Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2019; 25(31): 4502-4511
Published online Aug 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4502
Published online Aug 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4502
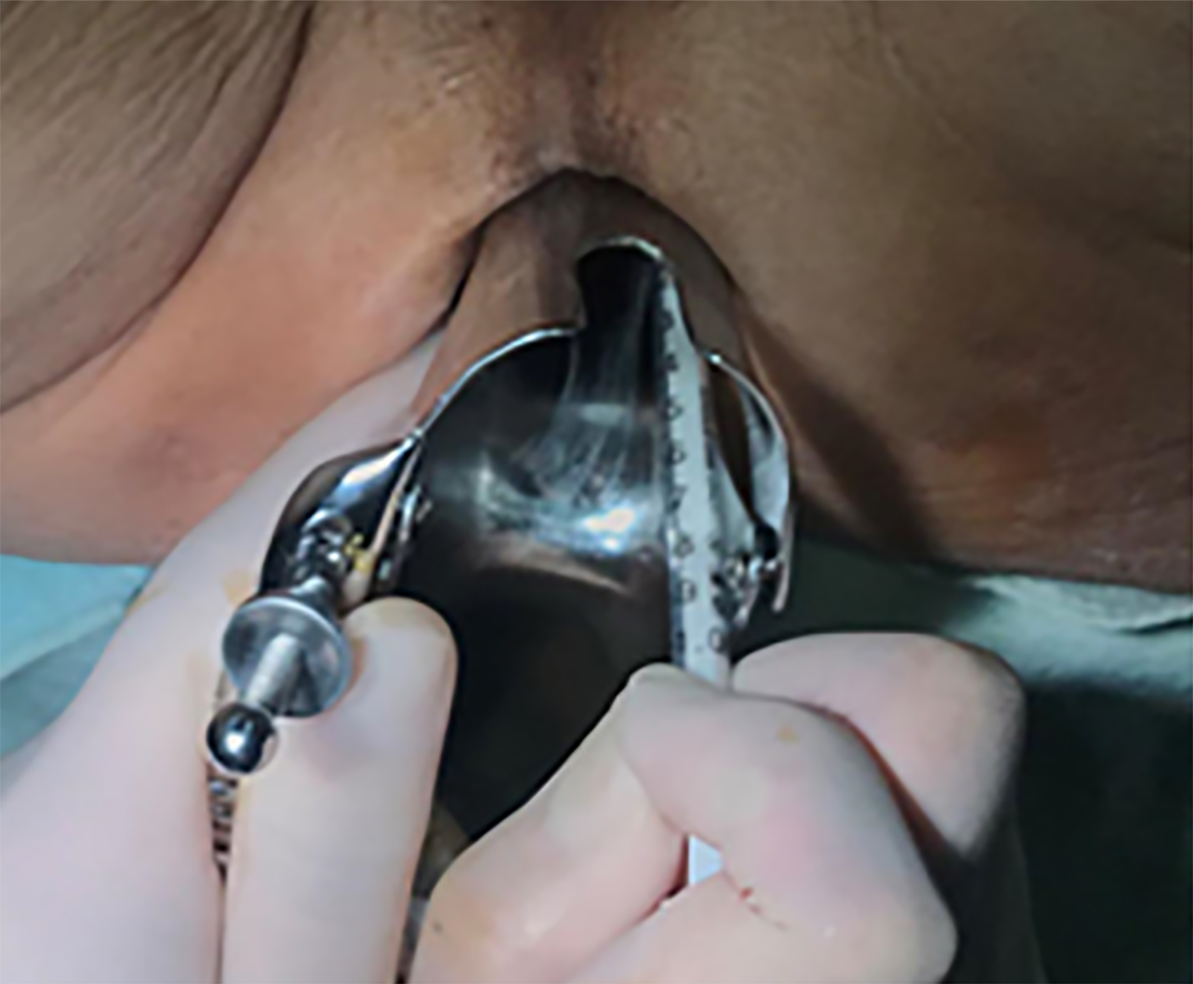
Figure 1 Injection of indocyanine green dye to sites on the anal side of the tumour.
