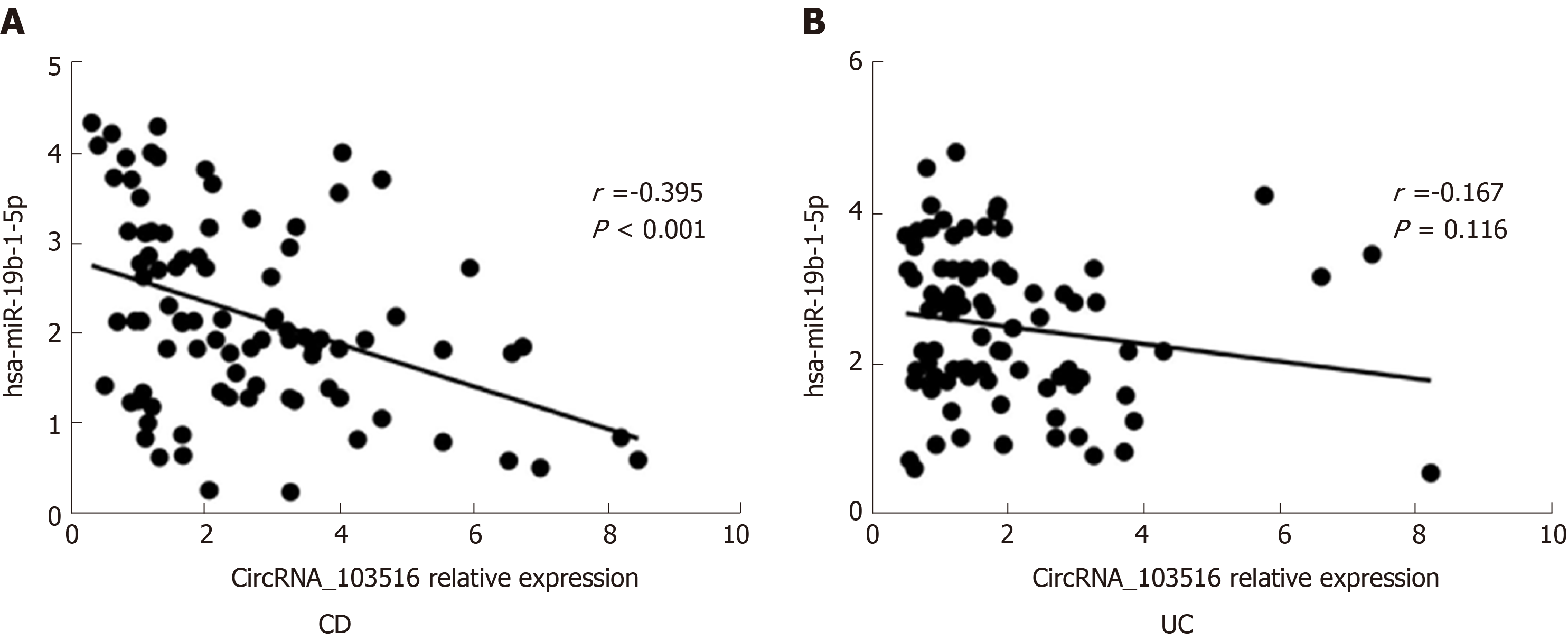
Figure 7 Correlations of circular RNA_103516 expression with hsa-miR-19b-1-5p in inflammatory bowel disease.
A: Correlation of circular RNA (circRNA)_103516 expression with hsa-miR-19b-1-5p in CD; B: Correlation of circRNA_103516 expression with hsa-miR-19b-1-5p in UC. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. CD: Crohn’s disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; CircRNA: Circular RNA.
- Citation: Ye YL, Yin J, Hu T, Zhang LP, Wu LY, Pang Z. Increased circulating circular RNA_103516 is a novel biomarker for inflammatory bowel disease in adult patients. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(41): 6273-6288
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i41/6273.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i41.6273