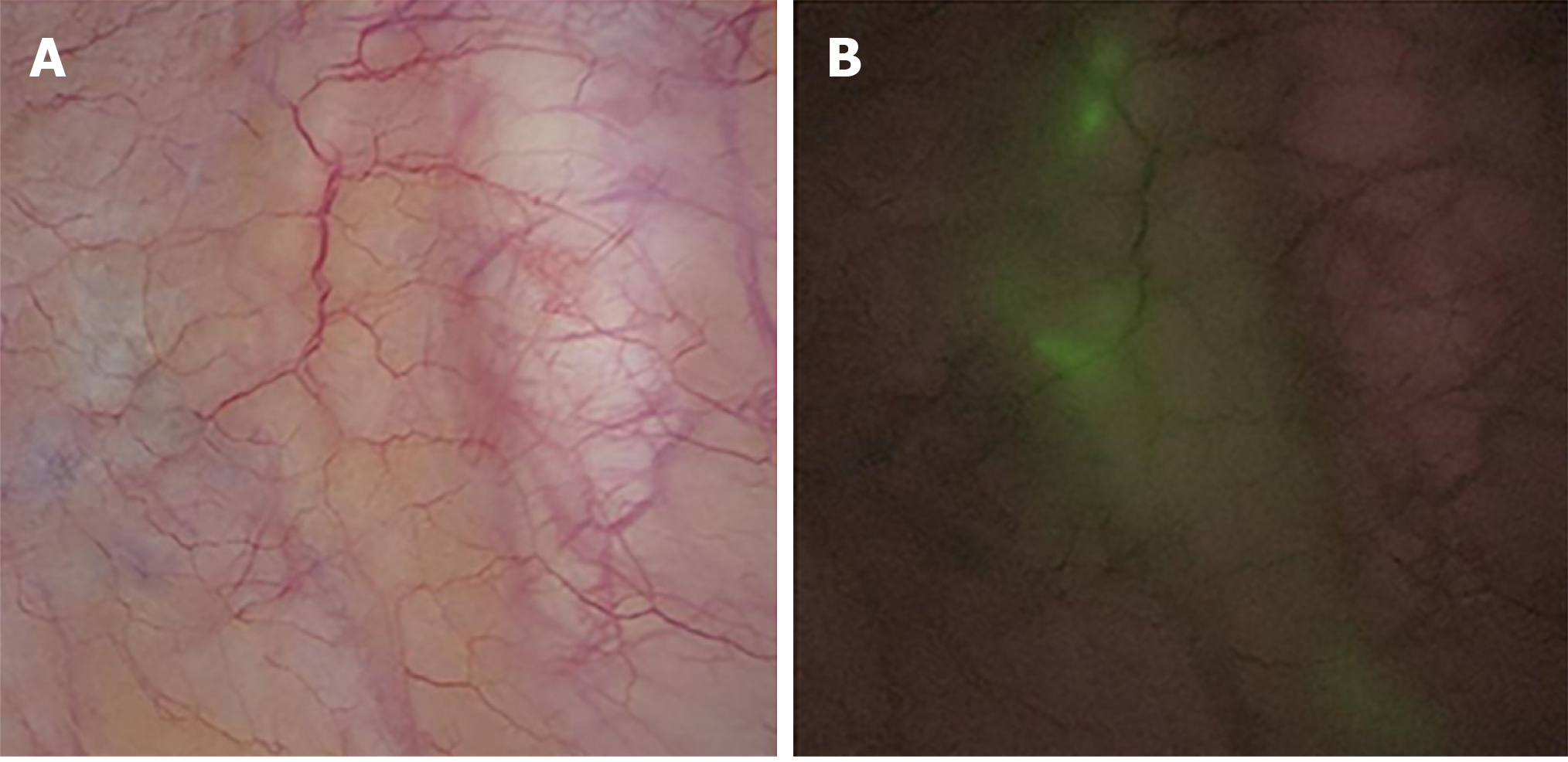
Figure 2 Determination of the direction of lateral lymph node drainage under the guidance of indocyanine green-enhanced near-infrared fluorescence-guided imaging.
A: Normal imaging; B: Indocyanine green-enhanced near-infrared fluorescence-guided imaging.
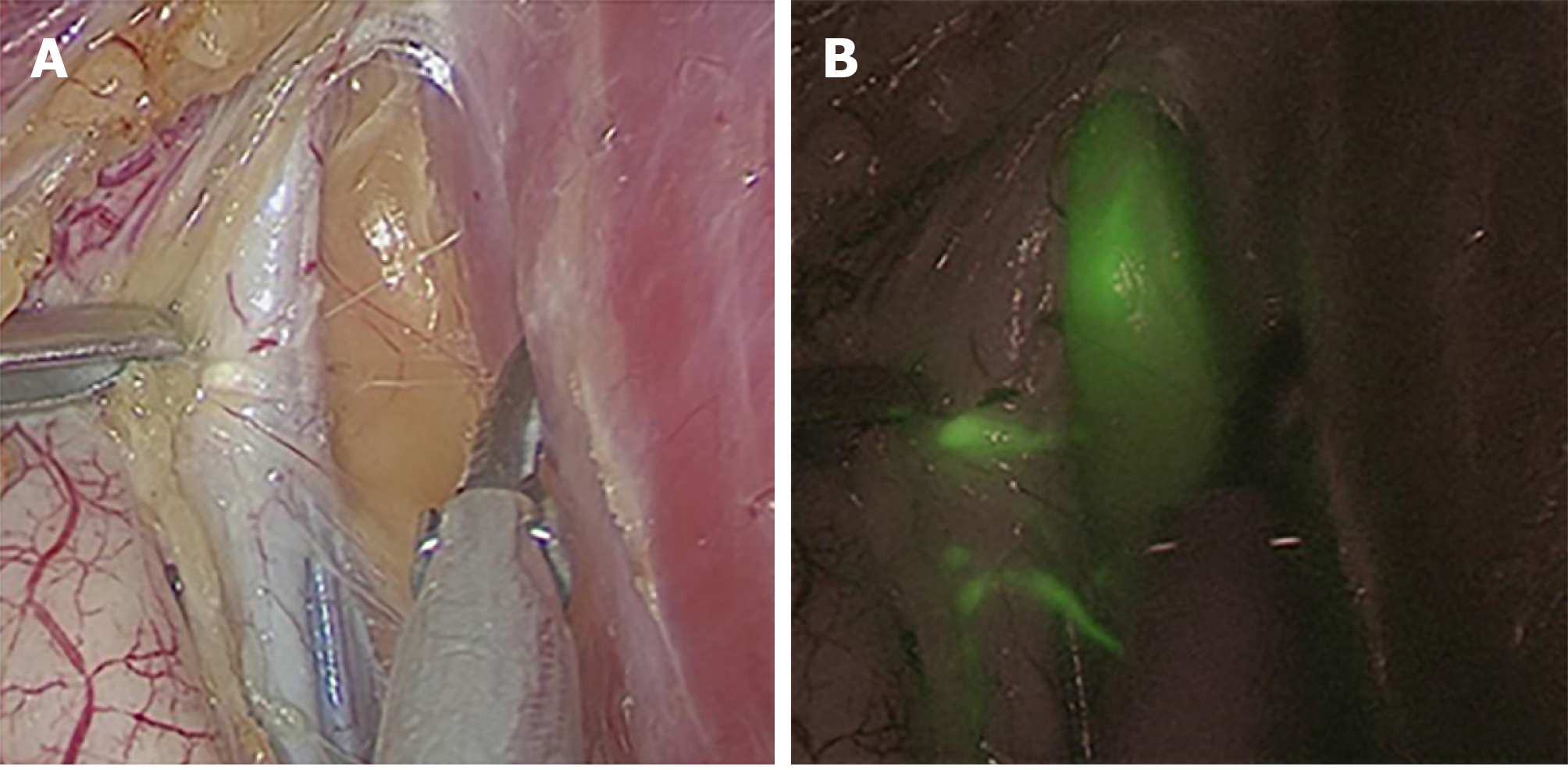
Figure 3 Distinguishing between lymph nodes and non-lymphatic soft tissues.
A: Normal imaging; B: Indocyanine green-enhanced near-infrared fluorescence-guided imaging.
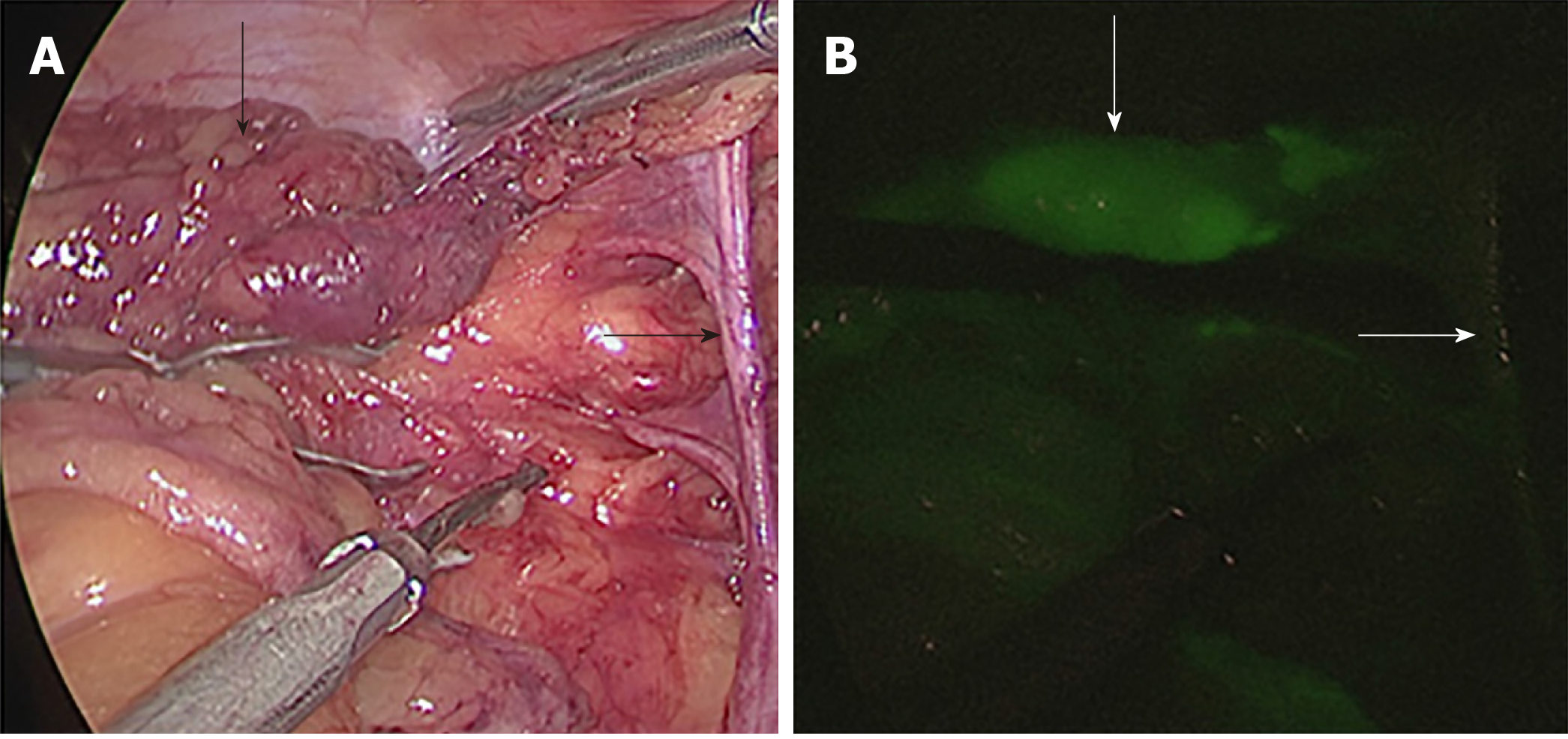
Figure 4 Examination of blood vessels, nerves, and residual soft tissues.
A: Normal imaging; B: Indocyanine green-enhanced near-infrared fluorescence-guided imaging.
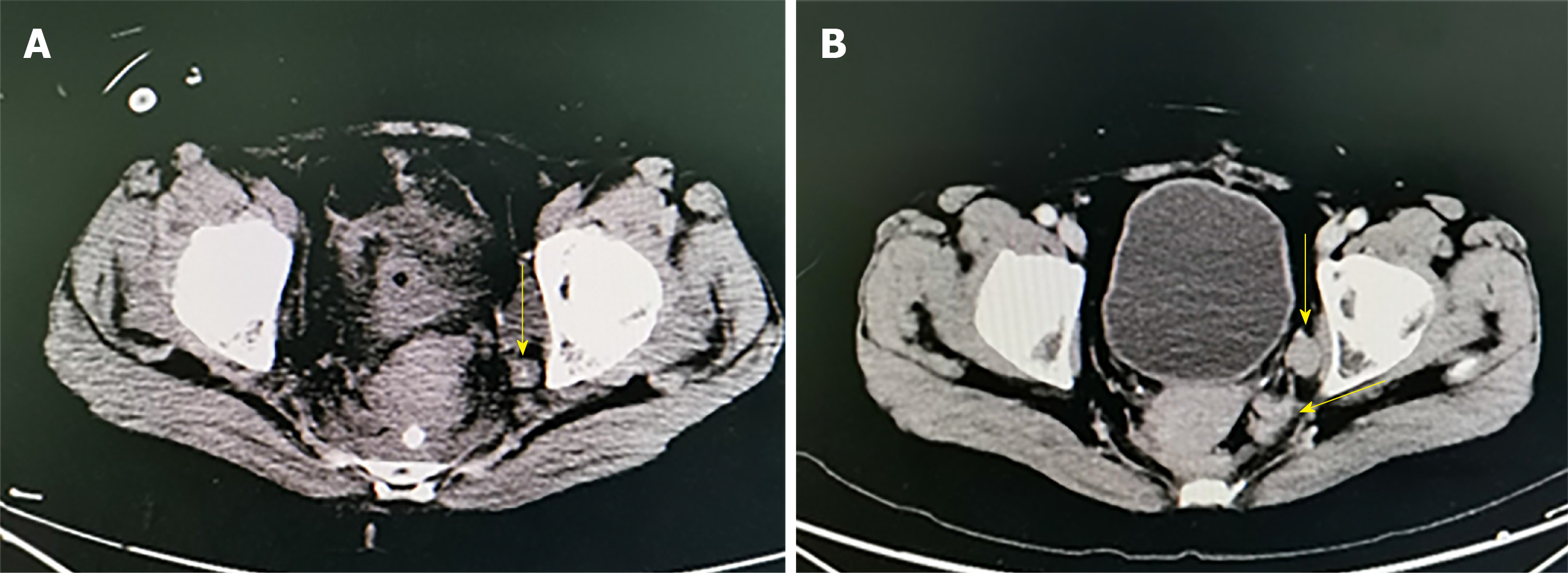
Figure 5 Residual lymph nodes revealed by computed tomography imaging of two cases.
A: Residual lymph nodes in the distal left internal iliac artery. B: Residual lymph nodes in the left obturator foramen region.
- Citation: Zhou SC, Tian YT, Wang XW, Zhao CD, Ma S, Jiang J, Li EN, Zhou HT, Liu Q, Liang JW, Zhou ZX, Wang XS. Application of indocyanine green-enhanced near-infrared fluorescence-guided imaging in laparoscopic lateral pelvic lymph node dissection for middle-low rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(31): 4502-4511
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i31/4502.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4502